Scott Hwang
This project was one of the requirements for completing the Deep Reinforcement Learning Nanodegree (DRLND) course at Udacity.com.
This project uitlizes the Tennis environment. In this environment, two agents play tennis with each other. Each agent is represented by a racket and they try to learn to hit a ball back and forth between each other across a net.
During one episode of play, an agent earns a reward of +0.1 every time it hits the ball over the net. A negative reward of -0.01 is given if the ball hits the ground or goes out of bounds. Ideally, the two agents should learn how to keep the ball in play to earn a high total reward.
The introduction to the course project indicates the state space consists of 8 variables corresponding to the position and velocity of the ball and racket. Each agent receives its own, local observation. On examination of the environment, it indicates that it's state size is 24 for each agent, so there must be other parameters in the state space.
The action space consists of two possible continuous actions, corresponding to movement towards (or away from) the net and jumping.
The environment is episodic. Each agent earns a score in one episode and the episode is then characterized by the maximum score between the agents. The maximum score between the two agents during one episode is average over 100 consecutive episodes. This 100-episode average of the maximum agent score must exceed +0.5 in order for the environment to be considered solved.
The installation of the software is accomplished with the package manager, conda. Installing Anaconda (https://www.anaconda.com/) will include conda as well as facilitate the installation of other data science software packages. The Jupyter Notebook App is also required for running this project and is installed automatically with Anaconda.
The dependencies for this project can be installed by following the instructions at https://github.com/udacity/deep-reinforcement-learning#dependencies. Required components include but are are not limited to Python 3.6 (I specifically used 3.6.6), and PyTorch v0.4, and a version of the Unity ML-Agents toolkit. Note that ML-Agents are only supported on Microsoft Windows 10. I only used Windows 10, so cannot vouch for the accuracy of the instructions for other operating systems.
-
Linux or Mac:
In a terminal window, perform the following commands:
conda create --name drlnd python=3.6
source activate drlnd
-
Windows:
Make sure you are using the anaconda command line rather than the usual windows cmd.exe.
conda create --name drlnd python=3.6
activate drlnd
The instructions at https://github.com/udacity/deep-reinforcement-learning indicate that you should enter the following on the command line to clone the the repository and install the dependencies:
git clone https://github.com/udacity/deep-reinforcement-learning.git
cd deep-reinforcement-learning/python
pip install .
However, for Windows 10, this did not work for me. The pip command fails when it tries to install torch 0.4.0. This version may no longer be available. I edited the dependencies shown in the requirements.txt file in the directory and changed the line for torch from
torch==0.4.0 to torch==0.4.1.
The pip command worked after the change. Otherwise you can install the required packages in the requirements folder manually. Sometimes these software packages change and you may need to refer to the specific instructions for an individual package. For example, https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/ may be helpful for installing PyTorch.
If you clone the DRLND repository, the original files from the project can be found in the folder deep-reinforcement-learning/p3_collab-compet
The github repository is https://github.com/snhwang/p3-collab-compet-SNH.git.
Download the environment from one of the links below. You need only select the environment that matches your operating system:
- Version 1: One (1) Agent
- Linux: click here
- Mac OSX: click here
- Windows (32-bit): click here
- Windows (64-bit): click here
- Version 2: Twenty (20) Agents
- Linux: click here
- Mac OSX: click here
- Windows (32-bit): click here
- Windows (64-bit): click here
Unzip (or decompress) the file which provides a folder. Copy folder into the folder p3_collab-compet-SNH. The Jupyter notebook for running the code is called Tennis-SNH.ipynb. The folder name indicated in Section1 of the notebook for starting the environment must match one of the folder you copied the environment into.
Create an IPython kernel for the drlnd environment:
python -m ipykernel install --user --name drlnd --display-name "drlnd"
These steps only need to be performed once.
- In a terminal window, specifically an Anaconda terminal window for Microsoft Windows, activate the conda environment if not already done:
- Linux or Mac:
source activate drlnd
-
Windows:
Make sure you are using the anaconda command line rather than the usual windows cmd.exe.
activate drlnd
- Change directory to the
p1_navigate_SNHfolder. Run Jupyter Notebook:
jupyter notebook
- Open the notebook
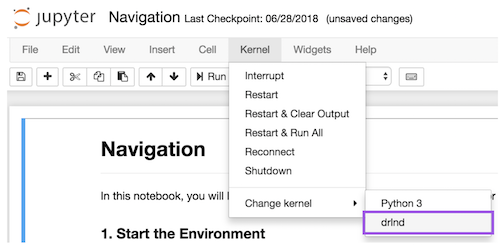
Tennis-SNH.ipynbto train with the multi-agent environment. Before running code in a notebook, change the kernel to match thedrlndenvironment by using the drop-downKernelmenu:
(taken from the Udacity instructions)
- To train the the agent(s) with the provided parameters, just "run all" under the Cell drop down menu of the Jupyter notebook.
