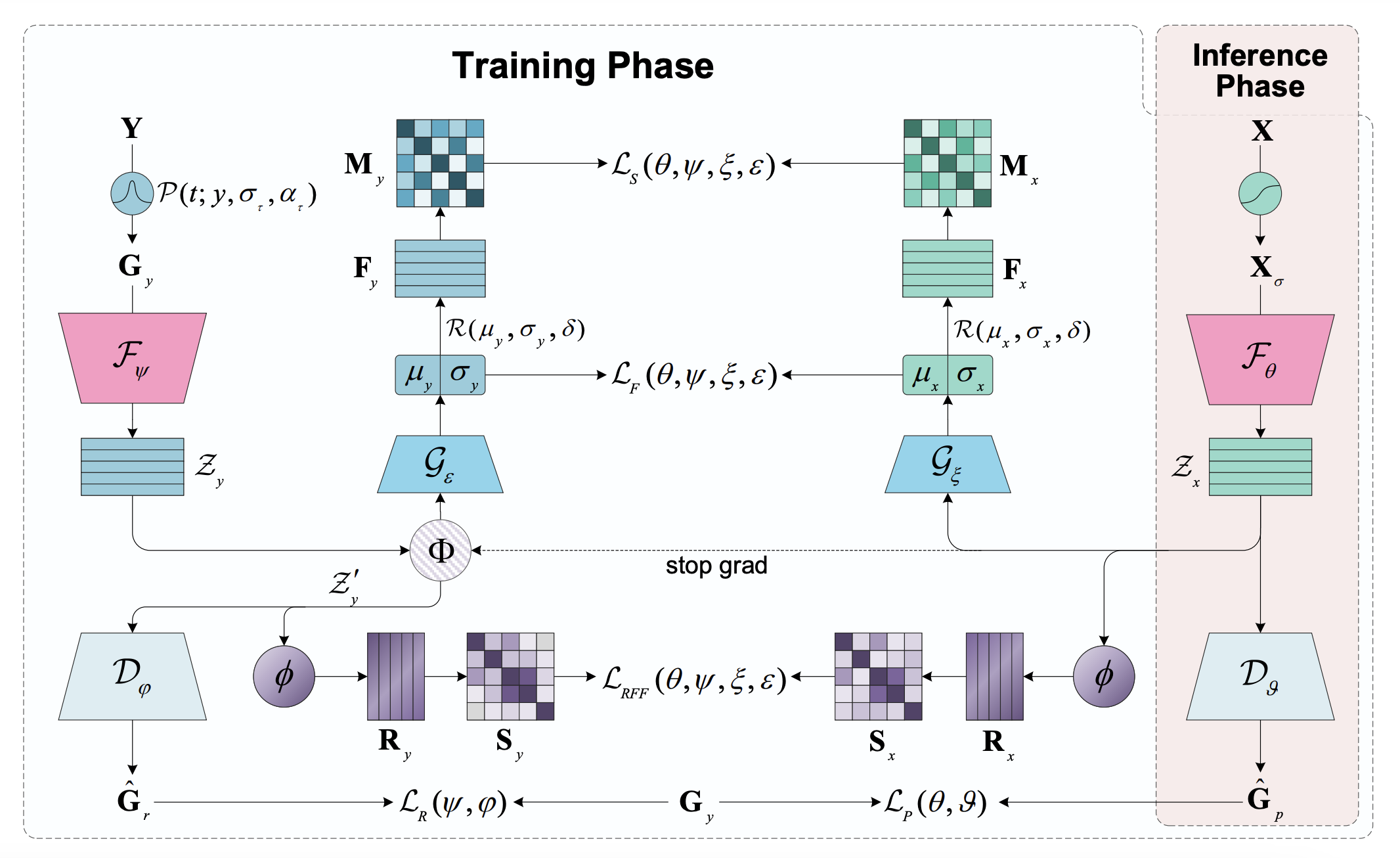
We introduce a Label Noise Robust Learning (LNRL) method for handling label noise in microseismic tasks with small-scale datasets. LNRL aligns feature representation and label representation distribution in multiple feature spaces, learns the correlation between instances and label noise, and mitigates the impact of label noise.
The code of this project is modified based on SeisT.
-
For training and evaluation
Create a new file named
yourdata.pyin the directorydataset/to read the metadata and seismograms of the dataset. And you need to use@register_datasetdecorator to register your dataset.(Please refer to the code samples
datasets/sos.py)
-
Model
Before starting training, please make sure that your model code is in the directorymodels/and register it using the@register_modeldecorator. You can inspect the models available in the project using the following method:>>> from models import get_model_list >>> get_model_list() ['seist','lnrl']
-
Model Configuration
The configuration of the loss function and model labels is inconfig.py, and a more detailed explanation is provided in this file. -
Start training
If you are training with a CPU or a single GPU, please use the following command to start training:python main.py \ --seed 0 \ --mode "train_test" \ --model-name "lnrl" \ --log-base "./logs" \ --device "cuda:0" \ --data "/root/data/Datasets/SOS" \ --dataset-name "sos" \ --sigma 600 \ --data-split true \ --train-size 0.8 \ --val-size 0.1 \ --shuffle true \ --workers 8 \ --in-samples 6000 \ --augmentation true \ --epochs 200 \ --patience 30 \ --batch-size 300
If you are training with multiple GPUs, please use
torchrunto start training:torchrun \ --nnodes 1 \ --nproc_per_node 2 \ main.py \ --seed 0 \ --mode "train_test" \ --model-name "lnrl" \ --log-base "./logs" \ --data "/root/data/Datasets/SOS" \ --dataset-name "sos" \ --sigma 600 \ --data-split true \ --train-size 0.8 \ --val-size 0.1 \ --shuffle true \ --workers 8 \ --in-samples 6000 \ --augmentation true \ --epochs 200 \ --patience 30 \ --batch-size 300There are also many other custom arguments, see
main.pyfor more details.
If you are testing with a CPU or a single GPU, please use the following command to start testing:
python main.py \
--seed 0 \
--mode "test" \
--model-name "lnrl" \
--log-base "./logs" \
--device "cuda:0" \
--data "/root/data/Datasets/SOS" \
--dataset-name "sos" \
--data-split true \
--train-size 0.8 \
--val-size 0.1 \
--workers 8 \
--in-samples 6000 \
--batch-size 300If you are testing with multiple GPUs, please use torchrun to start testing:
torchrun \
--nnodes 1 \
--nproc_per_node 2 \
main.py \
--seed 0 \
--mode "test" \
--model-name "lnrl" \
--log-base "./logs" \
--data "/root/data/Datasets/SOS" \
--dataset-name "sos" \
--data-split true \
--train-size 0.8 \
--val-size 0.1 \
--workers 8 \
--in-samples 6000 \
--batch-size 300It should be noted that the train_size and val_size during testing must be consistent with that during training, and the seed must be consistent. Otherwise, the test results may be distorted.
Copyright S.Li et al. 2024. Licensed under an MIT license.