SociTrack is a system for using ultra-wideband RF time-of-flight processing to perform indoor ranging and localization. It incorporates the SquarePoint module, containing a DecaWave DW1000 radio for UWB packet transmission and timestamping. This module provides node-to-node ranges over an I2C interface which can then be stored locally or transmitted externally.
If you would be interested in incorporating the SociTrack system or TotTag devices into your future research, please fill out this Interest Form
Note: This system is currently under heavy development. At the moment, it is provided as-is with no mechanism for external support, technical or otherwise. In the future, once the project has reached a steady state and staffing has ramped up, we may begin providing limited support. We will post any updates on that front here. Thank you for your understanding!
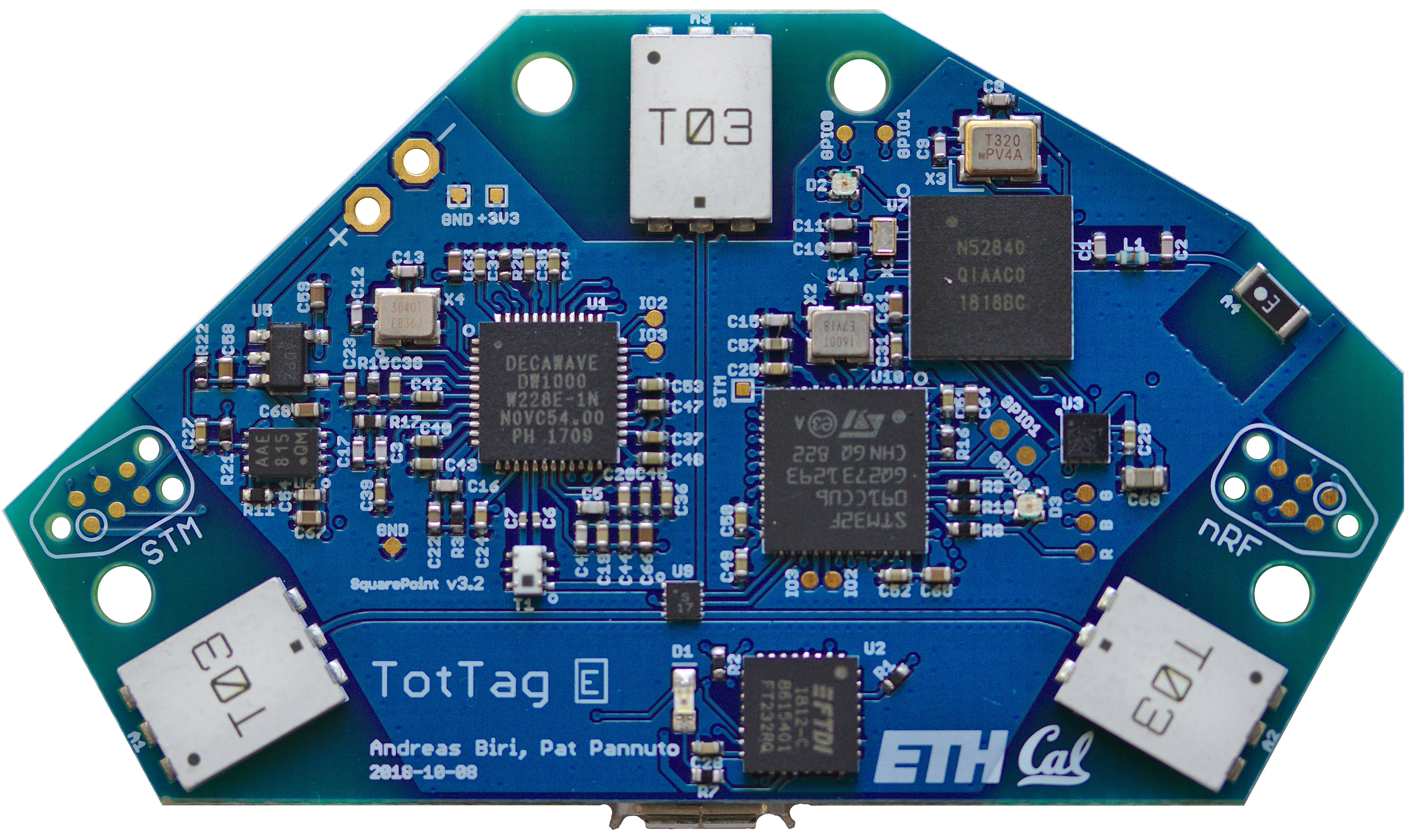
The SociTrack system is composed of several hardware pieces. At its core is the SquarePoint module, a 30mm x 15mm PCB that encompasses all of the core ranging hardware and firmware. SquarePoint is provided as an EAGLE board that allows for direct integration as a design block as part of the Lab11 EAGLE library. One example of a project that uses the SquarePoint module is the TotTag, which comprises an all-in-one tracking and localization system for mobile nodes. The TotTag hardware includes three UWB antennas and a Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) radio, plus a battery charging circuit, SD card for data logging, accelerometer, USB connectivity, and integrated sensor fusion. TotTag is able to provide ranges and position estimates directly to a mobile phone application in real-time and can be configured on-the-fly using a simple user interface over Summon.
SquarePoint, an EAGLE design block for UWB ranging, includes the following components:
- DecaWave DW1000 UWB radio
- STMicroelectronics STM32F091CCU6 MCU
- RF switch
The MCU contains all of the necessary code to control the DW1000 and run the ranging protocol. This module provides a simple abstraction layer for quick integration with a carrier board over an I2C interface without having to worry about any underlying implementation details.
The TotTag is a self-contained PCB which utilizes SquarePoint to provide ranging data for human interaction tracking. It includes:
- The SquarePoint module
- 3 UWB antennas
- Nordic Semiconductors nRF52840 BLE radio
- 3.3V LDO designed to be used with 4.2V LiPo batteries
- Battery charge management controller
- SD card holder
- microUSB connector including FTDI FT232R for debugging
- 3-axis accelerometer
The TotTag is designed to be a device that can be used as a ranging anchor, a
mobile tag, or a hybrid combination of both. It offers both infrastructure-free
and infrastructure-based network processing and allows for centimeter-accurate,
multi-day deployments. Both the schematic and board design are open-source and
can be found in the hardware/tottag folder; a suitable 3D
printable case is also provided in
hardware/cad/tottag-case.
The SociTrack software is freely available as an open-source Git repository. When cloning this repository, be sure to do
git clone --recursive https://github.com/lab11/socitrack.git
or to later run
git submodule init && git submodule sync
so that all submodules are cloned as well. All of the supporting libraries and build tools are in submodules for the various hardware platforms used in this project.
Found in software/squarepoint, the core firmware that
enables the SquarePoint module to work includes all of the logic implementing
our custom ranging protocol on top of the DecaWave DW1000 UWB radio. It makes
use of frequency and antenna diversity and leverages both one-way and two-way
ToF ranging to achieve efficient and reliable ranging in various environments.
The firmware architecture supports multiple runtime modalities that can
be selected on-the-fly; currently, we officially support:
- Standard: the full ranging protocol, using maximal diversity to achieve highly-reliable ranging measurements over 30 different channels.
- Calibration: automatically triggered by our calibration scripts, allowing for automated board-specific calibration functions which are then applied to future ranging measurements.
The TotTag code, located in software/tottag,
implements a BLE application that uses the SquarePoint module as an
I2C slave and provides for external BLE connectivity. It exposes BLE
services to configure and enable the device, to set the current time to enable
accurate timestamping of ranging data, as well as to access ranging data in
real-time.
The tools in the software/tottag/mobile_app
directory interact with TotTag and read data across the BLE interface. They uses
the Summon app (Google Play,
App Store) to
easily access and interact with the TotTag devices. The target website must be
configured in the TotTag code and can be hosted on a personal domain; we
recommend the use of a link shortener to reduce the BLE advertisement length.
This project requires the GNU ARM Embedded Toolchain. Please be aware that the some Linux distros provide out-of-date versions of this tool; as such, we strongly recommend that you install the newest version directly from ARM.
-
Andreas Biri, Neal Jackson, Lothar Thiele, Pat Pannuto, and Prabal Dutta. 2020. SociTrack: Infrastructure-Free Interaction Tracking through Mobile Sensor Networks. In The 26th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (MobiCom ’20), September 21–25, 2020, London, United Kingdom. ACM, New York, NY, USA, 14 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3372224.3419190
-
Andreas Biri, Pat Pannuto, and Prabal Dutta. 2019. Demo Abstract: Tot-Ternary - A Wearable Platform for Social Interaction Tracking. In The 18th International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks (co-located with CPS-IoT Week 2019) (IPSN ’19), April 16-18, 2019, Montreal, QC, Canada. ACM, New York, NY, USA, 2 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3302506.3312486
-
Benjamin Kempke, Pat Pannuto, Bradford Campbell, and Prabal Dutta. 2016. Surepoint: Exploiting ultra wideband flooding and diversity to provide robust, scalable, high-fidelity indoor localization. In Proceedings of the 14th ACM Conference on Embedded Network Sensor Systems (SenSys ’16), November 14-16, 2016, Stanford, CA, USA. ACM, New York, NY, USA, 13 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/2994551.2994570
-
Benjamin Kempke, Pat Pannuto, and Prabal Dutta. 2015. Polypoint: Guiding indoor quadrotors with ultra-wideband localization. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Hot Topics in Wireless (HotWireless ’15), September 11, 2015, Paris, France. ACM, New York, NY, USA, 5 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/2799650.2799651