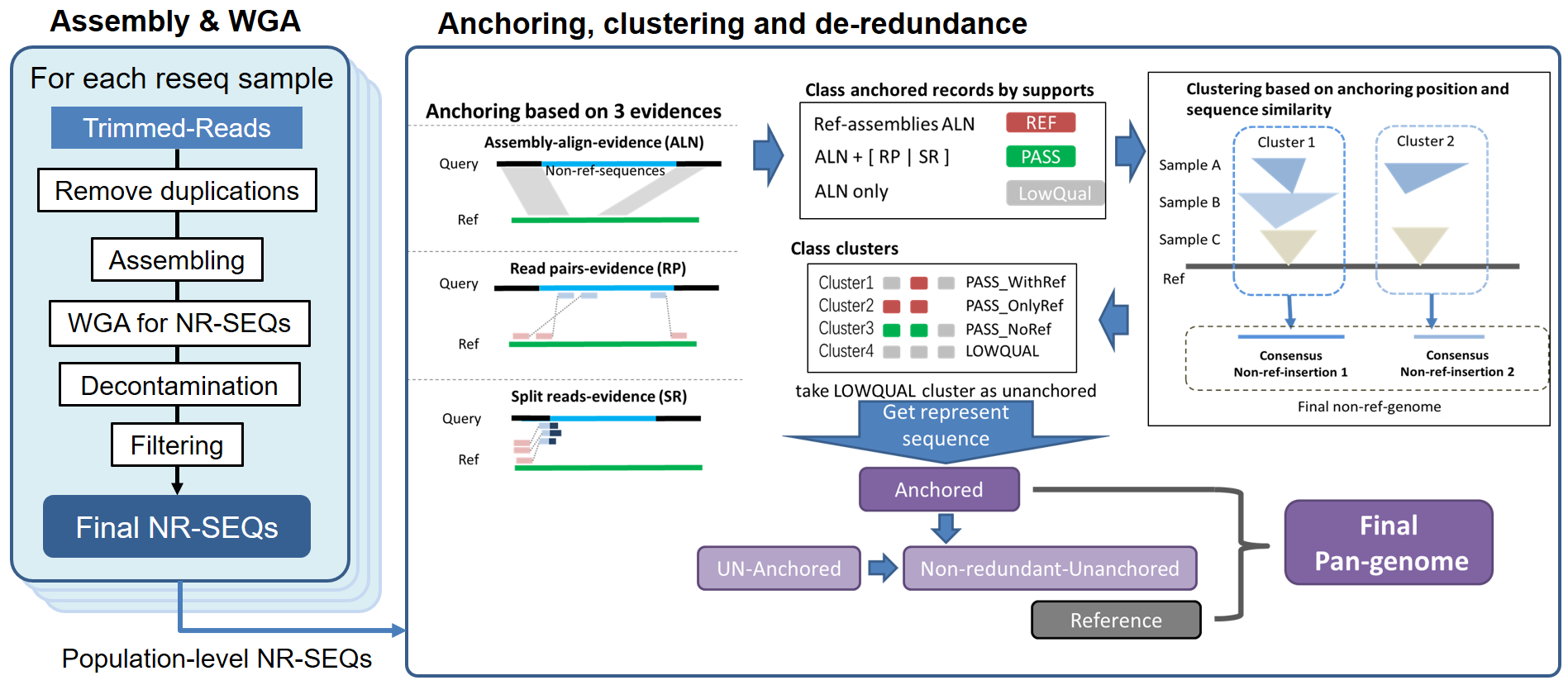
Constructing linear representation of pan genome from inputs of:
- A reference genome
- population level NGS deep sequencing short reads (> 20X depth of coverage)
- Other reference-level genome assemblies (Optional)
by:
- de novo assemble each individual from NGS reads
- identifying non-reference sequences(NR-SEQs) from whole genome alignment (WGA) to reference genome
- attempting to anchor them to reference genome from evidences of WGA and WGS pair-end read mapping
- clustering the anchored NR-SEQs and remove redundancies based on population level data to get the representative pan-genome sequences.
you will get outputs of:
- each individual's draft contigs
- WGA between each individual and reference
- NR-SEQs for each individual, with relative positions to the reference genome if there are supportive anchoring evidences
- Non-redundant non-reference sequence (NRNR-SEQ) representations of all the individuals
- the linear representation of the pan-genome would be
Reference+NRNR-SEQ
This pipeline was originally developed to construct the pan-Zea genome. However, all the requirements are assigned from input options, which makes it possible to be extended to any NGS based pan-genome construction with slightly modification to the parameters.
- Pan-Zea genome construction pipelines
The pipeline was written with bash and was only tested on Linux platform, we do not guarantee trouble-free running on other platforms.
Runtime environment:
- Linux, tested with version 3.10.0-862.el7.x86_64 (Red Hat 4.8.5-28)
- bash, tested with version 4.2.46(2)-release (x86_64-redhat-linux-gnu)
- perl 5, tested with v5.30.1
These softwares should be installed and available from $PATH environment variable to make sure the pipelines run successfully:
- idba_ud
- Quast5 (tested with v5.0.2)
- seqkit (tested with v0.14.0)
- csvtk (tested with v0.20.0)
- pigz (tested with v2.3.1)
- blastn (tested with v2.9.0)
- bwa (tested with v0.7.17-r1188)
- samtools (tested with v1.9)
- bedtools (tested with v2.27.1)
- bedops (tested with v2.4.35)
- bbtools: clumpify.sh stats.sh (tested with v38.42)
- popins (tested with vdamp_v1-151-g4010f61, and ignoring the velvet program because we used pre-assemblied contigs from idba_ud)
Once the prerequisites were correctly installed and assigned to $PATH, the pipelines could be executed by:
# get the usage of the pipelines:
bash /PATH/to/pan-Zea_genome_pipe/PANZ_individual_pipe.sh -h
bash /PATH/to/pan-Zea_genome_pipe/PANZ_cluster_pipe.sh -hFigure illustration of the pipeline:
The pipeline consists mainly of:
- run assembly using idba_ud to get genome assembly for each individual
- align each assembly to the reference genome using minimap2 (embedded in quast) and get primary NR-SEQs
- algin the primary NR-SEQs using blast against
NCBI nt databasefor decontamination- align the outputs to reference genome again with
bwa MEMand filter according tocoverage%andidentity%- get the split-reads (SR) and read-pairs (RP) by aligning the WGS paired-end reads of each individual to the reference genome using
popinsas the anchoring evidences- combine WGA information with evidences from SR and RP to anchor the NR-SEQs to reference genome
- clustering the anchored NR-SEQs, and get non-redundant representations according to population level evidences
- get non-redundant unanchored NR-SEQs, merge with reference sequence and anchored NR-SEQs as the linear pan-genome.
Let's say we have 150 bp WGS PE reads from one maize sample called TEST001:
# TEST001 PE read of 150 bp
TEST001_rd1.fq.gz
TEST001_rd2.fq.gzAnd a reference genome assembly: REF.fa
Firstly, we need to align the short reads of TEST001 to the reference genome using BWA MEM:
# build reference index for bwa
bwa index /path/to/REF.fa
# this would generate index files of REF.fa.{amb,ann,bwt,pac,sa}
# NOTE: make sure the indexes are in the same PATH with REF.fa
# Now run sequence alignment, and get sorted bam format alignment:
bwa mem /path/to/REF.fa /path/to/TEST001_rd1.fq.gz /path/to/TEST001_rd2.fq.gz |\
samtools view -@ -Shu - |\
samtools sort -O bam -o TEST001_bwa_sort.bam -note: this bam file was used for extracting "poorly-aligned reads" in popins only, using bam flies from other aligner such as Bowie2 would also work. But the BWA index of REF is mandatory.
Considering that TEST001 is a plant sample, we would like to search the result contigs against the NCBI nt database to remove "best-hit-not-plant" records. To achieve this, we need a local nt database, and a list of plant accessions within the database.
