springboot(3.X) netflix-cloud kafka saga
in-text citations: https://www.vinsguru.com/orchestration-saga-pattern-with-spring-boot/
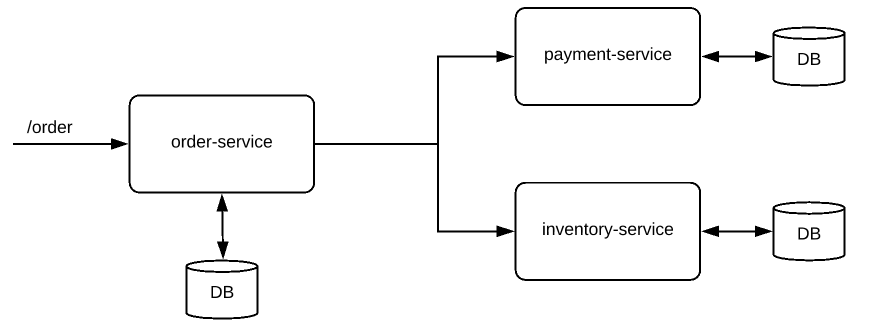
Let’s assume that our business rule says, when a user places an order, order will be fulfilled if the product’s price is within the user’s credit limit/balance & the inventory is available for the product. Otherwise it will not be fulfilled. It looks really simple. This is very easy to implement in a monolith application. The entire workflow can be considered as 1 single transaction. It is easy to commit / rollback when everything is in a single DB. With distributed systems with multiple databases, It is going to be very complex! Let’s look at our architecture first to see how to implement this.
We have below Microservices with its own DB.
order-service
payment-service
inventory-service
When the order-service receives the request for the new order, It has to check with the payment-service & inventory-service. We deduct the payment, inventory and fulfill the order finally! What will happen if we deducted payment but if inventory is not available? How to roll back? It is difficult when multiple databases are involved.
Event Sourcing:
In this approach every change to the state of an application is captured as an event. This event is stored in the database/event store (for tracking purposes) and is also published in the event-bus for other parties to consume.
The order-service receives a command to create a new order. This request is processed and raised as an order-created event. Couple of things to note here.
OrderCreated event basically informs that a new order request has been received and kept in the PENDING/CREATED status by order-service. It is not yet fulfilled. The event object will be named in the past tense always as it already happened! Now the payment-service/inventory-service could be interested in listening to those events and reserve/reject payment/inventory. Even these could be treated as an event. Payment reserved/rejected event. Order-service might listen to these events and fulfill / cancel the order request it had originally received.
This approach has many advantages.
There is no service dependency. payment-service & inventory-services do not have to be up and running always. Loose coupling Horizontal scaling Fault tolerant
Choreography Saga Pattern
The business workflow is implemented as shown here.
order-services receives a POST request for a new order It places an order request in the DB in the ORDER_CREATED state and raises an event payment-service listens to the event, confirms about the credit reservation inventory-service also listens to the order-event and conforms the inventory reservation order-service fulfills order or rejects the order based on the credit & inventory reservation status.
https://kafka.apache.org/downloads
- zookeeper run
{{kafka folder}}\bin\windows\zookeeper-server-start.bat config\zookeeper.properties - kafka run
{{kafka folder}}\bin\windows\kafka-server-start.bat config\server.properties
[https://www.graalvm.org/ ](https://github.com/graalvm/graalvm-ce-builds/releases/tag/vm-22.3.0)
- jdk19 install
- gradle 7.6 install
{
"orderId": "u100023123",
"userId": "TEST",
"productId": "BASDFASDFASDFASFD",
"productPrice": 1000.00
}