Receptive to suggestions and corrections, please make a pull request if you have tips!
- Audience
- Goal
- Structure
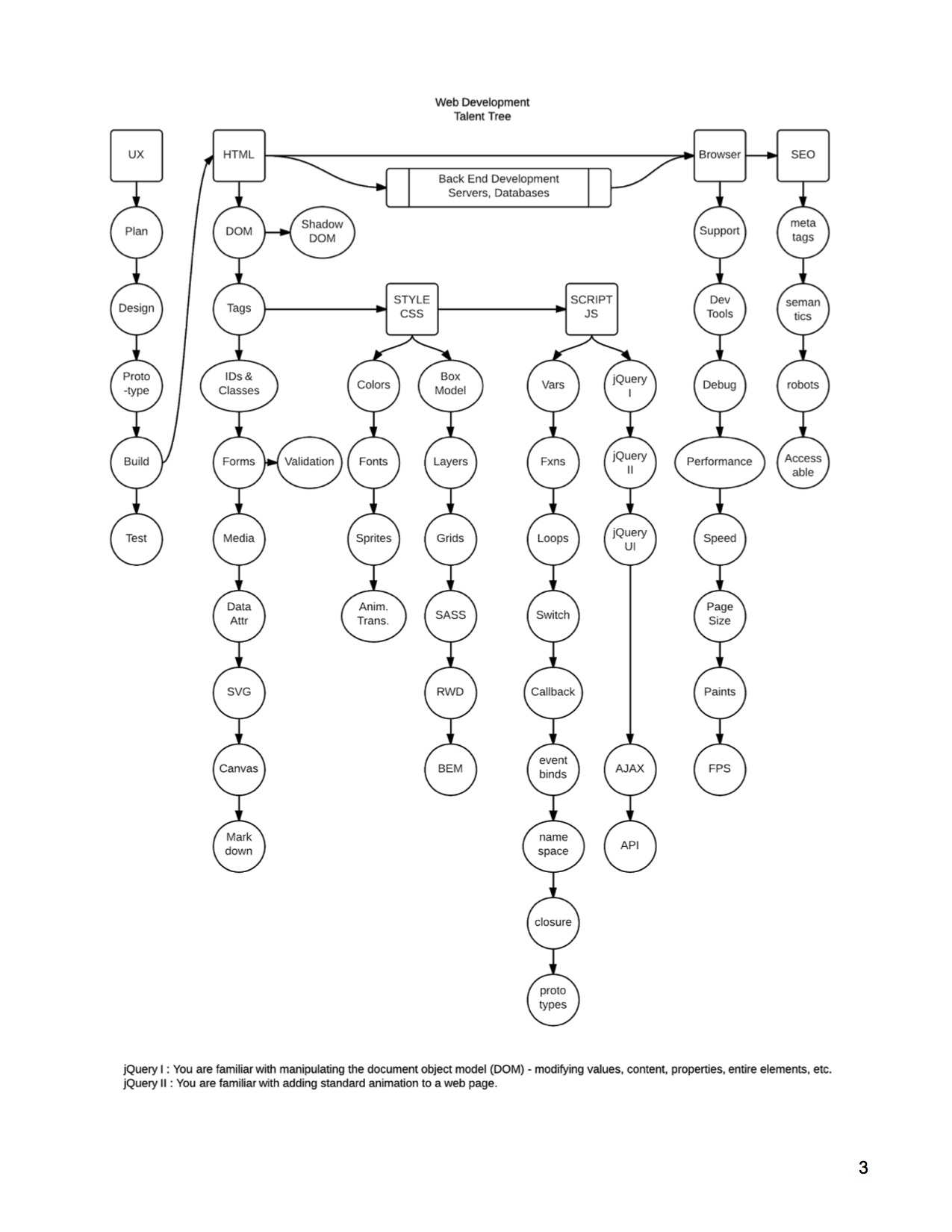
One of the greatest challenges to people entering web development is that there is a lot of information out there. You don’t know where to begin?! Where to go next?! Just take it step by step! Think of it as the best college course ever - do it one chapter at a time, at your own pace, there are no gen eds and there’s not even a final!
