uData MODBUS sensor porting guide(eng)
AliOS Things provides MODBUS library, related API can refer to mbmaster_api.h under kernel.
mb_status_t mb_rtc_init(mb_handler_t **handler, uint8_t port, uint32_t baud_rate, mb_parity_t parity); //初始化
/* mb_handler_t **handler handler */
/* port UART port */
/* baud_rate baudrate */
/* parity parity */
mb_status_t mb_read_holding_reginster(mb_handler_t* req_handler, uint8_t slave_addr, uint16_t start_addr, uint16_t quantity, uint8_t *respond_buf, uint8_t *respond_count);//read modbus register
/* mb_handler_t **handler handler */
/* uint16_t slave_addr slave device address */
/* uint16_t start_addr register address */
/* uint16_t quantity register quantity to read */
/* uint8_t *respond_buf register data out buffer */
/* uint8_t *respond_count count of data*/
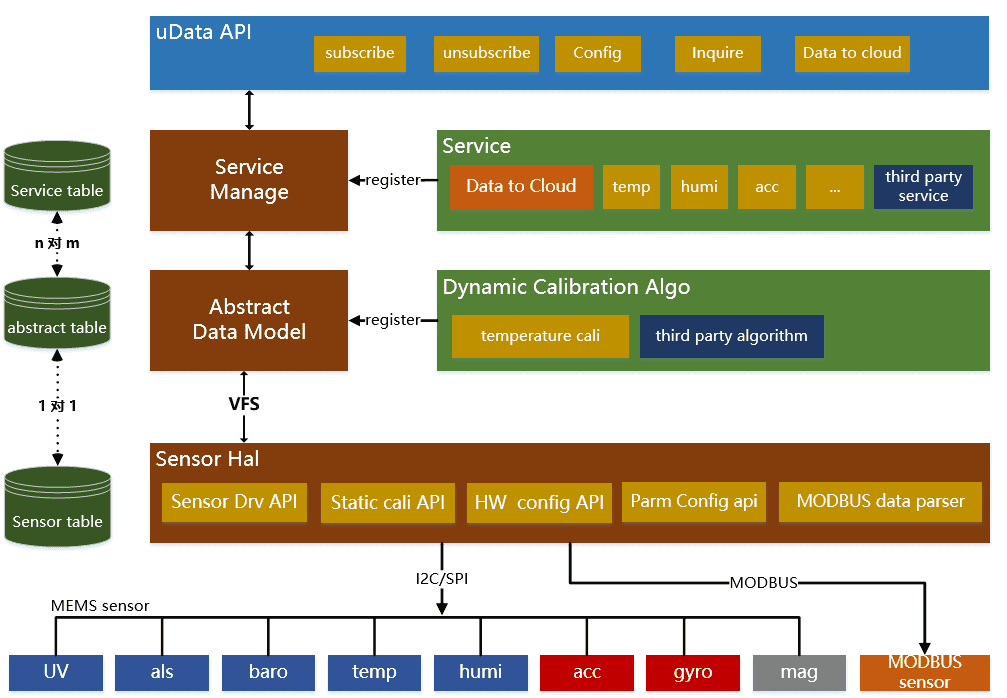
The MODBUS sensor driver is added by modifying it like the following configuration table. device\sensor\drv\sensor_drv_conf.h
const modbus_sensor_t modbus_sensors[] = {
{ "KunLunHaiAn", "JHFS-W1", "wind speed", dev_windspeed_path, TAG_DEV_WINDSPD,
SENSOR_OPEN, 0X30, 0x002A, 1, 0, 50 },
{ "KunLunHaiAn", "JHFX-W1", "wind direction", dev_winddirection_path, TAG_DEV_WINDDIR,
SENSOR_OPEN, 0X31, 0x002A, 1, 0, 50 },
{ "KunLunHaiAn", "JHYL-W1", "current precipitation", dev_rainfall_path, TAG_DEV_RAIN,
SENSOR_OPEN, 0X32, 0x0002, 1, 0, 50 },
{ "KunLunHaiAn", "JHYL-W1", "today precipitation", dev_todayrainfall_path, TAG_DEV_TODAYRAIN,
SENSOR_OPEN, 0X32, 0x0001, 1, 0, 50 },
};
The comments for the array structure are as follows:
typedef struct
{
const char * company; /* company */
const char * model; /* sensor model */
const char * name; /* sensor name */
const char * path; /* sensor path */
sensor_tag_e tag; /* sensor tag */
sensor_ability ability; /* sensor option to open or close */
unsigned char slave; /* slave device address */
unsigned short addr; /* register address */
unsigned short reg_cnt; /* Number of registers */
unsigned char byte_reverse; /* Whether data is reversed 0: high bytes first, 1: low bytes first */
unsigned short response_time; /* Read data timeout,slave response time in ms */
} modbus_sensor_t;
-
Bus initialization, call mb_rtc_init, pass the handle handler, UART port, baud rate, parity and other parameters.
mb_rtc_init(mb_handler_t **handler, uint8_t port, uint32_t baud_rate, mb_parity_t parity);
-
The sensor configuration parameters are loaded. The configuration parameters are specified in the modbus_sensor_t modbus_sensors table described above, and the user can define them themselves.
-
The sensor with the capability open in the table creates the sensor_obj_t structure node. As shown below, the sensor can be opened and the sensor data can be read through the open, read, etc. interfaces of the vfs.
typedef struct _sensor_obj_t
{
char * path;
sensor_tag_e tag;
dev_io_port_e io_port;
work_mode_e mode;
void * data_buf;
uint32_t data_len;
dev_power_mode_e power;
gpio_dev_t gpio;
dev_sensor_full_info_t info;
uint8_t ref;
int (*open)(void);
int (*close)(void);
int (*read)(void *, size_t);
int (*write)(const void *buf, size_t len);
int (*ioctl)(int cmd, unsigned long arg);
void (*irq_handle)(void);
} sensor_obj_t;
uData framework Migration Documentation Reference https://github.com/alibaba/AliOS-Things/wiki/AliOS-Things-uData-Framework-Porting-Guide
uData framework introduction https://yq.aliyun.com/articles/368257
uData framework introduction and porting documentation can refer to the link above.
When the regular MEMS sensor polls the read data, it can be read by the timer. When the MODBUS sensor is used, the read timeout period is uncontrollable. Here, a task is created separately for polling and reading the registered sensor driver, polling time user. Can be modified according to your needs.
static void abs_data_polling(void *p)
{
uint8_t i = 0;
uint64_t timestamp = 0;
uint64_t pre_timestamp = 0;
while (1) {
aos_msleep(200);
timestamp = aos_now_ms();
for (i = 0; i < abs_data_cnt; i++) {
if ((timestamp - g_abs_data_db[i]->cur_timestamp) >=
g_abs_data_db[i]->interval) {
abs_sensor_read(g_abs_data_db[i]->tag);
timestamp = aos_now_ms();
pre_timestamp = timestamp;
g_abs_data_db[i]->cur_timestamp = timestamp;
}
}
}
}
- The currently supported sensor models listed in the configuration table are modified by the user to control the sensor drive loading.
- Modify the enabled sensor slave, the sensor slave address is configured by the user, the slave is consistent with the configuration.
- Add sensors to the configuration table according to the modbus_sensor_t structure format
- Sensor capability is defined on or off, and the slave and sensor configurations are identical.
- If the sensor type is brand new, define the new path and tag in the sensor.h file as follows and add it to the configuration table.
#define dev_acc_path "/dev/acc"
#define dev_mag_path "/dev/mag"
#define dev_gyro_path "/dev/gyro"
#define dev_als_path "/dev/als"
#define dev_ps_path "/dev/ps"
#define dev_baro_path "/dev/baro"
#define dev_temp_path "/dev/temp"
#define dev_uv_path "/dev/uv"
#define dev_humi_path "/dev/humi"
#define dev_hall_path "/dev/hall"
#define dev_hr_path "/dev/hr"
#define dev_gps_path "/dev/gps"
#define dev_noise_path "/dev/noise"
#define dev_pm25_path "/dev/pm25" // pm2.5
#define dev_co2_path "/dev/co2"
#define dev_hcho_path "/dev/hcho"
#define dev_tvoc_path "/dev/tvoc"
#define dev_pm10_path "/dev/pm10" // pm10
#define dev_pm1_path "/dev/pm1" // pm1.0
#define dev_ph_path "/dev/ph"
#define dev_vwc_path "/dev/vwc"
#define dev_ec_path "/dev/ec" //electric conductivity
#define dev_salinity_path "/dev/salinity" //salinity
#define dev_tds_path "/dev/tds" //Total dissolved solids
#define dev_windspeed_path "/dev/windspeed"
#define dev_winddirection_path "/dev/winddirection"
#define dev_rainfall_path "/dev/rainfall"
/* add the new sensor type into the last position */
typedef enum
{
TAG_DEV_ACC = 0, /* Accelerometer */
TAG_DEV_MAG, /* Magnetometer */
TAG_DEV_GYRO,/* Gyroscope */
TAG_DEV_ALS, /* Ambient light sensor */
TAG_DEV_PS, /* Proximity */
TAG_DEV_BARO,/* Barometer */
TAG_DEV_TEMP,/* Temperature */
TAG_DEV_UV, /* Ultraviolet */
TAG_DEV_HUMI,/* Humidity */
TAG_DEV_NOISE, /* NoiseLoudness */
TAG_DEV_PM25,/* PM2.5 */
TAG_DEV_PM1P0, /* PM1.0 */
TAG_DEV_PM10,/* PM10 */
TAG_DEV_CO2, /* CO2 Level */
TAG_DEV_HCHO,/* HCHO Level */
TAG_DEV_TVOC,/* TVOC Level */
TAG_DEV_PH, /* PH value */
TAG_DEV_VWC,/*volumetric water content*/
TAG_DEV_EC, /* EC value */
TAG_DEV_SALINITY, /* SALINITY value */
TAG_DEV_TDS,/* Total dissolved solids */
TAG_DEV_WINDSPD,/* Total dissolved solids */
TAG_DEV_WINDDIR,/* Total dissolved solids */
TAG_DEV_RAIN,/* Total dissolved solids */
TAG_DEV_HALL,/* HALL */
TAG_DEV_HR, /* Heart Rate */
TAG_DEV_RGB,/* RGB sensor */
TAG_DEV_GS, /* Gesture sensor */
TAG_DEV_IR, /* IR sensor */
TAG_DEV_GPS,
TAG_DEV_SENSOR_NUM_MAX,
} sensor_tag_e;
Open the macro of the related service in uData.mk. As shown below, the related service will be registered in the static int udata_std_service_init(udata_type_e type) function.
GLOBAL_DEFINES += AOS_UDATA_SERVICE_ALS
GLOBAL_DEFINES += AOS_UDATA_SERVICE_PS
GLOBAL_DEFINES += AOS_UDATA_SERVICE_BARO
GLOBAL_DEFINES += AOS_UDATA_SERVICE_TEMP
GLOBAL_DEFINES += AOS_UDATA_SERVICE_UV
GLOBAL_DEFINES += AOS_UDATA_SERVICE_HUMI
GLOBAL_DEFINES += AOS_UDATA_SERVICE_NOISE
GLOBAL_DEFINES += AOS_UDATA_SERVICE_PM25
GLOBAL_DEFINES += AOS_UDATA_SERVICE_CO2
GLOBAL_DEFINES += AOS_UDATA_SERVICE_HCHO
GLOBAL_DEFINES += AOS_UDATA_SERVICE_TVOC
Users need can subscribe the sensors what they need in their own APP, as shown below.
ret = uData_subscribe(UDATA_SERVICE_TEMP);
if (ret != 0) {
LOG("%s %s %s %d\n", uDATA_STR, __func__, ERROR_LINE, __LINE__);
}
ret = uData_subscribe(UDATA_SERVICE_HUMI);
if (ret != 0) {
LOG("%s %s %s %d\n", uDATA_STR, __func__, ERROR_LINE, __LINE__);
}
Register the callback function int uData_register_msg_handler(void *func); The sensor data is passed in the callback function.
The MODBUS macro needs to be opened during compilation, and the compilation parameter modbus_sensor_enable=1 is added. Take uDataapp as an example.
aos make uDataapp@developerkit modbus_sensor_enable=1
| Home | Tutorial | Hardware | Porting Guide | Utilities | API Reference | Technical Docs | Certification |
Crafted with ❤️ by AliOS Things Team.
