Walthrough Running a Demo App • Getting Started • Quick Start for Application Development • Quick Start for Serverless Development • Commands and Features • Feedback
The OpenShift Toolkit Extension revolutionizes cloud-native application development by seamlessly integrating with Red Hat OpenShift Hybrid Cloud and Kubernetes. With this powerful extension, developers can harness the full potential of OpenShift and Kubernetes directly within their favorite code editor, streamlining the development process and enhancing productivity.
OpenShift Toolkit extension provides an end-to-end developer experience for Red Hat OpenShift. From seamless deployment to effortless scaling, the toolkit offers comprehensive support for building, testing, and deploying applications. Enjoy features like automatic containerization, built-in debugging, and real-time monitoring, empowering developers to focus on writing quality code while the toolkit handles the complexities of container orchestration and management.
OpenShift Application Development
- Developers can easily create, deploy, and live debug container applications running on OpenShift, podman, and Hybrid Cloud.
- Convert local codebases and git repositories into components that can be debugged on OpenShift through the Create Component guided workflow.
- Create new devfile based components from a template project using the Create Component or Devfile Registries View guided workflows.
OpenShift Serverless Workflow
- This extension provides the app developer the tools and experience needed when working with
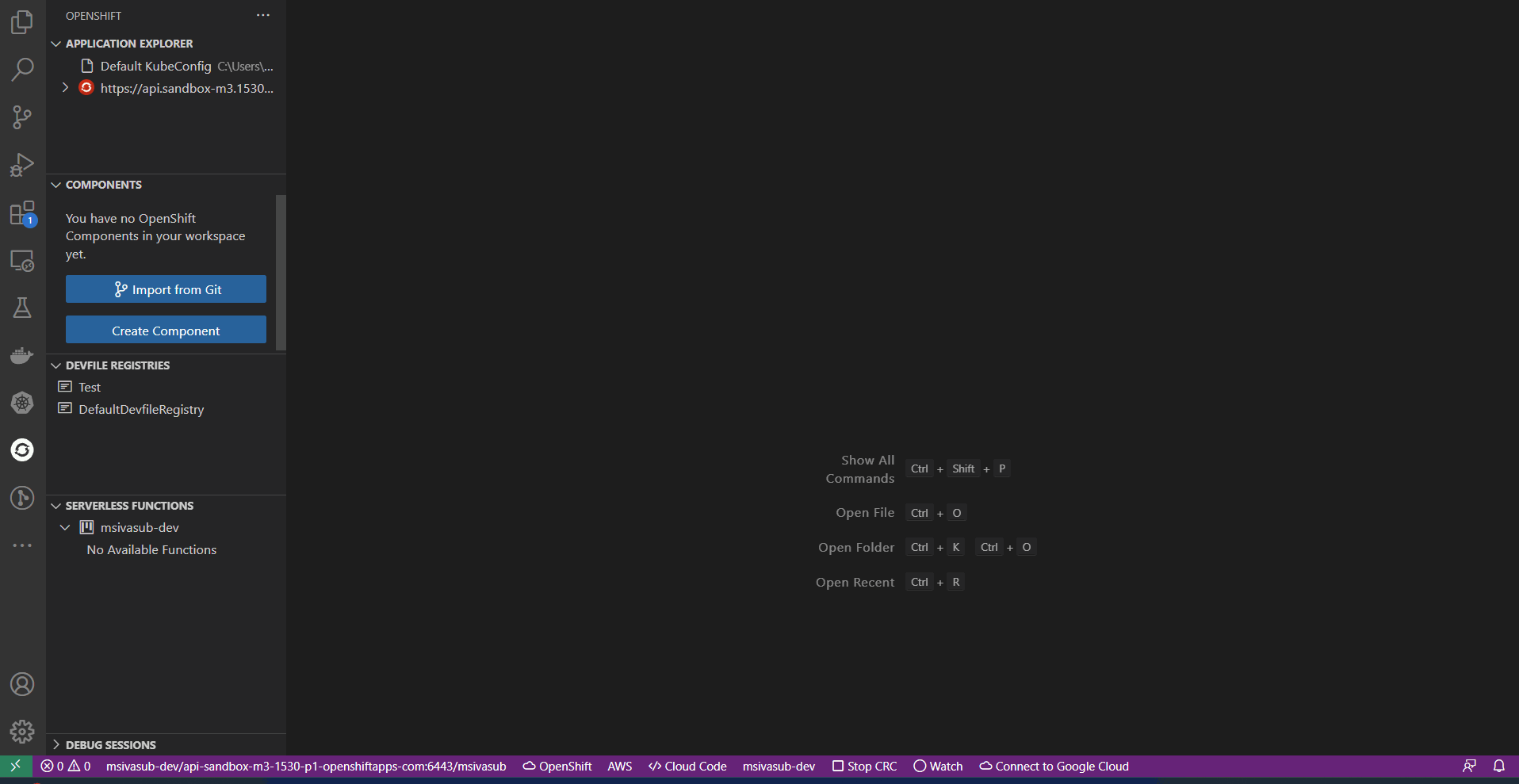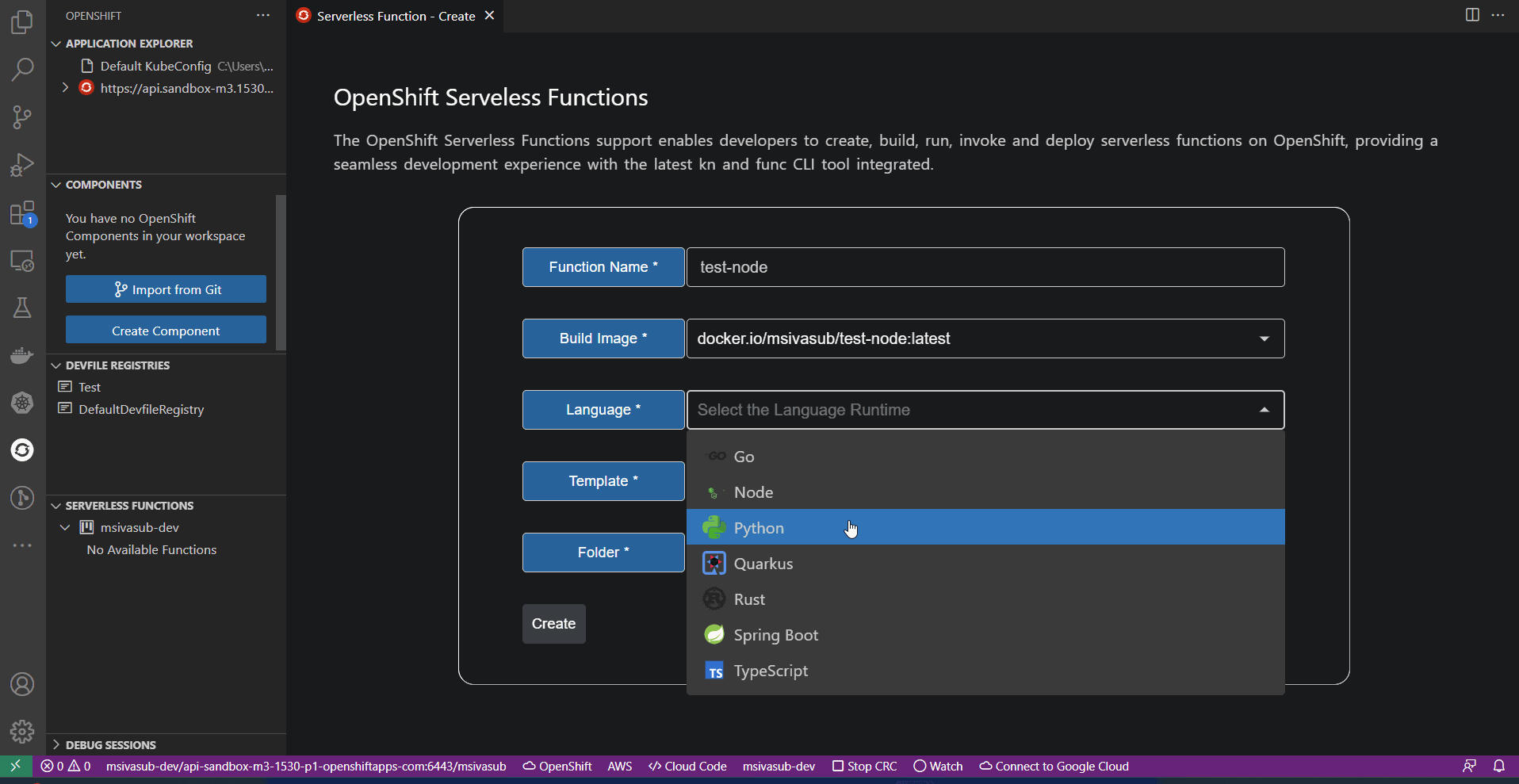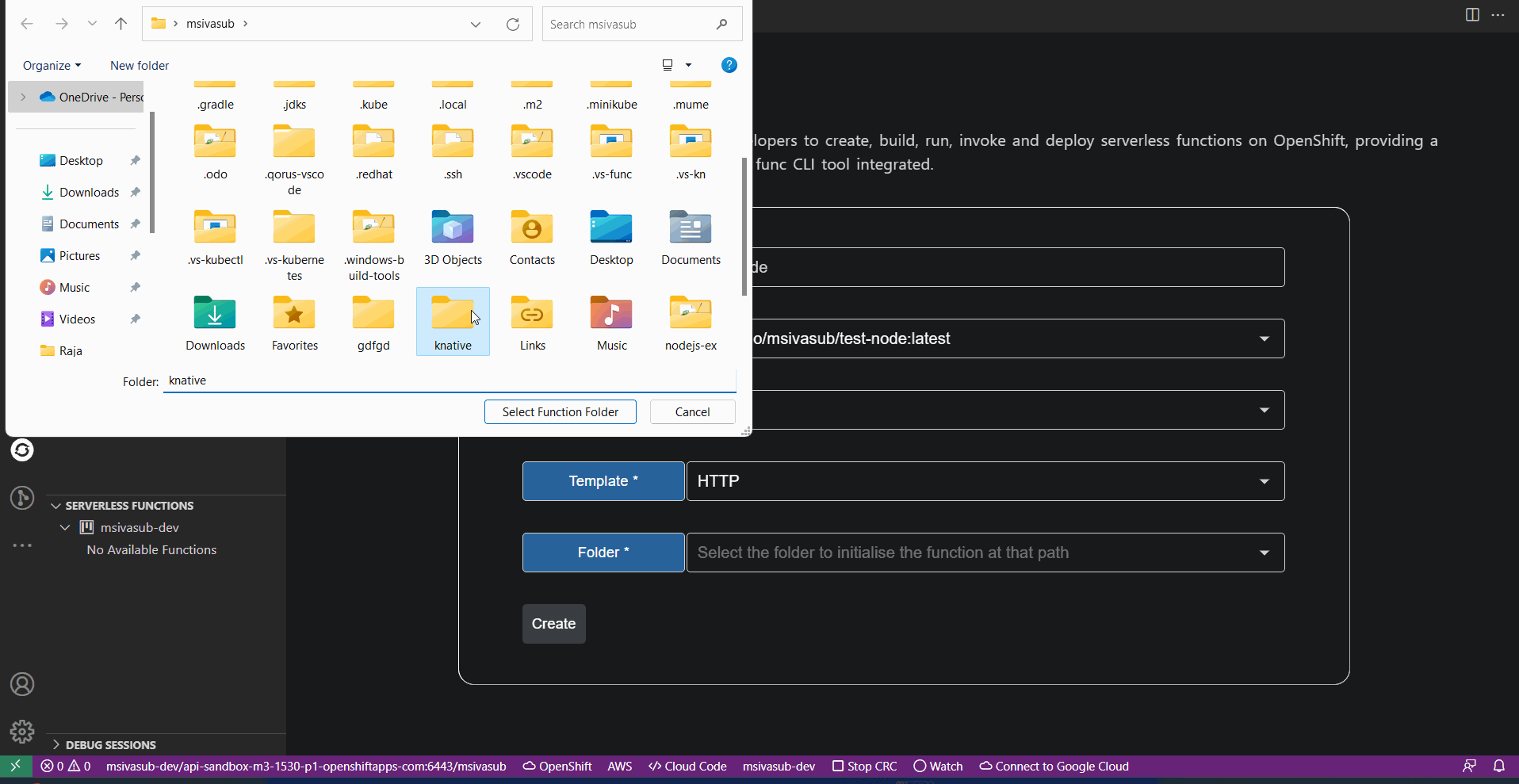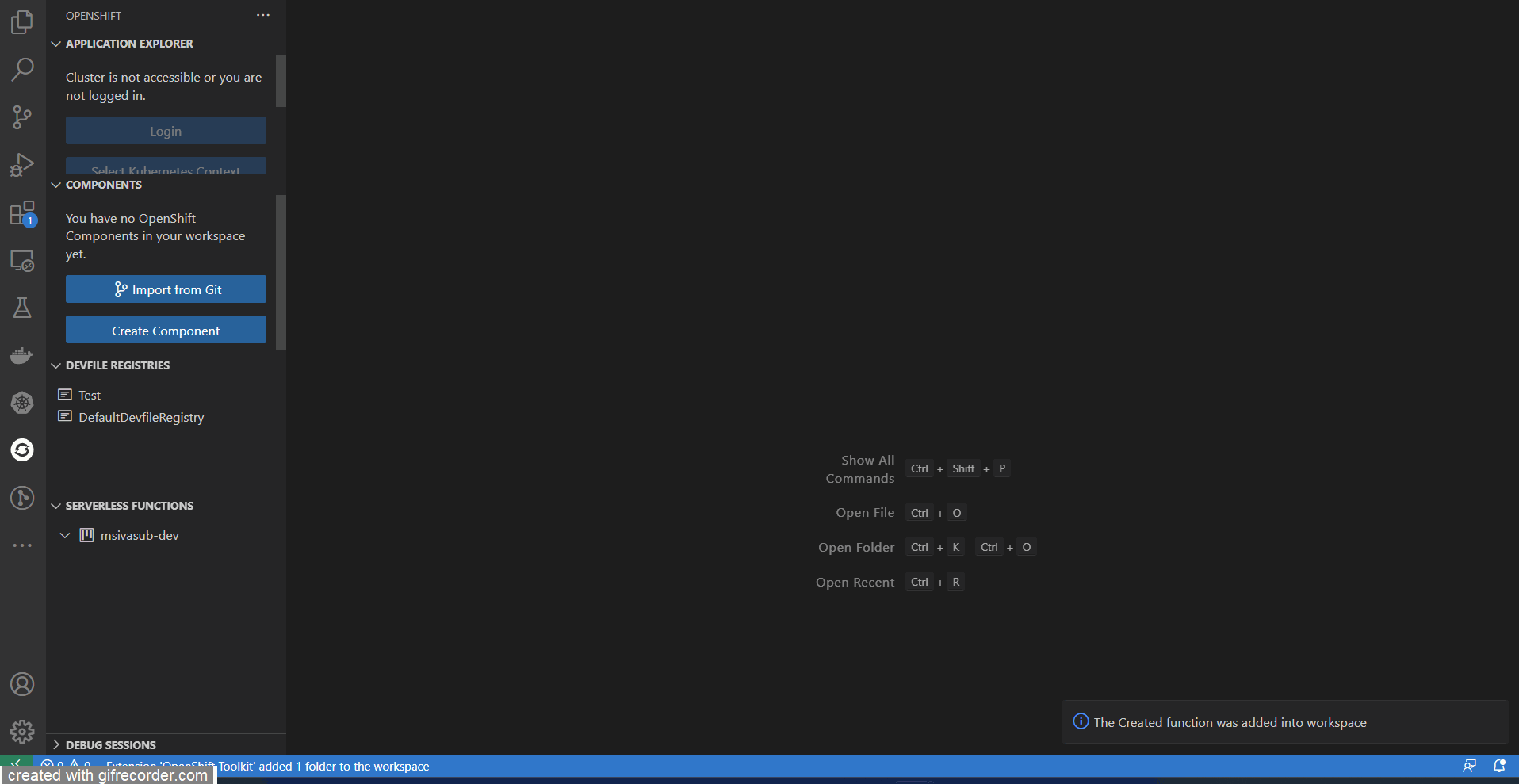
Knative & OpenShift Serverless Functionson a Kubernetes/OpenShift cluster. Using this extension, developers can develop and deploy functions in a serverless way through guided IDE workflow. - Users can create, run, deploy, build, invoke functions, and manage repositories directly from the UI.
