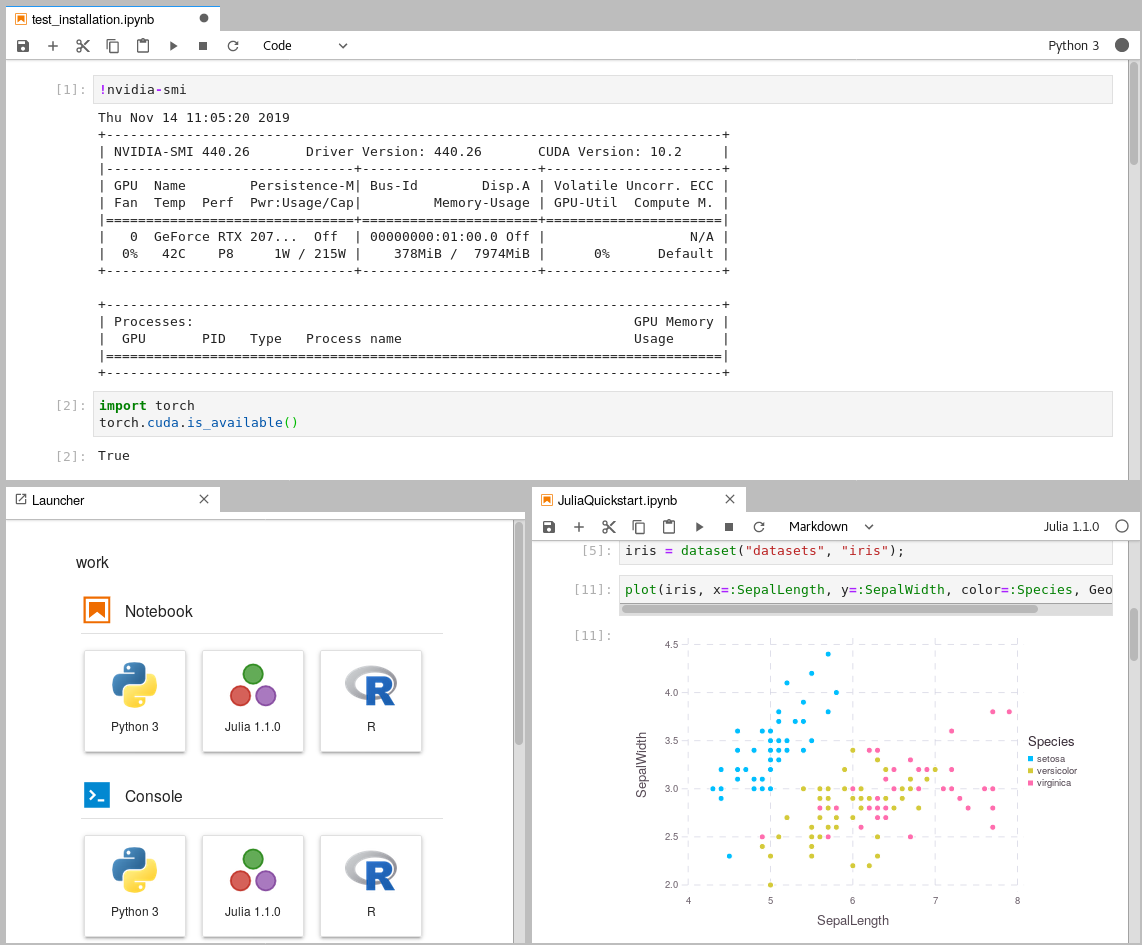
Leverage Jupyter Notebooks with the power of your NVIDIA GPU and perform GPU calculations using Tensorflow and Pytorch in collaborative notebooks.
First of all, thanks to docker-stacks for creating and maintaining a robost Python, R and Julia toolstack for Data Analytics/Science applications. This project uses the NVIDIA CUDA image as the base image and installs their toolstack on top of it to enable GPU calculations in the Jupyter notebooks. The image of this repository is available on Dockerhub.
