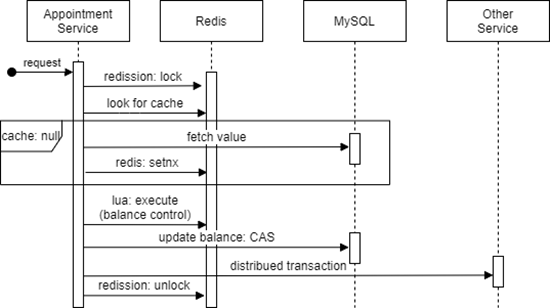
Manage the balance or inventory in the context of high concurrency transaction, such as sales promotion, to prevent oversell.
Use Redis to implement distributed lock, aiming to ensure idempotence.
- Combine the SetIfAbsent (setnx) and expire into an an atomic operation, inside the thread id should be the value.
- Unlock in the finally block. (The lock can be unlocked in advance)
- Prevent the key unlocked by other threads by mistake by comparing the thread id.
Redission is a framework in Java that provide lock function, that covering above factors.
The redisson-spring-boot-starter can coexist with spring-boot-starter-data-redis.
<!-- redis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.15.5</version>
</dependency>
spring:
redis:
host:
port:
password:
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
public fun() {
RLock transaction_lock = redissonClient.getLock(transaction_key);
try {
transaction_lock.lock();
...
} finally {
transaction_lock.unlock();
}
}
By default, the initial lockWatchdogTimeout is 30s, then if the current thread is not finished, the daemon thread will add extra 10s on the lockWatchdogTimeout. Off course, this configuration can be customized by yourself in .yml.
It is not suitable here to use distributed lock or distributed lock with segment caching, to control the balance of the whole product, since it will enfore the multithreading execution into linear execution, and cause block.
The recommened solution is to leverage the atomic feature of Redis (single thread with high availability), meaning that make the balance control linearly executed instead of the whole transaction. The atomic operations in Redis includes incr, or decr command, and even lua script.
Thus here we will apply Lua script to control balance since it allows to build a transaction inside. Before starting, here are some details you should be careful.
- Ensue the you have initialize the balance into the Redis before you use it.
- If needed you should use setIfAbsent (equal to setnx in command) to prevent rewriting among threads.
- Use the optimistic lock to synchronize back to the database, based on decrease and condition of being more than zero, rather than CAS(compare and swap) plus version increase.
Thanks for your patience, below are the pratical steps:
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean(name = "redisTemplate")
public RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisTemplate<String, String> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
RedisSerializer<String> redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
template.setConnectionFactory(factory);
// key序列化方式
template.setKeySerializer(redisSerializer);
// value序列化
template.setValueSerializer(redisSerializer);
// value hashmap序列化
template.setHashValueSerializer(redisSerializer);
// key haspmap序列化
template.setHashKeySerializer(redisSerializer);
return template;
}
}
In our case, we need to control the balance of both fund and investor.
local product = KEYS[1]
local qty = KEYS[2]
local fund_key = 'availability_fund_' .. product //appedn str
local investor_key = 'availabilit_investor_' .. product
local fund = redis.call('GET', fund_key)
local investor = redis.call('GET', investor_key)
if not fund or not investor then
return -1
end
if tonumber(fund) <= 0 or tonumber(investor) <= 0 then
return -1
end
if tonumber(fund) - tonumber(qty) < 0 then
return -1
end
local minuend_fund = 0 - tonumber(qty)
redis.call('DECRBY', investor_key, 1)
redis.call('INCRBYFLOAT', fund_key, minuend_fund)
return 1
@Configuration
public class LuaConfig {
@Bean
public DefaultRedisScript<Boolean> redisScript() {
DefaultRedisScript<Boolean> redisScript = new DefaultRedisScript<>();
redisScript.setScriptSource(
new ResourceScriptSource(new ClassPathResource(Constants.REDIS_LUA_SCRIPT_AVAILABILITY)));
redisScript.setResultType(Boolean.class);
return redisScript;
}
}
The path of Lua can be configured in your Contants class.
public static final String REDIS_LUA_SCRIPT_AVAILABILITY = "lua/availability.lua";
<update id="updateAvailability">
update Availability set
fund_availability = fund_availability - #{qty},
investor_availability = investor_availability - 1
where
product_id = #{productId} and
fund_availability - #{qty} >= 0 and
investor_availability >= 1
</update>
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate;
@Autowired
private DefaultRedisScript<Boolean> defaultRedisScript;
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@Transactional
public ResultVo<Appointment> saveTransaction(Appointment appointment, String token) {
ResultVo<Appointment> resultVo = new ResultVo<Appointment>();
Integer productId = appointment.getProductId();
Integer clientId = appointment.getClientId();
String fund_key = "availability_fund_" + productId;
String investor_key = "availabilit_investor_" + productId;
String transaction_key = "transaction_key_" + productId + clientId;
// 分布式锁-当前用户不能同时多次购买当前产品
RLock transaction_lock = redissonClient.getLock(transaction_key);
try {
transaction_lock.lock();
// 缓存查找
Object availability_fund = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(fund_key);
Object availabilit_investor = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(investor_key);
// 判断是否为空
if (availability_fund == null || availabilit_investor == null) {
Availability availability = availabilityService
.getOne(new QueryWrapper<Availability>().eq("product_id", appointment.getProductId()));
// NX - > 存在则不更新,防止覆盖
redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(fund_key, String.valueOf(availability.getFundAvailability()));
redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(investor_key,
String.valueOf(availability.getInvestorAvailability()));
}
// 判断库存
List<String> keys = Arrays.asList(productId.toString(), appointment.getSubscribeQty().toString());
Boolean execute = redisTemplate.execute(defaultRedisScript, keys);
if (execute == false) {
log.info("{}: 库存不足", productId);
resultVo.failure(500, "产品库存不足");
return resultVo;
}
// 更新库存
availabilityService.updateAvailability(appointment.getProductId(), appointment.getSubscribeQty());
// YOUR BUSINESS CODE BLOCK HRER
} finally {
transaction_lock.unlock();
}
resultVo.success(appointment);
return resultVo;
}
redisTemplate.delete(Constants.REDIS_KEY_PREFIX_AVAILABILITY_FUND + key);
redisTemplate.delete(Constants.REDIS_KEY_PREFIX_AVAILABILITY_INVESTOR + key);
If you want to continue to improve the performance in high concurrent situation, you can involve:
- Use Message Queue, such RabbitMQ, kafka to achieve decoupling and peak clipping, to prevent the overloading of database.
- Use the websocket to give the asynchronous response to client side, if you use above mq.
- Use distributed transation management to rollback the transation in failure case, if you have http call, such as feign or resttemplate, in your business part.
- Use hytrix or sentinel in your gateway to achieve flow limiting, by setting the threshold value of QPS or TPS.
https://juejin.cn/post/6844904030158716941#heading-8
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/361132817
This is the end, cheer up!