Re-implementation of the Supernova orbit propagator in a faster and more accessible package.
Hypernova is a fast orbit propagator implemented in C and wrapped for Python, designed for the University of Toronto Aerospace Team's FINCH mission. FINCH orbits in a 550 km Sun-Synchronous orbit, and as such the solvers and physics models used by Hypernova were selected for the best simulation fidelity in a low-Earth orbit.
Hypernova is on PyPI as hypernova-orbit. Install using the following command:
pip install hypernova-orbit
Note that a C compiler is required on your system in order for the C backend to be built.
You can install Hypernova from source as a Python package using the following command:
pip install git+https://github.com/utat-ss/hypernova
This will let you get the most cutting-edge builds of Hypernova before they're pushed to PyPI.
Hypernova uses cffi to wrap a fast C backend into easier-to-access functions in Python. The C backend does not come pre-compiled, and instead requires a compiler on the system to compile modules at install time. Hypernova is designed to automate this process, and it has been tested on the following operating systems:
- Windows 10 (x86)
- Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (x86)
- MacOS 12 (M1)
If you have issues installing Hypernova on your computer, please open an issue!
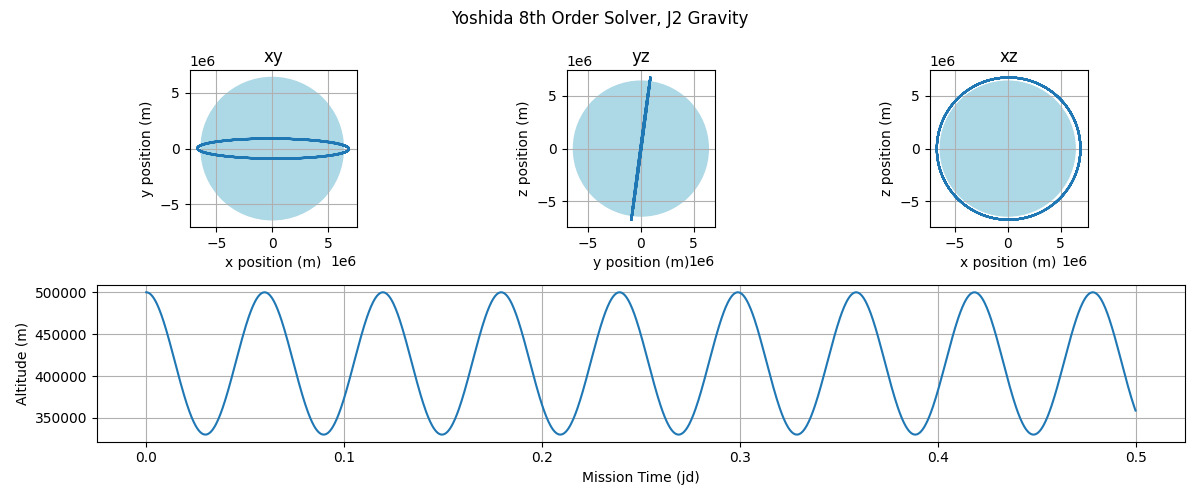
Hypernova comes with a few examples which you can run.
python -m hypernova.examples.basic_orbit_and_plot
This will generate the following output:
Hypernova is equipped with a testing suite to validate its functionality. The way to run the testing suite is to copy the scripts from the /tests folder into your working path and run pytest from your command terminal.