- A NVIDIA GPU
- Install Docker version 1.10.0+ and Docker Compose version 1.6.0+.
- Get access to your GPU via CUDA drivers within Docker containers. Therfore, check out this
medium article.
The CUDA toolkit is not required on the host system, as it will be deployed
in NVIDIA-docker.
You can be sure that you can access your GPU within Docker,
if the command
docker run --gpus all nvidia/cuda:10.1-base-ubuntu18.04 nvidia-smireturns a result similar to this one:Mon Jun 22 09:06:28 2020 +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | NVIDIA-SMI 440.82 Driver Version: 440.82 CUDA Version: 10.1 | |-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+ | GPU Name Persistence-M| Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC | | Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap| Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. | |===============================+======================+======================| | 0 GeForce RTX 207... Off | 00000000:01:00.0 On | N/A | | 0% 46C P8 9W / 215W | 424MiB / 7974MiB | 6% Default | +-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+ +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Processes: GPU Memory | | GPU PID Type Process name Usage | |=============================================================================| +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
- Clone the Repository or pull the image from
Dockerhub:
git clone https://github.com/iot-salzburg/gpu-jupyter.git cd gpu-jupyter
First of all, it is necessary to generate the Dockerfile that is based on
the NIVIDA base image and the docker-stacks.
As soon as you have access to your GPU within Docker containers
(make sure the command docker run --gpus all nvidia/cuda:10.1-base-ubuntu18.04 nvidia-smi
shows your GPU statistics), you can generate the Dockerfile, build and run it.
The following commands will start GPU-Jupyter on localhost:8848
with the default password asdf.
# generate a Dockerfile with python and without Julia and R
./generate-Dockerfile.sh --no-datascience-notebook
docker build -t gpu-jupyter .build/ # will take a while
docker run -d -p [port]:8888 gpu-jupyter # starts gpu-jupyter WITHOUT GPU supportTo run the container WITH GPU support, a local data volume and some other configurations, run:
docker run --gpus all -d -it -p 8848:8888 -v $(pwd)/data:/home/jovyan/work -e GRANT_SUDO=yes -e JUPYTER_ENABLE_LAB=yes --user root --restart always --name gpu-jupyter_1 gpu-jupyter The script start-local.sh is a wrapper for a quick configuration of the
underlying docker-compose.yml:
./start-local.sh -p 8848 # the default port is 8888With these commands we can see if everything worked well:
bash show-local.sh # a env-var safe wrapper for 'docker-compose logs -f'
docker ps
docker logs [service-name]In order to stop the local deployment, run:
./stop-local.shThe script generate-Dockerfile.sh generates a Dockerfile within the .build/
directory.
This implies that this Dockerfile is overwritten by each generation.
The Dockerfile-generation script generate-Dockerfile.sh
has the following parameters (note that 2, 3 and 4 are exclusive):
-
-c|--commit: specify a commit or"latest"for thedocker-stacks, the default commit is a working one. -
-s|--slim: Generate a slim Dockerfile. As some installations are not needed by everyone, there is the possibility to skip some installations to reduce the size of the image. Here thedocker-stackscipy-notebookis used instead ofdatascience-notebookthat comes with Julia and R. Moreover, none of the packages withinsrc/Dockerfile.usefulpackagesis installed. -
--no-datascience-notebook: As the name suggests, thedocker-stackdatascience-notebookis not installed on top of thescipy-notebook, but the packages withinsrc/Dockerfile.usefulpackagesare. -
--no-useful-packages: On top of thedocker-stackdatascience-notebook(Julia and R), the essentialgpulibsare installed, but not the packages withinsrc/Dockerfile.usefulpackages.
As .build/Dockerfile is overwritten, it is suggested to append custom installations either
within src/Dockerfile.usefulpackages or in generate-Dockerfile.sh.
If you think some package is missing in the default stack, please let us know!
Please set a new password using src/jupyter_notebook_config.json.
Therefore, hash your password in the form (password)(salt) using a sha1 hash generator, e.g., the sha1 generator of sha1-online.com.
The input with the default password asdf is appended by a arbitrary salt e49e73b0eb0e to asdfe49e73b0eb0e and should yield the hash string as shown in the config below.
Never give away your own unhashed password!
Then update the config file as shown below and restart the service.
{
"NotebookApp": {
"password": "sha1:e49e73b0eb0e:32edae7a5fd119045e699a0bd04f90819ca90cd6"
}
}Please check version compatibilities for CUDA and Pytorch
respectively CUDA and Tensorflow previously.
To update CUDA to another version, change in Dockerfile.header
the line:
FROM nvidia/cuda:10.1-base-ubuntu18.04
and in the Dockerfile.pytorch the line:
cudatoolkit=10.1
Then re-generate and re-run the image, as closer described above:
./generate-Dockerfile.sh
./start-local.sh -p 8848The docker-stacks are used as a
submodule within .build/docker-stacks. Per default, the head of the commit is reset to a commit on which gpu-jupyter runs stable.
To update the generated Dockerfile to a specific commit, run:
./generate-Dockerfile.sh --commit c1c32938438151c7e2a22b5aa338caba2ec01da2To update the generated Dockerfile to the latest commit, run:
./generate-Dockerfile.sh --commit latestA new build can last some time and may consume a lot of data traffic. Note, that the latest version may result in a version conflict! More info to submodules can be found in this tutorial.
A Jupyter instance often requires data from other services. If that data-source is containerized in Docker and sharing a port for communication shouldn't be allowed, e.g., for security reasons, then connecting the data-source with GPU-Jupyter within a Docker Swarm is a great option!
This step requires a running Docker Swarm on a cluster or at least on this node. In order to register custom images in a local Docker Swarm cluster, a registry instance must be deployed in advance. Note that the we are using the port 5001, as many services use the default port 5000.
sudo docker service create --name registry --publish published=5001,target=5000 registry:2
curl 127.0.0.1:5001/v2/This should output {}. \
Afterwards, check if the registry service is available using docker service ls.
Additionally, GPU-Jupyter is connected to the data-source via the same docker-network. Therefore, This network must be set to attachable in the source's docker-compose.yml:
services:
data-source-service:
...
networks:
- default
- datastack
...
networks:
datastack:
driver: overlay
attachable: true In this example,
- the docker stack was deployed in Docker swarm with the name elk (
docker stack deploy ... elk), - the docker network has the name datastack within the
docker-compose.ymlfile, - this network is configured to be attachable in the
docker-compose.ymlfile - and the docker network has the name elk_datastack, see the following output:
sudo docker network ls # ... # [UID] elk_datastack overlay swarm # ...
The docker network name elk_datastack is used in the next step as a parameter.
Finally, GPU-Jupyter can be deployed in the Docker Swarm with the shared network, using:
./generate-Dockerfile.sh
./add-to-swarm.sh -p [port] -n [docker-network] -r [registry-port]
# e.g. ./add-to-swarm.sh -p 8848 -n elk_datastack -r 5001where:
- -p: port specifies the port on which the service will be available.
- -n: docker-network is the name of the attachable network from the previous step, e.g., here it is elk_datastack.
- -r: registry port is the port that is published by the registry service, default is
5000.
Now, gpu-jupyter will be accessible here on localhost:8848
with the default password asdf and shares the network with the other data-source, i.e.,
all ports of the data-source will be accessible within GPU-Jupyter,
even if they aren't routed it the source's docker-compose file.
Check if everything works well using:
sudo docker service ps gpu_gpu-jupyter
docker service ps gpu_gpu-jupyterIn order to remove the service from the swarm, use:
./remove-from-swarm.shThis project has the intention to create a robust image for CUDA-based GPU-applications, which is built on top of the docker-stacks. You are free to help to improve this project, by: