- A real-world guide to continuous testing
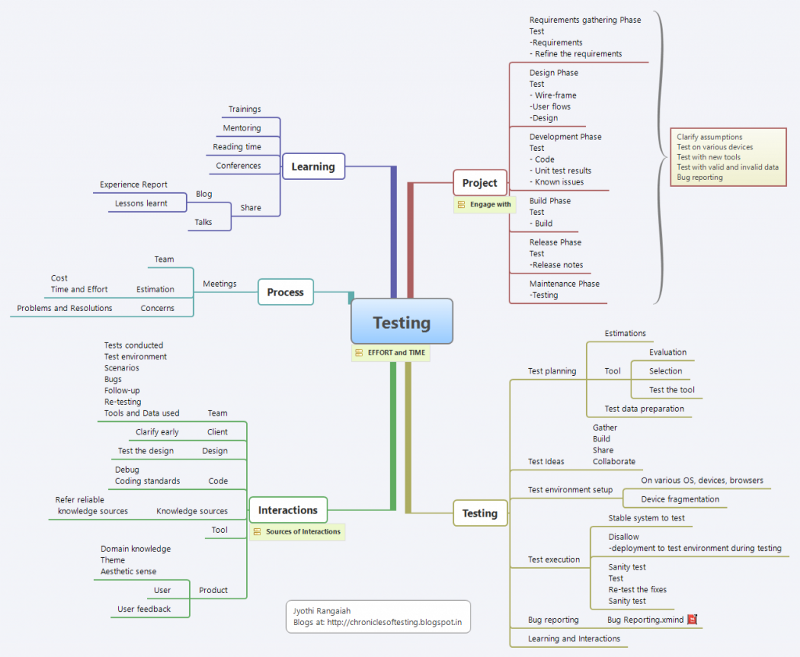
- Career Path of a Tester!
- AUTOMATED TEST CLASSIFICATION
- TECHNICAL TEST STRATEGY
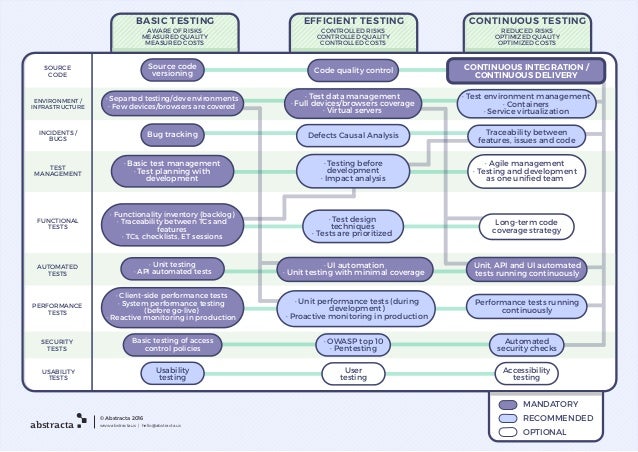
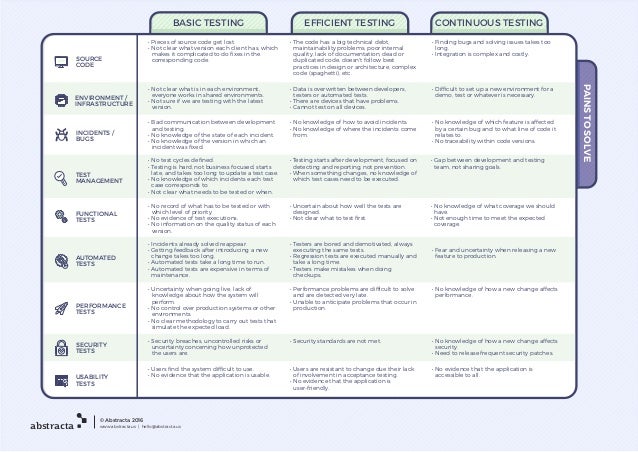
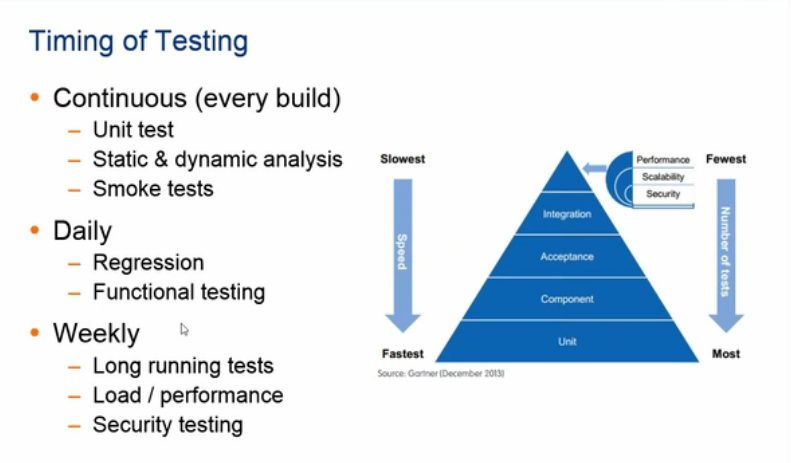
- Continuous Testing
- What Tools Should I Learn?
- Hiring Good Testers
https://www.thinksys.com/qa-testing/software-testing-metrics-kpis/
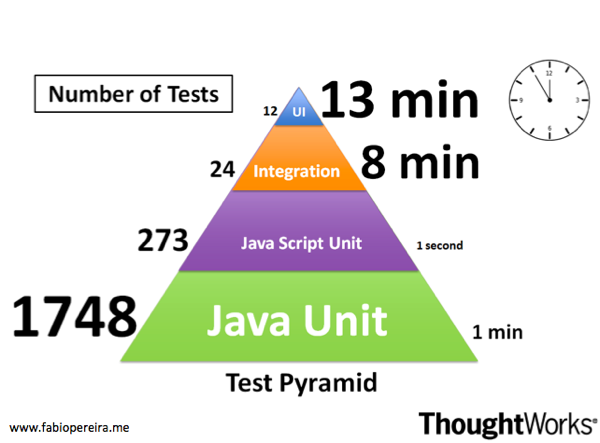
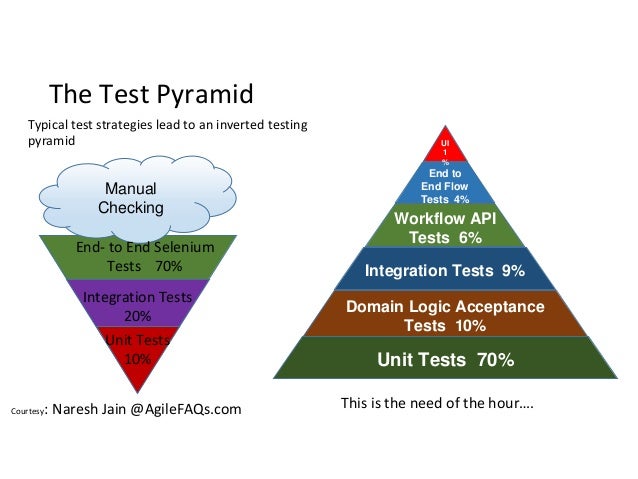
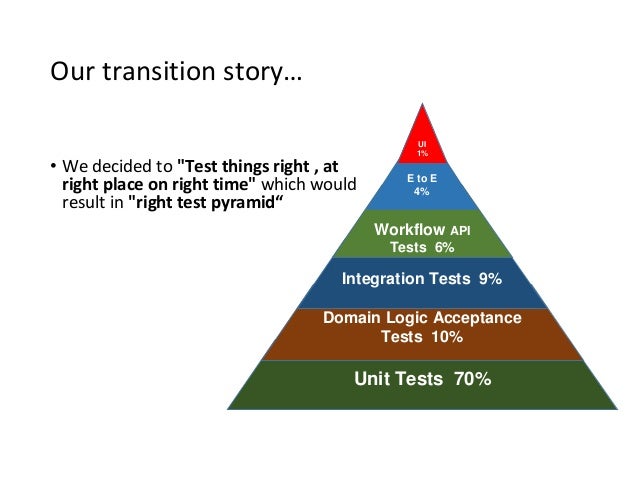
As a good first guess, Google often suggests a 70/20/10 split: 70% unit tests, 20% integration tests, and 10% end-to-end tests.
7 Quick Steps To Become a Great Automation Testing Engineer https://dzone.com/articles/7-quick-steps-to-become-a-great-automation-testing?
https://abstracta.us/2015/08/31/the-true-roi-of-test-automation/ https://dzone.com/articles/the-roi-of-automated-testing https://dzone.com/articles/additional-considerations-for-automated-testing
The following types of testing can be automated
- Functional – testing that operations perform as expected.
- Regression – testing that the behavior of the system has not changed.
- Exception or Negative – forcing error conditions in the system.
- Stress – determining the absolute capacities of the application and operational infrastructure.
- Performance – providing assurance that the performance of the system will be adequate for both batch runs and online transactions in relation to business projections and requirements.
- Load – determining the points at which the capacity and performance of the system become degraded to the situation that hardware or software upgrades would be required.
Automated testers must follow the following guidelines to get the benefits of automation:
- Concise: As simple as possible and no simpler.
- Self-Checking: Test reports its own results; needs no human interpretation.
- Repeatable: Test can be run many times in a row without human intervention.
- Robust: Test produces same result now and forever. Tests are not affected by changes in the external environment.
- Sufficient: Tests verify all the requirements of the software being tested.
- Necessary: Everything in each test contributes to the specification of desired behavior.
- Clear: Every statement is easy to understand.
- Efficient: Tests run in a reasonable amount of time.
- Specific: Each test failure points to a specific piece of broken functionality; unit test failures provide "defect triangulation".
- Independent: Each test can be run by itself or in a suite with an arbitrary set of other tests in any order.
- Maintainable: Tests should be easy to understand and modify and extend.
- Traceable: To and from the code it tests and to and from the requirements.
https://github.com/groupon/Selenium-Grid-Extras
http://www.nalashaa.com/7-key-best-practices-of-software-test-automation/
Podcast: The Testing Show https://www.qualitestgroup.com/resources/the-testing-show/
Patterns in Automation https://www.automatetheplanet.com/failed-tests-analysis-decorator/ https://www.automatetheplanet.com/strategy-design-pattern/ https://seleniumcamp.com/talk/design-patterns-in-test-automation/ https://blog.aspiresys.com/testing/design-patterns-in-test-automation-world/
- Reliable: Tests perform precisely the same operations each time they are run, thereby eliminating human error
- Repeatable: You can test how the software reacts under repeated execution of the same operations.
- Programmable: You can program sophisticated tests that bring out hidden information from the application.
- Comprehensive: You can build a suite of tests that covers every feature in your application.
- Reusable: You can reuse tests on different versions of an application, even if the user interface changes.
- Better Quality Software: Because you can run more tests in less time with fewer resources
- Fast: Automated Tools run tests significantly faster than human users.
- Cost Reduction: As the number of resources for regression test are reduced.
The following areas must be automated first
- Highly redundant tasks or scenarios
- Repetitive tasks that are boring or tend to cause human error
- Well-developed and well-understood use cases or scenarios first
- Relatively stable areas of the application over volatile ones must be automated.
What Is Regression Testing? Best Practices, Tutorials, and More https://dzone.com/articles/what-is-regression-testing-best-practices-tutorial?
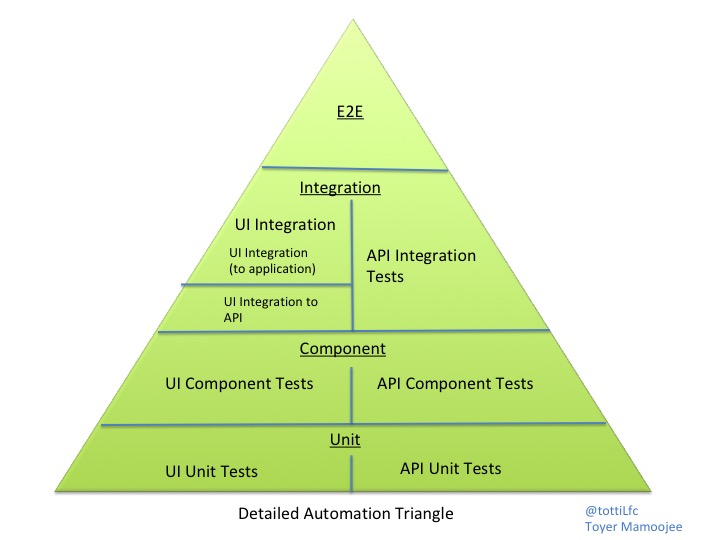
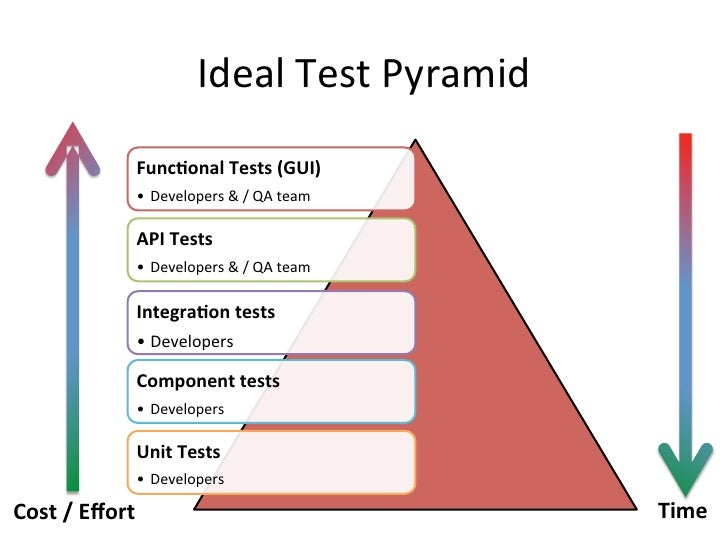
- Unit tests are written by the programmers for the programmers to ensure that the code is working at the deepest/lowest level. They should execute in milliseconds and target a 100% code coverage (at least 90%).
- Component tests are a part of the acceptance tests and check the behavior of individual component. A component encapsulate a specific set of business rules. These kind of tests should be very quick as well because they are decoupled from the other components and should cover about half the system.
- Integration tests are required to check the communication between components in order to verify that the “plumbing” has been done correctly. They ensure that the architectural structure of the system is correct. About 20% of the system is covered by integration tests.
- System tests are executed at the highest level of the system, from the UI to check the whole application and its construction (load tests are in this category for instance). They check about 10% of the system.
- Manual/exploratory tests are done by humans to explore the application for unexpected behaviors. They need the human creativity to hunt possible hidden bugs.
The main idea is that you want more unit tests than any other level of test because they:
- test the behaviour of the class / component rather than its implementation
- have no dependencies on other classes / components
- are easy to write & maintain (due to their independence)
- quick to run
Integrationn tests which:
- test the integration between components / features / external 3rd party services
- are dependant on the other components / features / external 3rd party services being available & stable enough to execute tests against.
- ensure dependencies of the system being developed continue to work as expected
- are slower than unit tests to run, but faster than acceptance tests to run
Acceptance tests are:
- a tool for conversing with business stakeholders (as they are generally written in human-readable language)
- a means of knowing when we’re done (developing a component / feature)
- checking the UI by actually clicking buttons on that UI
- High dependency on other components / features
- Brittle – easily broken if the UI changes
- Slowest of the 3 automated test levels to run
http://abstracta.academy/software-test-analyst-certification
http://apps.testinsane.com/mindmaps/Page/1/date_desc
- Bug Tracking: Eventum, JIRA
- Test Case Management: MS Excel
- Task Management: Trello , KanbanFlow, MS Excel
- Collaboration Software: Confluence,MS Excel
- Website Redirect & HTTP Headers: Redirects Checker
- Google Analytics Analyzer: Google Chrome Add-on Tag Assistant, Google Analytics Debugger
- SSL/TLS Certification Checker: Symantec SSL Checker, SSL Shopper Checker, Qualys SSL Server Test
- Broken Links Checker: My Links,
- Developer Tools: Browser Developer Tools, FireBug, Chris pederick Web Developer
- Screen Capture: qSnap, Jing, Awesome Screenshot, Screencastify, Snipping Tool
- Responsive Design Testing: Responsinator, Troy Responsinator,
- Visual Regression Testing: applitools.com, PhantomCSS
- API Functional Testing: SoapUI OpenSource, PostMan
- Code Viewer: JSON Viewer
- Fonts Identify: WhatFont
- Performance Testing: BlazeMeter Recorder, Page Speed Insights, YSlow, GTMetrix
- Print Friendly: CleanPrint
- Save for Later: Pocket, Basket
- Server-side automation testing tools: JMeter, Selenium, QTP, and FitNesse
- Unit testing tools: OCUnit, TestNG
- Custom test harness: C#, JS, Java, and C++
- Mobile Application Testing: Appium
- Reporting: Allure
Test Automation Equipments: Watir|Microfocus Test Partner|Microfocus Silk TestTM | Empirix e-Tester|Selenium|AutomatedQA TestComplete|IBM Rational Functional TesterTM | HP Unified Functional TestingTM , Performance test Equipments: Apache Jmeter|Microfocus Silk PerformerTM |OpenSTA|HP Load RunnerTM|Microfocus QALoad|Emprix’s e-Load Test Management Equipments: Microfocus SilkCentral Testmanager| IBM Rational Quality Manager| TestLink |HP Quality Center Defect Management Equipments: JIRA|PVCS Tracker|Bugzilla|TestTrack|TestDirector|SpiraTest Memory Leak Equipments: Wily Introscope|Repro|Coverity Prevent|Purify|Quest Jprobe|Zone Ranger Code Coverage Equipments: Borland Optimizelt|Koalog Code Coverage|Cenqua Clover|Rational Pure Coverage Configuration Management Equipments: IBM Rational Clearcase|Perforce|Visual Source Safe|CVS
-
Website testing
-
Web Application Functional Testing
-
Mobile Application Functional Testing
-
Visual Regression Testing
-
Application Security Testing
-
Performance testing
-
API Testing
-
Penetration Testing
-
Database testing
-
Reponsive Design Testing
-
INITIATION
- Statement of Work
- Requirement Gathering
-
TEST REQUIREMENT & PLANNING
- Estimation
- Traceability Matrix
- Test Plan
- Risk Assessment
-
ENVIRONMENT SETUP & TEST DECISION
- Software / Hardware Configuration
- Vendor
- Test Scenarios & Cases
- Test Data Preparation
-
EXECUTION & DEFECT TRACKING
- Test Execution
- Capture Results
- Reviews & Analysis
- Share Insights
-
CLOSURE REPORTING / MAINTENANCE
- Summary Reports
- Recommendations Report
- Client Acceptance
- Project Closure
- Test plan questions
- Web Test Automation Test plan
- Mobile Test Automation Test plan
- Performence Test plan
http://www.zarantech.com/blog/quality-assurance-project-management/
https://abstracta.us/2015/09/21/how-to-plan-test-case-automation-with-development-2/
http://www.seapine.com/papers/test-case-writing-best-practices http://quicksoftwaretesting.com/test-case-writing-tips/ http://www.testandtry.com/2010/02/24/8-tips-to-create-complete-test-cases/ How to Write a Test Case for Your Project and Your Team https://dzone.com/articles/how-to-write-a-test-case-for-your-project-and-your

- Title: Login Page – Authenticate Successfully on gmail.com
- Description: A registered user should be able to successfully login at gmail.com.
- Precondition: the user must already be registered with an email address and password.
- Assumption: a supported browser is being used.
- Test Steps:
- Navigate to gmail.com
- In the ’email’ field, enter the email of the registered user.
- Click the ‘Next’ button.
- Enter the password of the registered user
- Click ‘Sign In’
- Expected Result: A page displaying the gmail user’s inbox should load, showing any new message at the top of the page.
- General mobile application quality assurance
- Mobile automation testing
- Mobile games testing
- Cross-platform testing
- OEM package validation
- Device-specific validation
- Performance testing
- Compliance testing: PCI and HIPPA
- Carrier-specific validation testing
- Publisher validation testing: OEM HIG and publisher conformance
- Usability testing
- Security testing
- Energy profiling
- Field simulation testing
- Manual functional testing
- Compatibility testing
- Usability testing
- Test automation
- Performance testing
- Security testing
- Smoke testing
- Localization testing
- Usability testing
- Reliability testing
- Some strategies and factors to consider during this process include the following:
- Test fixed bugs promptly. The programmer might have handled the symptoms but not have gotten to the underlying cause.
- Watch for side effects of fixes. The bug itself might be fixed but the fix might create other bugs.
- Write a regression test for each bug fixed.
- If two or more tests are similar, determine which is less effective and get rid of it.
- Identify tests that the program consistently passes and archive them.
- Focus on functional issues, not those related to design.
- Make changes (small and large) to data and find any resulting corruption.
- Trace the effects of the changes on program memory.
- You can do integration testing in a variety of ways but the following are three common strategies:
- The top-down approach to integration testing requires the highest-level modules be test and integrated first. This allows high-level logic and data flow to be tested early in the process and it tends to minimize the need for drivers. However, the need for stubs complicates test management and low-level utilities are tested relatively late in the development cycle. Another disadvantage of top-down integration testing is its poor support for early release of limited functionality.
- The bottom-up approach requires the lowest-level units be tested and integrated first. These units are frequently referred to as utility modules. By using this approach, utility modules are tested early in the development process and the need for stubs is minimized. The downside, however, is that the need for drivers complicates test management and high-level logic and data flow are tested late. Like the top-down approach, the bottom-up approach also provides poor support for early release of limited functionality.
- The third approach, sometimes referred to as the umbrella approach, requires testing along functional data and control-flow paths. First, the inputs for functions are integrated in the bottom-up pattern discussed above. The outputs for each function are then integrated in the top-down manner. The primary advantage of this approach is the degree of support for early release of limited functionality. It also helps minimize the need for stubs and drivers. The potential weaknesses of this approach are significant, however, in that it can be less systematic than the other two approaches, leading to the need for more regression testing.
- Is the error due to a defect in unit 1?
- Is the error due to a defect in unit 2?
- Is the error due to defects in both units?
- Is the error due to a defect in the interface between the units?
- Is the error due to a defect in the test?
The benefits of automated unit testing https://www.codeproject.com/articles/5404/the-benefits-of-automated-unit-testing
Better Unit Tests through Design Patterns: Repository, Adapter, Mocks, and more… http://www.benday.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/08/benday-agile-2014-unit-testing-v2.pdf
Selenium & Java Training - WeekEnd Batch http://www.naveenautomationlabs.com/2017/12/selenium-java-training-course-content_29.html
Sample Resume - Automation QA Engineer - 2-7 Years http://www.naveenautomationlabs.com/2017/12/sample-resume-automation-qa-engineer-2.html
- Continuos Integration (CI) and unit tests
- Code coverage and static analysis
- Continuous Delivery / Automated deployment
- Integration / E2E / Visual testing
- Performance testing
- Security testing (DevSecOps)
- Exploratory testing
- Testing in Production (TiP)
https://joecolantonio.com/testtalks/
http://adventuresinqa.com/2017/04/24/how-to-get-started-in-software-testing/
- auditing and performance metrics for Progressive Web Apps
- Analyze your site performance
- Website Speed Test
- Web Page Analyzer
- WebSitePulse
- Test a website's performance
- YSlow
- PageSpeed Insights
- gtmetrix.com
Functional testing is typically conducted by providing an appropriate input to the function being tested (in line with the typical inputs expected in real-world use cases), and then verifying the result by comparing it to the expected result. This type of testing can answer questions about the capabilities of a software application, such as what actions users are able to perform.
It’s typically approached from one of two perspectives:
- Requirements-focused testing, which prioritizes requirements based on risk criteria in order to evaluate the most critical and important features and functions first.
- Business-process-focused testing, which relies on knowledge of end-user business requirements to evaluate an application’s performance in the context of typical use cases.
There are several specific functional testing techniques. The two primary techniques include white box testing and black box testing, although there are additional techniques including:
- Smoke testing.
- Unit testing.
- User acceptance testing.
- Integration testing.
- Interface testing.
- System testing.
- Localization testing.
- Regression testing.
- Globalization testing.
- Security testing.
- Usability testing.
- Operational readiness testing.
- Endurance testing.
- Interoperability testing.
- Maintainability testing.
- Ergonomics testing.
- Availability testing.
- Recoverability testing.
- And others!
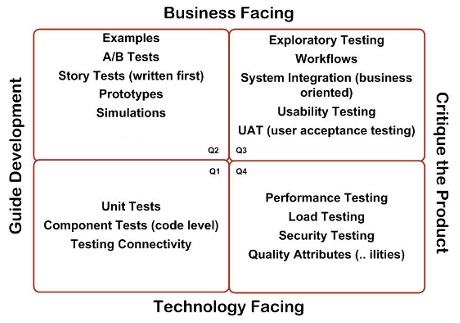
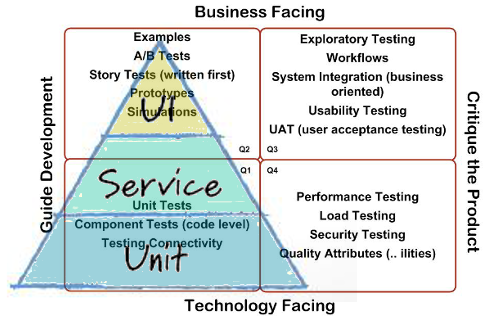
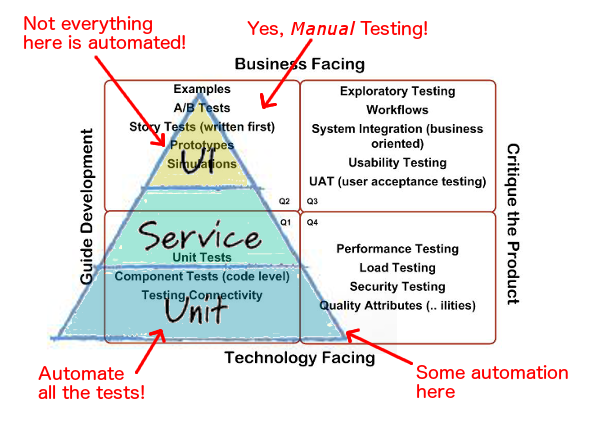
The four quadrants are described below:
Quadrant Q1 – At unit level contains unit Tests, technology facing, tests subject to full automation and continuous integration. Quadrant Q2 – At system level, business facing, these are functional tests, examples, story tests, user experience prototypes, and simulations based on the acceptance criteria, be manual or automated. Created as a part of definition of done for a story Quadrant Q3 – At system or user acceptance level, business facing, contains tests exploratory testing, scenarios, process flows, usability testing, user acceptance testing, alpha testing, and beta testing. These tests are often manual and are user-oriented. Quadrant Q4 – At system or operational acceptance level, technology facing performance, load, stress, and scalability tests, security tests, maintainability, memory management, compatibility and interoperability, data migration, infrastructure, and recovery testing. These tests are often automated.
- Sanity Testing is a surface-level testing, meaning that a tester checks whether whole functionality of the software works in a proper way. Regression Testing does not imply a surface-level testing.
- Sanity Testing is a part of Regression Testing.
- Testers carry out Sanity Testing if they have limited time for performing testing. Regression Testing is carried out when there is enough time for it.