- Get local nt database:
# download nt database from NCBI
# NOT run:
# wget https://ftp.ncbi.nih.gov/blast/db/FASTA/nt.gz
# gunzip nt.gz- Get all plant accessions within nt db:
# 1. parse nt db to get [Gi_access] -> [Taxonomy_id] relationship:
blastdbcmd -db nt -entry all -outfmt "%a,%l,%T" > nt_all_accession_length_taxid.csv
# 2. get all Taxonomy IDs belonging to Viridiplantae (33090)
# using TaxonKit: https://github.com/shenwei356/taxonkit
taxonkit list --ids 33090 --indent "" > plant.taxid.txt
# 3. get all plant accessions:
cat nt_all_accession_length_taxid.csv |\
perl -F"," -lane '
BEGIN{
open(IN,"plant.taxid.txt");
while(<IN>){
chomp;
$h{$_}=1;
}
$,="\t";
}
$a=join(",",@F[0..$#F-2]);
print $a if $h{$F[-1]};
' > plant_nt_accession.txt
Now we have everything needed as inputs:
# >> In bash:
# inputs
export rd1 = "/path/to/TEST001_rd1.fq.gz"
export rd2 = "/path/to/TEST001_rd2.fq.gz"
export ref = "/path/to/REF.fa" # bwa indexed
export sr_bam="/path/to/TEST001_bwa_sort.bam"
# dbs
export nt_db= "/path/to/nt_db/nt"
export pl_acc= "/path/to/plant_nt_accession.txt"And we could simply run the pipeline as:
# run pipeline for TEST001:
bash /path/to/PANZ_individual_pipe.sh -1 ${rd1} -2 ${rd2} -g 500 -t 8 -X TEST001 -R ${ref} -l 100 -D ${nt_db} -P ${pl_acc} -N 0.4 -c 0.8 -i 0.9 -B ${sr_bam} -l 150 -q 10 -A 3 -S 3This command would automatically do:
- assembly TEST001 draft contigs from WGS reads
- filter out too short contigs (< 500 bp), then align the remaining contigs to reference genome to get the raw NR-SEQs (kept sequences with unaligned length > 100 bp)
- decontaminating raw NR-SEQs with proportion of not-plant-sequences >= 40%
- align NR-SEQs to reference again with BWA, filter out record with identify >= 90% and coverage >= 80%
- parse the poorly-mapped-to-reference PE reads of TEST001
- map these reads to reference to get RP and SR evidences (supported by at least 3 RP and SR hits) for anchoring
- get the final anchored information for TEST001
The outputs are located in a dir named TEST001, with plenty of result files. Here we will introduce the key outputs that used in the downstream pipelines, while the detailed Introduction of the outputs of PANZ_individual_pipe.sh are illustrated later.
-
TEST001.unaligned.pmrcfiltered.fa.gz: records the final NR-SEQs that passed all the filters. The ID of each sequence is in a format of
[PREFIX]_[contigIDs]_[start]-[end], e.g.: TEST001_scaftig0000000113_scaffold_112_32176-33759 -
TEST001_00_FINAL_ALL.vcf: records all the anchored NR-SEQs as INS in vcf format. The quality tag
LowQualmeans "supported with Read-pair evidence, but no precise position evidences (SR or WGA)", whilePASSmeans with evidences indicate the precise anchor positions and passed the filters. -
TEST001_05_FINAL_UNANCHORED.tsv: records all the un-anchored NR-SEQs either due to no anchoring evidences or evidences not strong enough to pass the cutoffs.
Assume we have already finished PANZ_individual_pipe.sh for WGS reads of another 99 samples TEST002 - TEST100. So we now have 100 result dirs:
# > ls -1
TEST001/
TEST002/
...
...
TEST099/
TEST100/We will need to list all the required NR-SEQ outputs of the 100 samples as the downstream inputs:
# list all NR-SEQs
ls /path/to/100SampleOuts/TEST{001..100}/*.unaligned.pmrcfiltered.fa.gz > pop_nrseq_list.txt
# list all anchored info
ls /path/to/100SampleOuts/TEST{001..100}/*_00_FINAL_ALL.vcf > pop_anchor_list.txt
# list all un-anchored info
ls /path/to/100SampleOuts/TEST{001..100}/*_05_FINAL_UNANCHORED.tsv > pop_unanchor_list.txtNow we could run PANZ_cluster_pipe.sh with command as:
# run cluster pipeline with 100 threads
bash /path/to/PANZ_cluster_pipe.sh -t 100 -V pop_anchor_list.txt -U pop_unanchor_list.txt -S pop_nrseq_list.txt -d 200 -D 2000 -c 0.8 -i 0.9 -w 10 -n 3 -r 1 -k Fthis pipeline would automatically do:
- grouping the population level anchored NR-SEQs based on left and right anchoring positions. In this case, we grouped NR-SEQs into one if they have left or right positions within 200 bp (
-d 200), and a final merge of two clusters within 2000 bp- for each group, identify sequence clusters based on cd-hit search with coverage >=80% and identify >= 90%
- for each sequence cluster, check if they could be well supported. In this case, check if they have at least 3 WGS members or at least one reference genome member, Take the others as unanchored.
- select the longest sequence in each cluster as representation of non-redundant anchored NR-SEQs.
- map the unachored sequences to the non-redundant anchored NR-SEQs, and remove similar records with the same identify and coverage cutoffs as in step2
- map the remaining un anchored sequences to each other to get the non-redundant representation of un-anchored NR-SEQs
- combining the non-redundant NR-SEQs and the reference genome, as the representation of pan-genome
STEP1-6 are embedded in PANZ_individual_pipe.sh, with options:
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
PANZ_individual_pipe.sh -- identify and anchor non-ref-sequences
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# parameters ([R]: Required; [O]: Optional)
-h show help and exit.
-1 <file> [O] File path of PE_reads_1.fq.gz, coupled with '-2'
-2 <file> [O] File path of PE_reads_2.fq.gz, coupled with '-1'
-g <int> [O] cutoff length for final assembly scaftigs (Default:500).
-t <int> [O] number of threads (Default: 4)
-x <string> [R] PREFIX for the sample, used to generate outputs.
-f <file> [O] File path of scaftig.fa.gz, will ignore -1 -2 and skip
idba_ud assembly step. If there is properate scaftig
file (Named as: Prefix_scaftig\$scftig_len.fa.gz, eg:
Sample1_scaftig500.fa.gz), the program will use that
file instead of -f scaftig file for downstream analysis.
(NOTE: sequence name of the scaftig file should start
with 'PREFIX_', same as -x PREFIX )
-R <file> [R] File path of reference.fa, should have bwa indexed.
-l <int> [O] min length for extract unaligned sequences (Default: 100)
-D <file> [R] Path of blastDB for cleaning. Use NCBI NT databse.
-P <file> [R] Path of list of 'within ids' in the blastDB, one record
per line.(eg.: if your species is plant, list all plant
ids in the blastDB. )
-N <0-1> [O] Cleaning scaftig cutoff. Filter out scaftigs with Non-
withinSP-seq-length-rate > this value. (Default: 0.4)
-c <0-1> [O] coverage cutoff for filtering unaln sequence (Default: 0.8)
-i <0-1> [O] identity cutoff for filtering unaln sequence (Default: 0.9)
-B <file> [R] File path of all-reads-align-to-ref-raw.bam, used to get
poorly mapped reads in PopIns.
-L <int> [O] Input WGS reads length (Default: 150)
-q <int> [O] map Quality cutoff for bam based filtering (Default: 10)
-A <int> [O] read-pairs support cutoff (Default: 3)
-S <int> [O] split-reads support cutoff (Default: 3)
-z <path> [O] Path of the sub-scripts dir. (Default: $(dirname $0)/src)
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
NOTEs:
- The input files should be with absolute paths; eg. use "/home/data/read.fastq.gz" rather than "./read.fastq.gz"
- If the user-defined scaftigs.fa.gz were assigned through
-foption, the-1 / -2options would be ignored and the de novo assembling step would be skipped - The idba_ud assembly parameters were hard-coded in line 44 of
/src/pan00_IDBA_assembly.shas--mink 20 --maxk 100 --step 20. So if you want to change the assembly parameters, you would have to modify the code line manually. We were sorry for that inconvenience, and would consider to make them optional in the future.
--------------------------------------------------
Clustering PANZ_individual_pipe.sh outputs
--------------------------------------------------
USAGE:
bash $0 <OPTIONS>
OPTIONS: (R:required O:optional)
-h show help and exit.
-t <num> O set threads (default 2)
-V <list> R VCF file list
-U <list> R UNANCHORED list
-S <list> R unaln sequences
-d <num> O pre distance (default 200 bp)
-D <num> O final distance (default 2000 bp)
-c <0-1> O coverage cutoff (default 0.8)
-i <0-1> O identity cutoff (default 0.9)
-w <num> O cdhit word length (default 10)
-n <num> O Min support number (default 3)
-r <num> O Min REF support number (default 1)
-k <T/F> O Keep all intermediate files if 'T'(default F)
--------------------------------------------------If you use this pipeline in your work, or you would like to know more details, please refer to:
Gui, S., Wei, W., Jiang, C. et al. A pan-Zea genome map for enhancing maize improvement. Genome Biol 23, 178 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-022-02742-7