OpenShift and Helm Integration
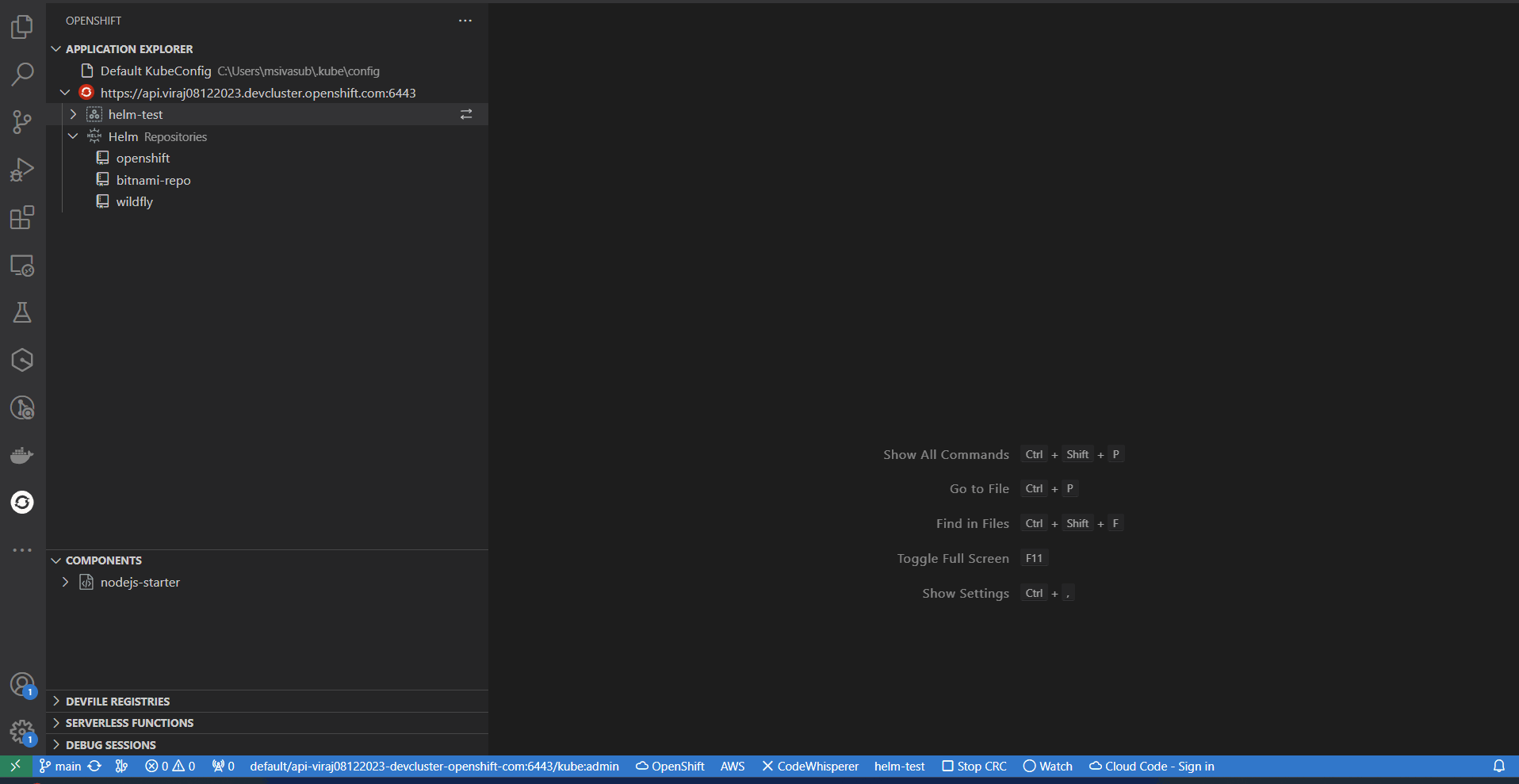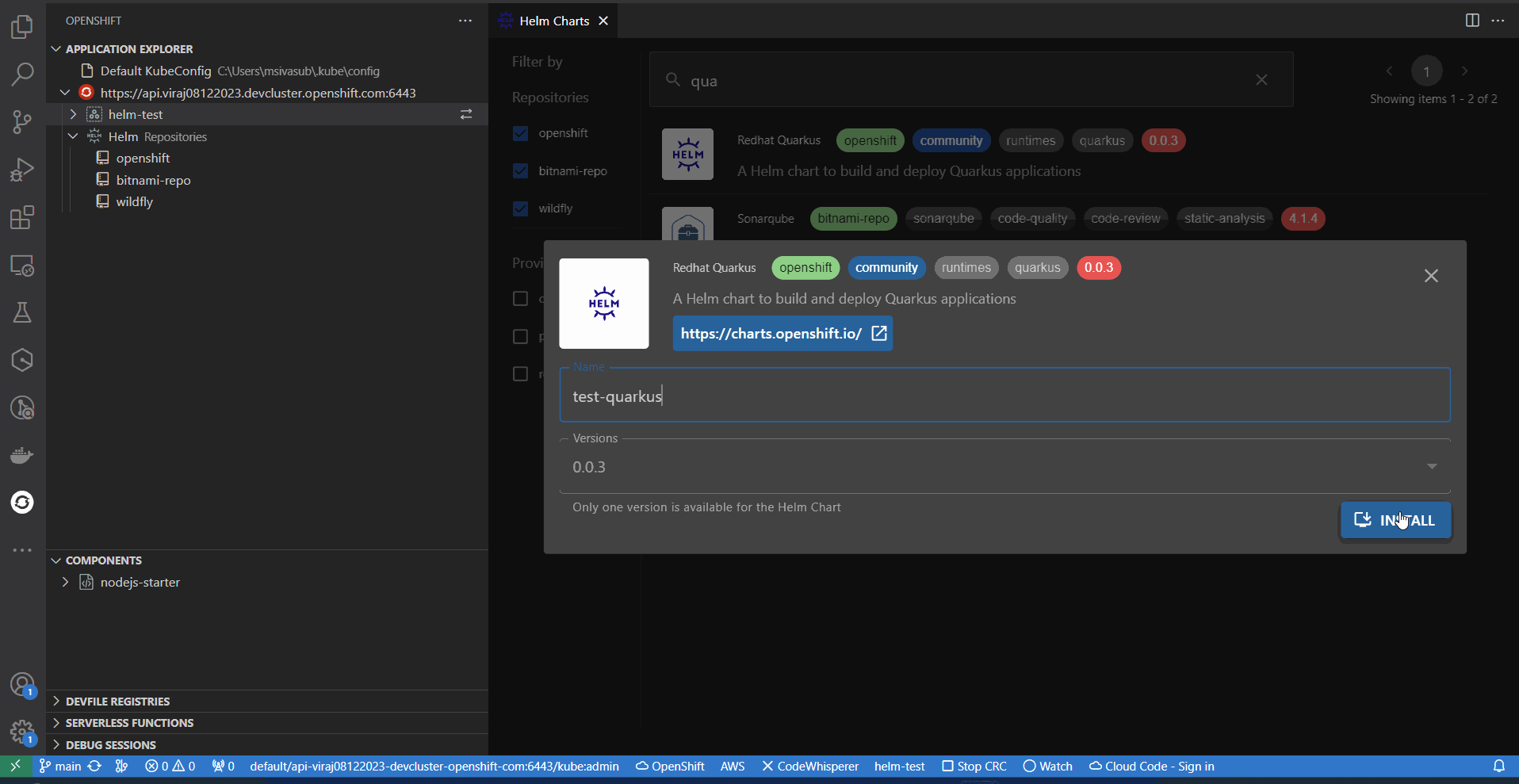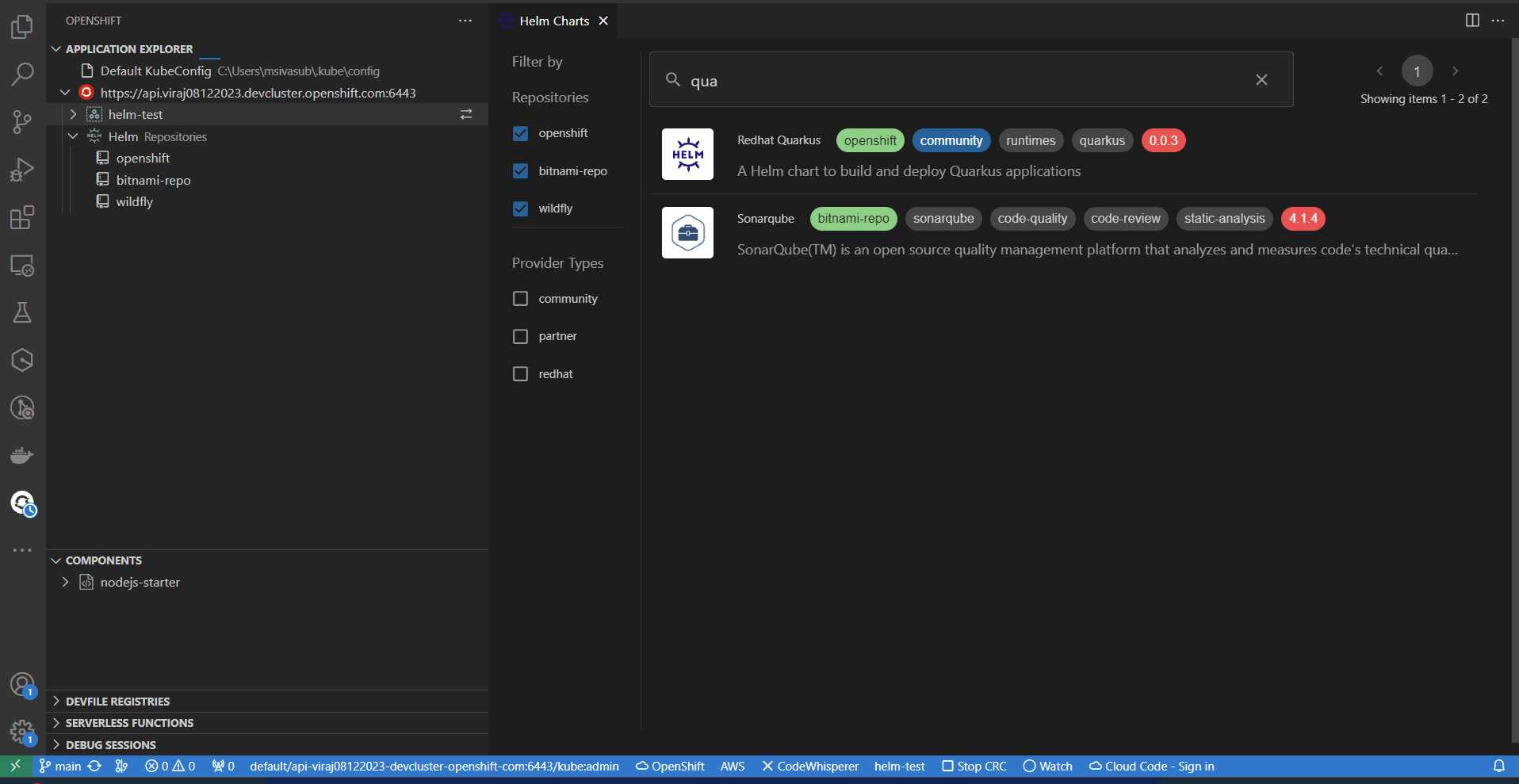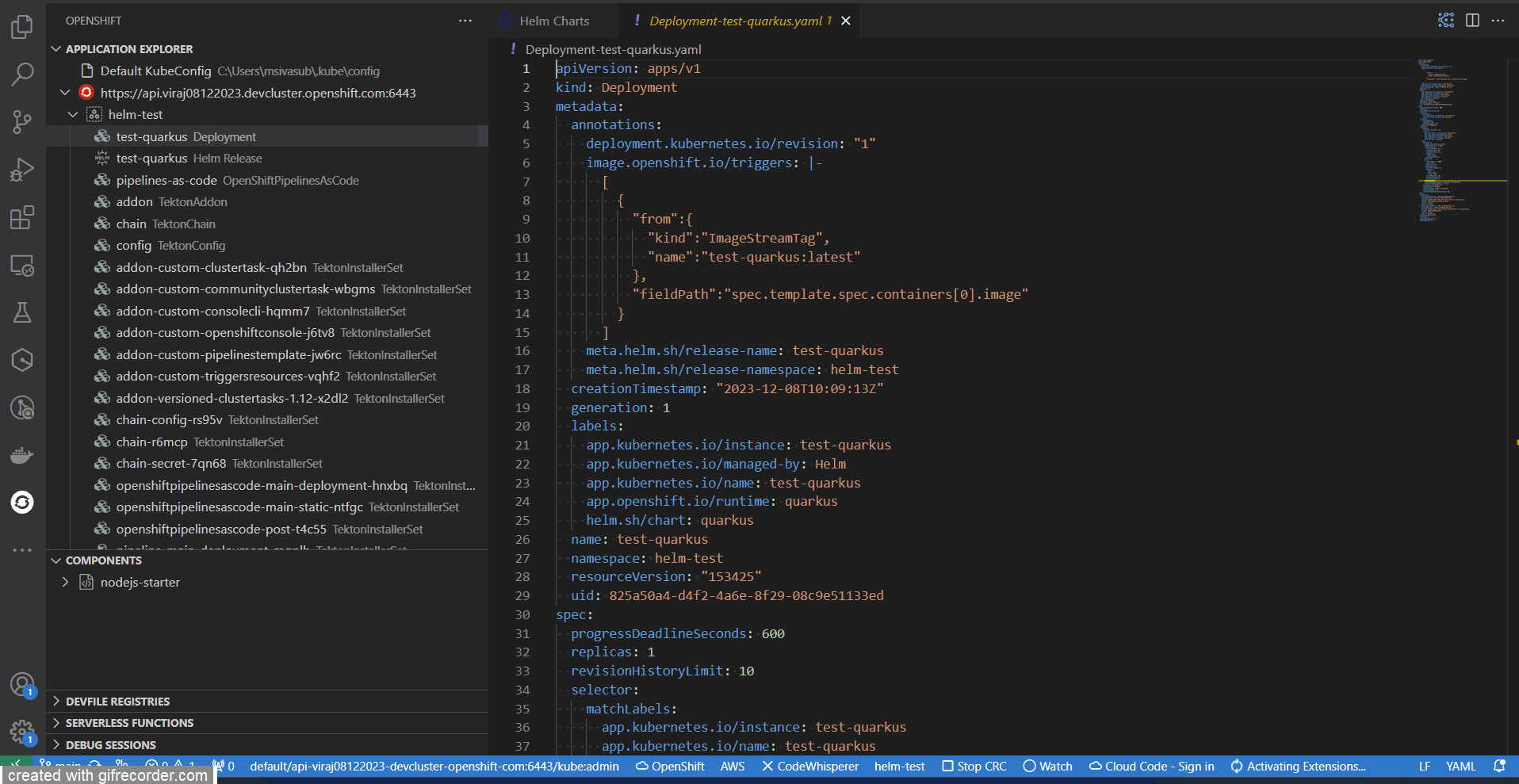
- Browse & Install Helm Charts on to the cluster directly from IDE.
- Developers can view and edit Resources YAML manifests, and view logs for pods, deployments, and deployment configs.
OpenShift Cluster Provisioning
- Run local instance of OpenShift 4.x using OpenShift Local directly from IDE
- Connect & Provision free Developer Sandbox for Red Hat OpenShift instance without leaving the IDE
Open this extension in the Visual Studio Code Marketplace
The OpenShift Toolkit extension provides multiple views to the user once it is launched.
1. Application Explorer View: Showcases the cluster connected to and the resources present in the cluster. The cluster URL, Project, Deployment, and Deployment Configs are shown in the tree view.
2. Components View: Displays the components created and also the actions associated with the component based on the state in which it is (running or stopped). Allows users to create components from an existing local codebase, from an existing git repository, or a template project.
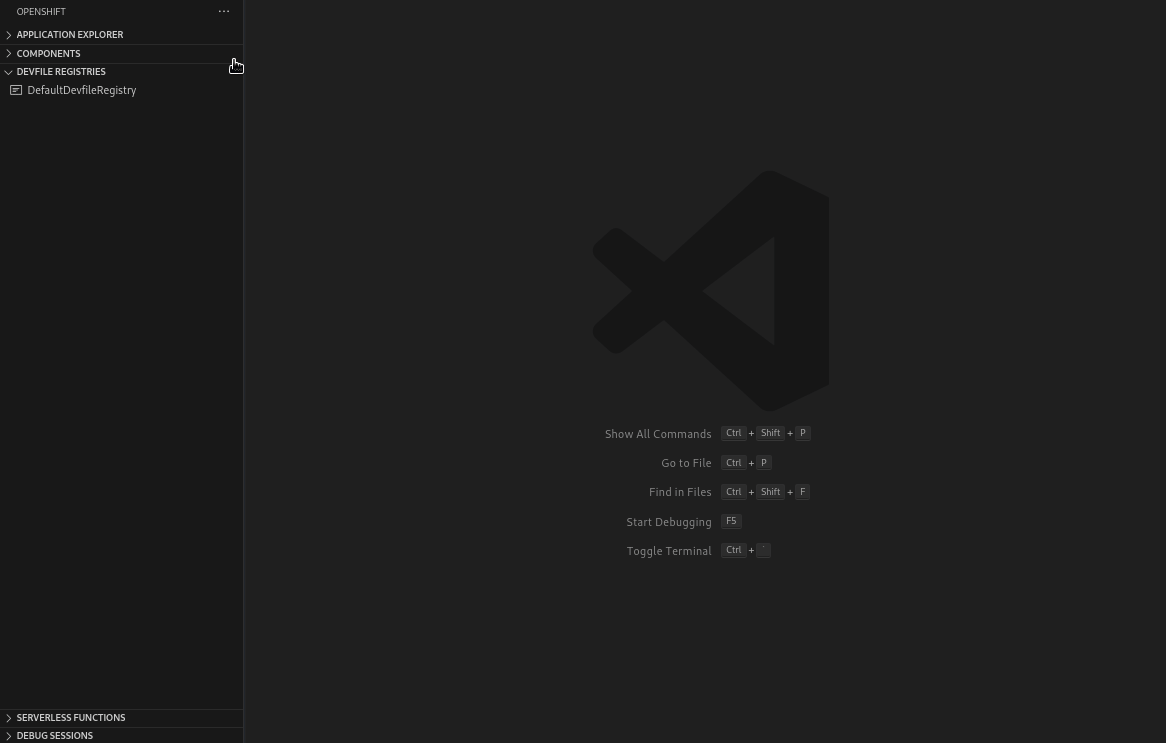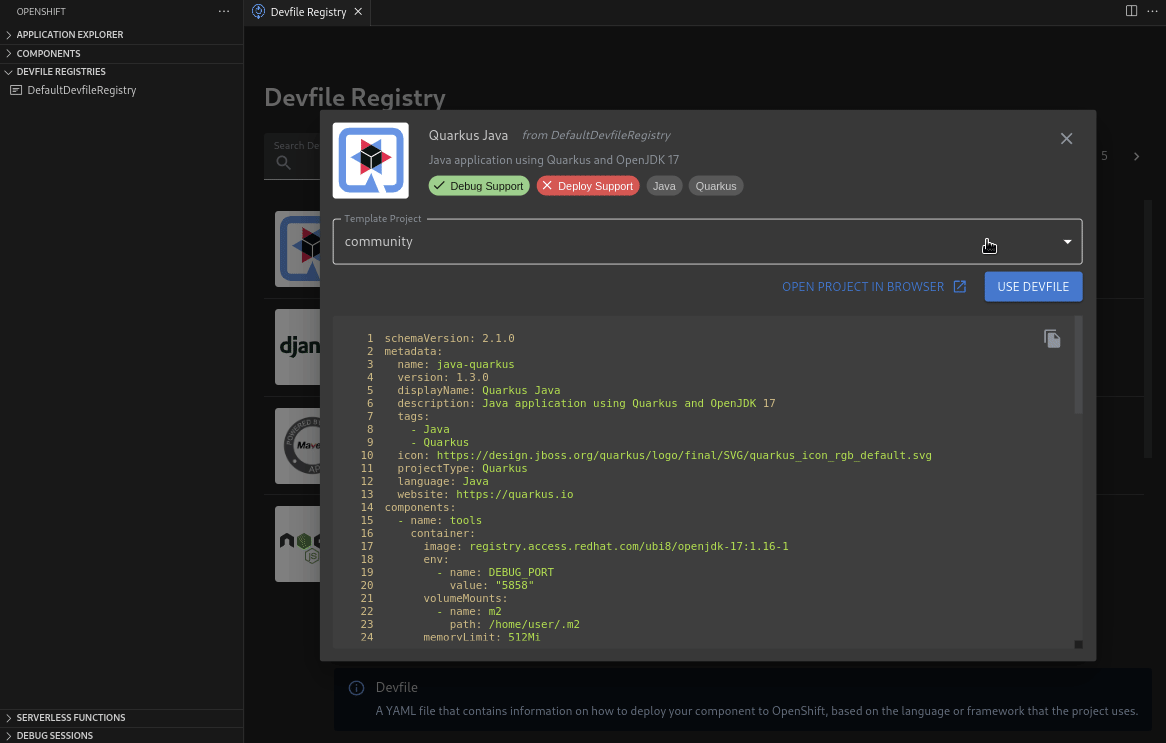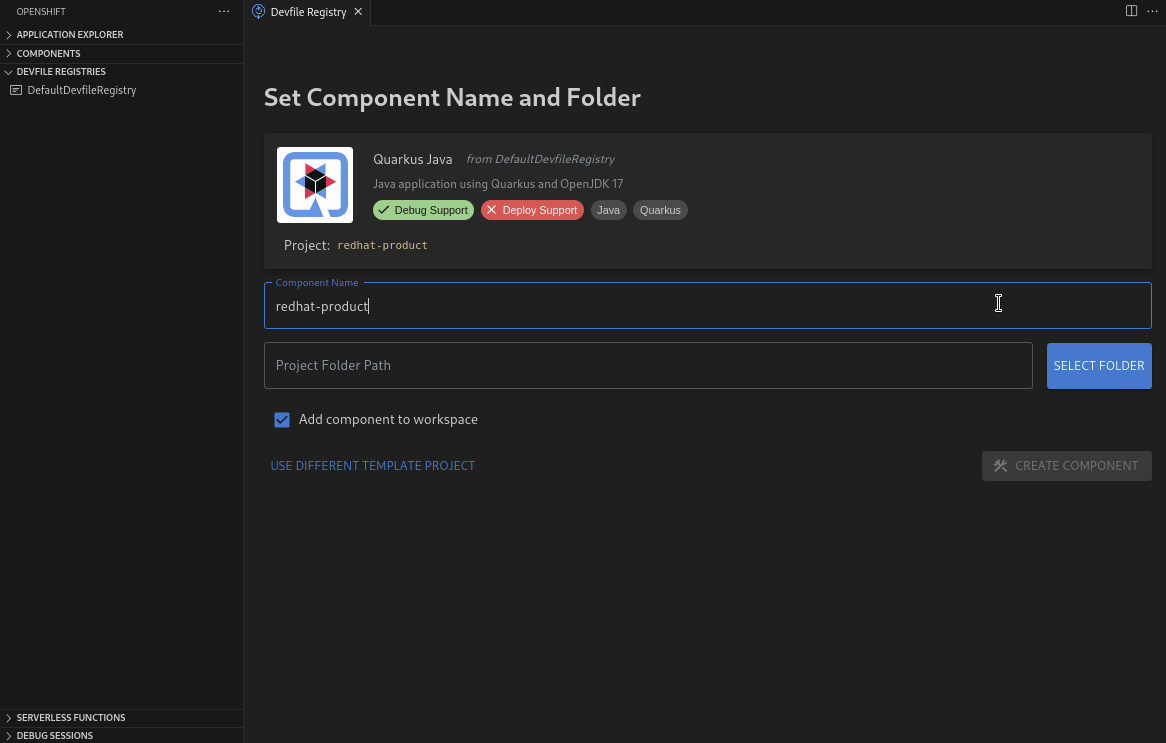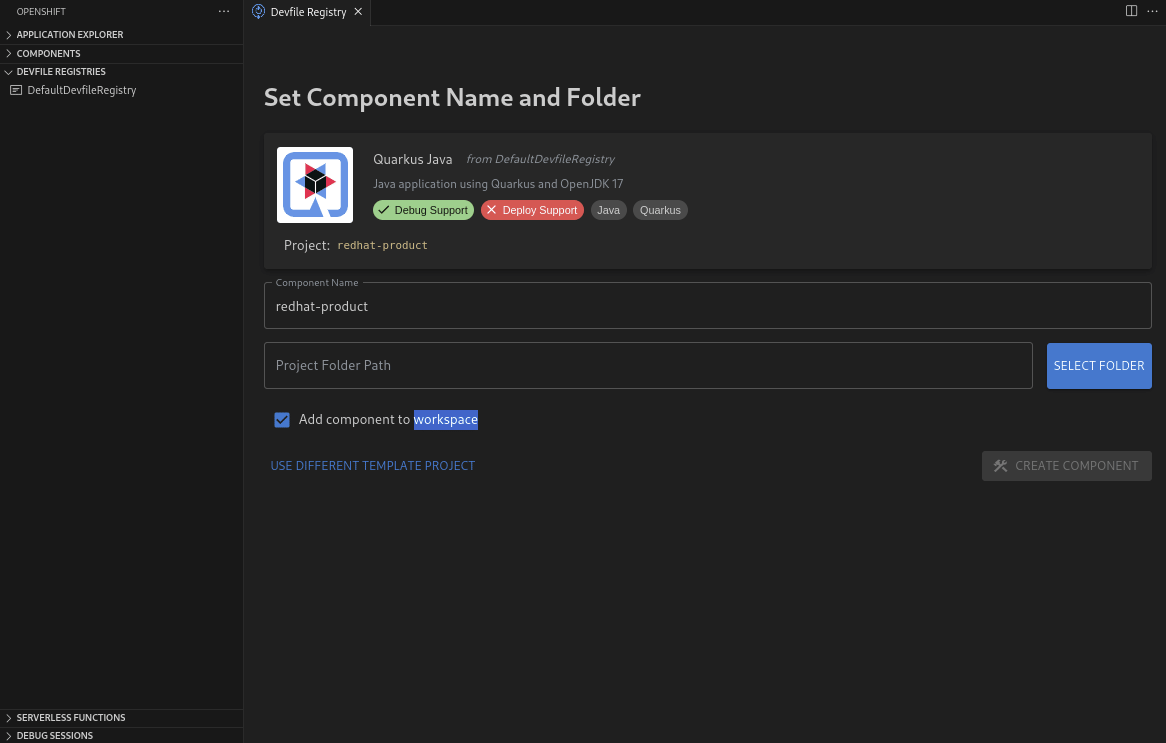
3. Devfile Registries View: Contains the Default Devfile Registry to browse and create components from the devfile stacks provided. Users can add their custom registry to the view and create components.