Don’t be afraid of this!
Once you have the basics, you can pretty much get off the train at any point, or keep going and see your salary rise with it. In web development, the more of the whole picture that you can do, the better the jobs and the more you get paid.
Speaking of salary, let’s talk job titles for a minute, before we jump in to what the positions do. Web development is a cluster of confusion of conflicting titles - nothing is standardized. Jobs will use “designer” and “developer” and “engineer” interchangeably, although increasingly “design” means user experience/graphics, “development” means coding and web-page performance, and “engineer” means programming and complex applications. Each area also has multiple “steps” that can be full positions on their own. Some example positions are:
- UX Designer
- Goal: You are capable of converting project requirements to an attractive design that promotes a pleasant user experience. D&D Design a web page or site from research to prototype. This is a newer field as Web Designers/Developers have come to understand the need for good research data to drive design choices. Individual job titles include UI Designer (wireframing, planning), UX Designer (research & testing), Interaction Designer (apps), Graphic Designer (web), Prototyper.
- Web Designer
- Goal: You are capable of converting project requirements to an attractive design that promotes a pleasant user experience. D&D Sounds just like UX Designer, eh? These are the folks that build basic web pages, from their own designs or from someone else. Good graphic design, HTML/CSS code, and basic jQuery will get you by. Pair it with knowing Wordpress themes and their basic PHP, and you can freelance fairly easily.
- Front End Developer
- Goal: None or very little design, this position builds more complex web pages from prototype or design comp to live website, using very good HTML/CSS, jQuery and/or custom JavaScript, with a focus on performance, devices, and browser support. Higher level Front End Devs may use advanced JavaScript frameworks like Angular.js and Node.js for complicated client-side applications. Large websites or design firms may have several developers, each with their own strengths (one better in CSS, one better in JavaScript, etc), and most of the JS frameworks offer specialized job positions.
- Back End Developer
- Goal: You are capable of architecting and building an application's backend to efficiently store and retrieve data. D&D Hehheh back end. Server-side programming, database writing and management, server administration, using languages such as PHP, Ruby, Java, ASP, etc. Can specialize in any number of the languages and technologies behind the databases and servers. Usually well-paying positions.
- UX Engineer Description
- This combines UX Designer and Front End Developer into a higher paid position. “These developers translate prototypes and mock-ups into a user-friendly site architecture that's intuitive to use and visually pleasing. UI engineers should be fluent in technologies like HTML, CSS and JavaScript and have an eye for design and visual aesthetics. Knowledge of multiple programming languages and frameworks is also a plus.” money.cnn.com
*More reading on the job title situation: http://css-tricks.com/job-titles-in-the-web-industry/ *
Okay okay, you’ve read some job descriptions, but what does that mean as far as a paycheck? Well, it can mean a lot. In general, the more code you know, the more you get paid.
“JavaScript is the one thing that can control your income. If you’re willing to stay up late, and get good at it, that’s all that matters.” - My recruiter in IT desperate for JS people
Job postings usually require a degree or 2-3 years experience in the field. That “experience” can be just working on code, however, so sharing your code can act as a portfolio of your experience. UX Designers may need to show workflows and wireframes, but for the rest, employers want to see your code to know that you can write it cleanly and concisely. Here are some general numbers (please note the word general - no need for nit picking here)
| Job Title | Median Starting Salary |
|---|---|
| Web Content Developer (Basic HTML, basic CSS): | $40,000 |
| Graphic Design: | $45,000 |
| Basic Web Designer (HTML, CSS, jQuery): | $50,000 |
| Web Developer Average Salary Range: | $60,000 - $100,000* |
| Web Analyst: | $65,000 |
| Database Admin: | $70,000 |
| Software Engineer: | $90,000 |
| UX Engineer: | $90,000 |
| Software Architect: | $120,000+ |
| *Refer to quote about Javascript |
- http://money.usnews.com/careers/best-jobs/rankings/best-technology-jobs
- http://money.cnn.com/pf/best-jobs/
User Interface, User Experience Comes first because it’s the reason for developing a great web in the first place. It is not a prerequisite for getting a job as a front-end developer (if that is your goal), but it will make you a better one, and will be important in your work.