- Testers perform Sanity Testing manually. Testers can perform Regression Testing manually or with the help of different automated tools.
- Sanity Testing does not influence the product cost. Since Regression Testing takes much time and efforts, it increases the product cost.
- Non-complete test cases are conducted in the software in the course of Sanity Testing. In the course of Regression Testing complete test cases are conducted in the software.
- Testers should not know many details on the software while performing Sanity Testing. Regression Testing is more extended.
- Script is used for Regression Testing, but for Sanity Testing it is not.
https://github.com/Cognifide/aet
- http://techean.com/certified-ethical-hacker-full-course/
- https://www.mediafire.com/folder/vkjc94ocqx386/EC-Council_-_Certified_Ethical_Hacker_%28CEH%29_v9#vkjc94ocqx386
- Web Analytics Automation Testing Framework
- WAAT
- Web Analytics Automation Testing Framework https://essenceoftesting.blogspot.sg/2016/07/any-waat-users-out-there.html https://github.com/anandbagmar/WAAT
https://essenceoftesting.blogspot.com/2011/04/waat-web-analytics-automation-testing.html https://www.slideshare.net/abagmar/the-what-why-and-how-of-web-analytics-testing-web-iot-big-data http://mrselenium.blogspot.com/2014/12/automated-analytics-testing-published.html
- REST-Assured framework overview
- REST-Assured: going deeper
- Restful API Testing
- Testing RESTful APIs
- apickli - REST API integration testing framework with cucumber.js
- Cucumber steps to easily test REST-based XML and JSON APIs
- JSON driven test runner for REST APIs
- Behat
- Galen Framework - Automated testing of look and feel for your responsive websites https://www.sitepoint.com/5-mobile-app-testing-tools/
- Damn Vulnerable Web Services (http://www.dvwa.co.uk/)- Damn Vulnerable Web Services is an insecure web application with multiple vulnerable web service components that can be used to learn real world web service vulnerabilities.
- MOBILE APP OR MOBILE WEB?
- SDLC vs STLC
- [Agile, DevOps, and What They Mean for Testers](https://www.stickyminds.com/interview/agile-devops-and-what-they-mean-testers-interview- jeff-payne)
- Ideas On How To Succeed As A Tester
- How to come up with test ideas
https://dzone.com/articles/load-testing-and-stress-testing https://dzone.com/articles/the-software-tester-modern-vs-traditional http://angiejones.tech/test-automation-for-machine-learning/? http://www.getzephyr.com/insights/benefits-automated-test-management
How to Plan an Effective Test Automation in Agile Project https://dzone.com/articles/how-to-plan-an-effective-test-automation-in-agile
http://blogs.agilefaqs.com/2011/02/01/inverting-the-testing-pyramid/
http://istqbexamcertification.com/what-is-definition-of-done-test-levels-in-agile-software/ http://istqbexamcertification.com/what-are-testing-techniques-in-agile-development/ http://istqbexamcertification.com/difference-between-regression-testing-and-retesting/ http://istqbexamcertification.com/mobile-application-development-and-testing-checklist/ http://istqbexamcertification.com/what-is-release-and-iteration-planning-in-agile-methodology/ http://istqbexamcertification.com/what-is-continuous-integration-in-agile-methodology/ http://istqbexamcertification.com/what-are-test-levels-in-agile-methodology/ http://istqbexamcertification.com/what-is-testing-and-configuration-management-in-agile-development/ http://istqbexamcertification.com/communicating-test-status-progress-and-product-quality-in-agile-methodology/ http://istqbexamcertification.com/what-is-the-role-of-a-tester-in-agile-methodology/ http://istqbexamcertification.com/what-is-planning-poker-effort-estimation-in-agile-methodology/ http://istqbexamcertification.com/what-are-testing-techniques-in-agile-development/ http://istqbexamcertification.com/what-is-exploratory-testing-in-agile-methodology/ http://istqbexamcertification.com/what-are-the-tools-in-agile-projects/ http://istqbexamcertification.com/what-are-build-and-distribution-tools-in-agile-software-testing/