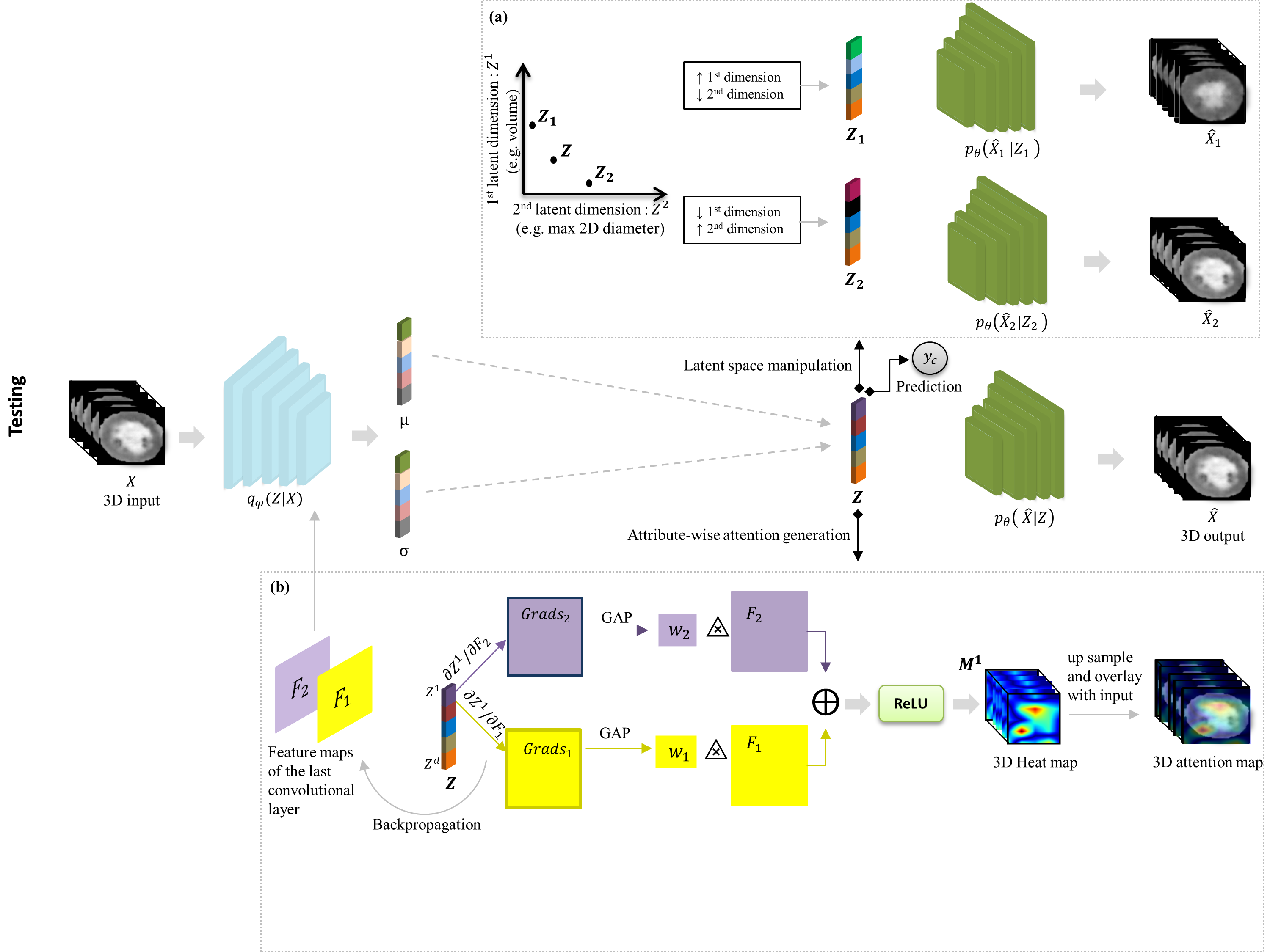
Attri-VAE: attribute-based, disentangled and interpretable representations of medical images with variational autoencoders
This repository contains the source for training and evaluation of the proposed Attri-VAEmodel.
To access the paper please refer here and please cite as if you are using the code in this repository in any manner.