Not the designer. Not the developer. Not the business owner. Not Google search.
That doesn’t mean the user is always right, however, as they are prone to personal biases and sticking to old patterns. UX Designers use research and creativity to make the user’s experience optimal - usually, this means getting the information the user wants fast and easily.
User research in general is very important - start with asking the classic who, what, when, where, why, and how questions.
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/User_experience_design
- http://www.adaptivepath.com/ideas/the-anatomy-of-an-experience-map/
- Omnigraffle https://www.omnigroup.com/omnigraffle
- Balsamiq http://balsamiq.com/
Graphic design is about aesthetics and usability. Good designs are inviting and easy to understand, by solid use of color, typography, balance, hierarchy and white space. D&D
Software such as Photoshop and devices like drawing tablets are used to create layouts, work with type, touch-up photos, and other activities to add professional polish to your designs. D&D
- Top Tools for Graphic Designers http://graphicdesignclasses.net/design-tools/
- Sketch http://bohemiancoding.com/sketch/
Your users will access your creations with a wide variety of screen sizes, resolutions, browsers, internet connection speeds, and from all different kinds of locations. Laptops, desktops with huge monitors, desktops with tiny monitors, desktops with vertical monitors, desktops with three monitors, mobile, tablets, TVs, e-Readers. They navigate using scroll, mousing, touch pads, touch screens, keyboards, voice commands. Colors look different on different screens. It’s hard to imagine all the different combinations and possibilities, and soon will be impossible as the internet is integrated into every part of our lives. This gives rise to two important UX concepts:
Sometimes called “mobile-first” (the smallest of screens normally), it’s the principle of delivering the content of your website in a flexible manner so that it looks good across all devices. More on how to do this is in Development, but this is the why.
- http://everydaydesigner.net/design/change-your-focus-and-design-content-first
- “Content first design” http://responsivedesign.is/design/content-first-design
- “Content First” presentation notes http://www.lukew.com/ff/entry.asp?1598
Some of our users have poor eyesight, are colorblind, have disabilities, or otherwise use their computers differently than we do. These users are no less important than any others. Accessibility means they can still access your content, even if they can’t see the design.
Modeling a new design without building all the underlying functionality is a fast and efficient way to convey ideas, test a new concept, and identify problems you didn't anticipate. D&D Now you’re getting into very basic code and page layout!
- http://www.smashingmagazine.com/2010/06/16/design-better-faster-with-rapid-prototyping/
- http://www.sitepoint.com/tools-prototyping-wireframing/
The main language for creating web pages, HTML is written in the form of tags enclosed in angle brackets
like this
. D&D Semantic HTML refers to using tags that relate to the type of content within them (not how it looks). For example, is descriptive only and non-semantic, while and are semantic. HTML is the structure of the content on the page, divorced from the presentation. Understand what the DOM is and how DOM traversal works Learn best practices for using classes & IDs with CSS and JS HTML5 Form Tags and Placeholders- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Semantic_HTML
- http://www.html5rocks.com/en/
- http://www.codecademy.com/tracks/web
- HTML5 Starter Package http://html5boilerplate.com/ Advanced: HAML, Markdown
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is a language for styling web pages. CSS rules target elements in the HTML document to specify the presentation, such as font, color, spacing, and size. D&D Know & understand the Box Model, Floats and Positioning http://cfg.good.is/lessons/css-the-box-model-floats-and-positioning
- hexadecimal value or named http://www.w3schools.com/tags/ref_colorpicker.asp
- cross-browser opacity
- gradients http://www.colorzilla.com/gradient-editor/
- color palettes
- box-shadows http://www.cssmatic.com/box-shadow
- icon fonts http://icomoon.io/
- unicode http://unicode-table.com/en/
- pts, pxs, ems, rems http://pxtoem.com/
- http://www.narga.net/understanding-font-sizing-in-css-em-px-pt-percent-rem/
- layouts and columns
- responsive widths
- Bootstrap
Advanced: SASS/SCSS, LESS, Compass, BEM, OOCSS
JavaScript is the dominant language for client-side programming. It executes in the user’s browser to manipulate the HTML document after it has loaded. This may be as simple as showing hidden elements, or more advanced like contacting the server to load more data. D&D
- http://www.codecademy.com/tracks/javascript
- http://www.jslint.com/
- http://youmightnotneedjquery.com/
- http://code.tutsplus.com/tutorials/24-javascript-best-practices-for-beginners--net-5399
- http://jsfiddle.com
- http://javascriptissexy.com/
- http://www.codecademy.com/tracks/javascript
- JS Cheat Sheet http://overapi.com/javascript/
Once you’re comfortable with the JavaScript language, there’s a multitude of libraries and frameworks to accomplish common tasks and enhance your development. D&D JS helps you do things like updating the content on page without refreshing it, lazy load images, validate forms, show tooltips and error messages, and much more. jQuery, Modernizr, d3.js, _underscore, waypoints.js, parallax.js Advanced: Angular.js, Node.js, Ember.js, Backbone.js, grunt.js
So important, I underlined it. This is what employers look for in good code.
The developer who learns to recognize duplication, and understands how to eliminate it through appropriate practice and proper abstraction, can produce much cleaner code than one who continuously infects the application with unnecessary repetition.
Use comments in your code to document for yourself and for others. Someone else should be able to go through your code and understand what it’s doing and why.
Modular programming is a programming style that breaks down program functions into modules, each of which accomplishes one function and contains all the code and variables needed to accomplish that function.
“This is my craft. I care about my tools and want the best.” - Chad
Macs vs PCs yada yada. You will find some code jobs working with Microsoft-specific software or technologies, but for the rest of it, Macs have been established in the field, and you may be required to use one in your job. My job requires a Macbook Pro w/ Thunderbolt and a 240GB SSD (solid state drive) - which basically means it is powerful, and it has to be, to run the Virtual Machines we use. Macs also traditionally have had better graphics drivers, which is important for graphics work and screen resolution. Finally, a lot of the software we use is written only for Macs, as you’ll see later.
Try different ones out, especially code editors - it’s worth finding one that you like.
- 5 Best Code Editors http://lifehacker.com/five-best-text-editors-1564907215
I personally was very intimidated by the Terminal, and wouldn’t open it unless I absolutely had to. I have a talent for breaking things. Also, never having had any classes in Computer Science, I didn’t even know basic commands. I’m more comfortable with it now, and have built my own cheat sheet of basic commands. You’ll need to use it at Advanced levels to run some of the javascript frameworks, ruby gems, start and stop servers, etc.
| Command | Action | Command | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| O | [O]pen Read-Only | E | [E]dit |
| R | [R]ecover | Q | [Q]uit |
| A | [A]bort | I | [I]nsert |
| D | [D]elete it | esc :q! | quit without saving |
| esc :wq | write/save and quit | sudo | super user permissions |
| cd | change directory | ||
| ex: cd /Users/jan/Documents/Pictures |
Keeping versioned files is important for backup and rolling back changes. Versioning software is important so that multiple people can work on the same files without mucking things up. There are two major technologies used: Git and Subversion (SVN).
- Learn git in 15 minutes https://try.github.io/levels/1/challenges/1
- https://github.com/
- Cornerstone for SVN https://www.zennaware.com/cornerstone/index.php
Compilers, or preprocessors, are automated software that make doing the work of development easier. For example, they turn SASS into CSS, minify CSS and JS, and check for errors.
Less necessary, but you may run into them, particularly if you need to test your work in Internet Explorer.
- http://www.vmware.com/ runs the VMs
- https://modern.ie/en-us VMs for various versions of Windows that run IE
Chrome, FireFox, Safari, IE, Opera, Mobile (iOS, Safari, Chrome, etc). Learn the differences, especially when it comes to CSS, and how to access and use their dev tools. Front End developers should know browser paints / compositing / layers, and how to maximize performance.
- Performance Matters #perfmatters http://alistapart.com/column/performance-matters
- Testing: Browserstack, VMs, Physical Devices, Mobile Emulators
Acronym is included first if that is the most often way you will see the term.
- Client Side
- The webpages that load (render) in your user’s browsers, on their devices.
- Server Side
- Databases and software living elsewhere that tell browsers what to load.
- Framework
- Basically a code template, where someone else has worked out all the hard bits to make things happen, and you just load it in and use the parts you need. These have specific features that are used often, and save having to re-write it every time. Example: jQuery UI is a framework with basic User Interface elements (buttons, lists, menus, etc).
- Library
- Essentially the same thing as a framework. You may run into people who debate the semantics of it, but for beginner purposes, they are both pre-written sets of code that perform a specific function and save you having to write it all yourself.
- Designing in the browser
- Using browser dev tools to create pages without Photoshop, etc.
- Responsive Web Design (RWD)
- The idea that people are accessing your site on all sorts of websites, and accessing a forced desktop site on a mobile phone is an annoying user experience.
- Progressive Enhancement
- Users access your site on different devices, and not all of them can handle CSS or JavaScript. Build your content with good HTML, so that they will always at least see that, and then use CSS or JS to enhance your content - don’t make seeing content dependent on them.
- Graceful Degradation
- Ok, so in reality, most of us build websites that use CSS and JS and look good in the newest browsers. You don’t want to leave all those other people behind though, so at the very least, pages should look good and not break in older browsers.
- DOM (Document Object Model)
- The compilation of HTML tags in a document(eh?eh?) that gets turned into a webpage. Traversed from top to bottom.
- API (Application Programming Interface)
- Think of API’s as plug and socket. If Pinterest wants to post your pins to Facebook, Facebook exposes some of their code in a semi-public way (the sockets, the API) so that Pinterest can write code that hooks to it (the plug). Together, they share all your pins to your news feed, and everyone sees your obsession with fingernail art.
- AJAX (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML)
- Javascript (and XML) are like the DOM, in that they are read and processed top to bottom. This means that one thing is processed before the next thing gets a turn. AJAX lets you say “Start this, and while that’s running, go on to the other things.”
- CMS (Content Management System)
- A series of databases that store content (blog posts, products for sale, news articles, videos, etc) in an easy-to-manage way. Wordpress is a joint CMS and content publishing platform.
- http://www.w3.org/ W3C, the World Wide Web Consortium, who decide web standards
- http://www.w3schools.com/ *With a caveat - you will hear this site disparaged greatly among experienced developers, as they are a for-profit website not actually associated with the W3C. Some errors have been found in their information as well, I have heard. That said, I have learned a great deal from this website, and have never found any wrong information. It’s a free tool, so keep the usual limitations of free tools in mind.
- http://caniuse.com/ Search for browser support of HTML, CSS, JS and other features
- http://codepen.io/ CodePen is a playground for the front end side of the web
- https://developer.mozilla.org Developer resources from Firefox
- https://github.com/dypsilon/frontend-dev-bookmarks A giiiiiant list of front end resources
- http://code.tutsplus.com/ Development tutorials and info
- http://css-tricks.com/
- Google like a pro. It’s your greatest tool. Jan’s Excellent Google Tip: Under Search Tools, set the range to Past Year. It will filter out old information.
- http://stackoverflow.com/ You’ll use it almost as much as Google.
- http://www.smashingmagazine.com/
- http://alistapart.com/ A List Apart - industry leaders
- http://www.bento.io/ Everything you need to know about web development.
- http://www.awwwards.com/ The awards for design, creativity and innovation on the internet
- https://dribbble.com/ Show and tell for designers
- https://www.behance.net/ Design inspiration
- http://www.adequatelygood.com/ Adequately Good - industry leaders
- http://www.webdesignerdepot.com/
- https://news.ycombinator.com/ Hacker News
- https://news.layervault.com/ Designer News
- http://www.smashingmagazine.com/2014/02/14/learning-resources-roundup/ Useful Learning Resources For Web Designers