3. Serverless Functions View: Lists the available functions created in the cluster and provides the option to Create, Build, Deploy, and Run functions. It also allows you to Manage Repositories for the function template.
4. Debug Sessions View: Once the debug session is active, the associated component running in debug mode is displayed in this view.
The extension provides users with multiple ways to provision an instance of OpenShift to get started. Click on Add OpenShift Cluster which opens webview to select the way to get connected with a new OpenShift instance.
Red Hat OpenShift Developer Sandbox
The extension allows users FREE access to the Developer Sandbox for Red Hat OpenShift. From Add Cluster View, users can provision and connect to the dev sandbox instance using the guided workflow. The sandbox provides you with a private OpenShift environment in a shared, multi-tenant OpenShift cluster that is pre-configured with a set of developer tools.
Local instance of OpenShift
The extension allows the developers to provision a local instance of the OpenShift cluster using the guided workflow from the extension. It runs OpenShift Local which provides a single node local OpenShift 4.x cluster.
Tip
Please follow this guide to understand the guided workflow to provision OpenShift locally.
Provision Hybrid Cloud
To install OpenShift Container Platform 4 in the public cloud, in your data center, or on your laptop please visit Red Hat Hybrid Cloud console. Here are different scenarios to try OpenShift:
- Red Hat OpenShift Cluster Manager - This 60-day, self-supported trial lets you install and run the Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform on the infrastructure you manage.
- Red Hat OpenShift Dedicated - Red Hat OpenShift Dedicated is a fully managed service of Red Hat OpenShift on Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Google Cloud.
- Azure Red Hat OpenShift - Azure Red Hat OpenShift is a fully-managed service of Red Hat OpenShift on Azure, jointly engineered, managed and supported by Microsoft and Red Hat.
- Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS (ROSA) - Build, deploy, and manage Kubernetes applications with Red Hat OpenShift running natively on AWS.
Users can create components in a faster and intuitive way in a few clicks using the following workflows:
This guided workflow allows you to configure a project so that it can be run and debugged on OpenShift/Kubernetes. Users can deploy applications from:
- Existing local code base,
- Existing code base on a remote git repository,
- Create a new project from a pre-defined template directly from IDE.
This workflow generates a file called devfile.yaml (a Devfile) that contains instructions on how to deploy the project to OpenShift/Kubernetes based on the project's language or framework.
Once you have this setup, you can debug your project on OpenShift/Kubernetes by right-clicking on the project in the Components in the OpenShift sidebar, then selecting 'Start Dev'.
In the Devfile Registries view, there is an action to Open Registry View which opens a webview to browse devfile stacks consisting of supported registries. Users can create components directly from any selected stack and deploy them on OpenShift
Browse the catalog to discover and install Helm Charts on cluster, directly from VSCode.
Creates a Function in the mentioned directory with the specified language/runtime selected and handles HTTP events.
Tip
For more Serverless Functions Actions, please visit the detailed section here
The extension supports several commands to interact with OpenShift clusters and resources. The commands are accessible via the command palette (Cmd+Shift+P ⌘⇧P on macOS or Ctrl+Shift+P ⌃⇧P on Windows and Linux), Visual Studio Code View title buttons and tree context menus.
Tip
For more detailed information about specific commands and dependencies, please read the extension commands guide.
See the change log.
This is an open-source project open to anyone. This project welcomes contributions and suggestions!
For information on getting started, please take a look at the CONTRIBUTING instructions.
Download the most recent openshift-toolkit-<version>.vsix file from the release and install it by following the instructions here. Stable releases are archived here.
If you find an issue, please file a bug and we will fix it as soon as possible.
- File a bug in GitHub Issues.
- Open a Discussion on GitHub.
MIT, See LICENSE for more information.
The Red Hat OpenShift Toolkit for Visual Studio Code collects anonymous usage data and sends it to Red Hat servers to help improve our products and services. Read our privacy statement to learn more. This extension respects the redhat.telemetry.enabled setting which you can learn more about at https://github.com/redhat-developer/vscode-redhat-telemetry#how-to-disable-telemetry-reporting.
Note that this extension also abides by Visual Studio Code's telemetry level: if telemetry.telemetryLevel is set to off, then no telemetry events will be sent to Red Hat, even if redhat.telemetry.enabled is set to true. If telemetry.telemetryLevel is set to error or crash, only events containing an error or error property will be sent to Red Hat.