The parameters of the learning agent can be changed in Section 4 of the notebook. The parameters for running the simulation and training the agent can be modified in Section 5. The parameters are described below. During training, multiple checkpoints are saved for running the trained agent later:
checkpoint_actor_first.pth and checkpoint_critic_first.pth: The first time an agent achieves a scores >0.5
checkpoint_actor.pth and checkpoint_critic.pth: The first time the agents achieve a 100-episode-average maximum score of >0.5. Keep in mind, that the agent's neural networks were changing during training during those 100 episodes. After training, a run of 100 episodes without any training can be performed using one of the checkpoints to see how well it performs.
checkpoint_actor_best_agent_max.pth and checkpoint_critic_best_agent_max.pth: The actor and critic network weights for the model that achieve the highest maximum.
checkpoint_actor_best_avg_max.pth and checkpoint_critic_best_avg_max.pth: The actor and critic network weights for the model that achieve the highest 100-episode average of the maximum episode score.
checkpoint_actor_final.pth and checkpoint_critic_final.pth: The most recent version of the neural networks, trained by the last episode in the training run.
Run the notebook named Tennis-SNH-pretrained.ipynb to read in a saved checkpoint and run the environment without further training. Make sure the the network type and the weights stored in the checkpoints match. The agent(s) are defined in Section 3. Please make sure the network name ('SELU' or 'RELU') matches the type of neural network weights stored in the checkpoint, e.g.:
agent = Agent(
state_size = state_size,
action_size = action_size,
num_agents = num_agents,
network = 'RELU'
)
The default is 'RELU' if not specified and I did not get 'SELU' to work. I recommend just using 'RELU,' or not specifying so that it just always uses the default. The name of the checkpoint can be changed in Section 4 of the notebook. The following examples shows how to run the agents using the checkpoint files for the neural networks which achieved the highest maximum agent score in a single episode. which a agent through 100 episodes and provide scores as well as the final average score. The final parameter is the number of episodes to run and can also be changed:
load_and_run(
agent,
env,
"checkpoint_actor_best_agent_max.pth",
"checkpoint_critic_best_agent_max.pth",
100
)
- Tennis-SNH.ipynb: Jupyter notebook to train the agent(s) and to save the trained the neural network weights as checkpoints. This notebook is set up for version 2 with multiple agents.
- Tennis-SNH-pretrained.ipynb: Notebook to read in a saved checkpoint and run the agent without additional learning.
- model.py: The neural networks
- agent.py: Defines the learning agent based on DDPG (python class Agent)
- Multiple files with the prefix
.pth: Checkpoint files contained the weights of previously training neural networks.
These parameters and the implementation are discussed more in the file Report.md.
batch_size: Batch size for neural network training
lr_actor: Learning rate for the actor neural network
lr_critic: Learning rate for the critic neural network
noise_theta (float): theta for Ornstein-Uhlenbeck noise process
noise_sigma (float): sigma for Ornstein-Uhlenbeck noise process
actor_fc1 (int): Number of hidden units in the first fully connected layer of the actor network
actor_fc2: Units in second layer
actor_fc3: Units in third fully connected layer. This parameter does nothing for the "RELU" network
critic_fc1: Number of hidden units in the first fully connected layer of the critic network
critic_fc2: Units in second layer
critic_fc3: Units in third layer. This parameter does nothing for the "RELU" network
update_every: The number of time steps between each updating of the neural networks
num_updates: The number of times to update the networks at every update_every interval
buffer_size: Buffer size for experience replay. Default 2e6.
network (string): The name of the neural networks that are used for learning.
There are only 2 choices, one with only 2 fully connected layers and RELU activations and one
with 3 fully connected layers with SELU activations. Their names are "RELU" and "SELU," respectively.
Default is "RELU."
n_episodes (int): Maximum number of training episodes
max_t (int): Maximum number of timesteps per episod
epsilon_initial (float): Initial value of epsilon for epsilon-greedy selection of
an action
epsilon_final (float): Final value of epsilon
epsilon_rate (float): A rate (0.0 to 1.0) for decreasing epsilon for each episode.
Higher is faster decay.
gamma_initial (float): Initial gamma discount factor (0 to 1). Higher values favor
long term over current rewards.
gamma_final (float): Final gamma discount factor (0 to 1).
gammma_rate (float): A rate (0 to 1) for increasing gamma.
beta_initial (float): For prioritized replay. Corrects bias induced by weighted
sampling of stored experiences. The beta parameters have no effect if the agent
unless prioritized experience replay is used.
beta_rate (float): Rate (0 to 1) for increasing beta to 1 as per Schauel et al. (https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.05952)
tau_initial (float): Initial value for tau, the weighting factor for soft updating
the neural network. The tau parameters have no effect if the agent uses fixed Q
targets instead of soft updating.
tau_final (float): Final value of tau.
tau_rate (float): Rate (0 to 1) for increasing tau each episode.
Please refer to report.pdf for more details about the algorithm and for some results: