Performance-oriented sequential neural networks and ML-tuned dataframes in < 350 lines of pure C++.
// required imports
#include <vector>
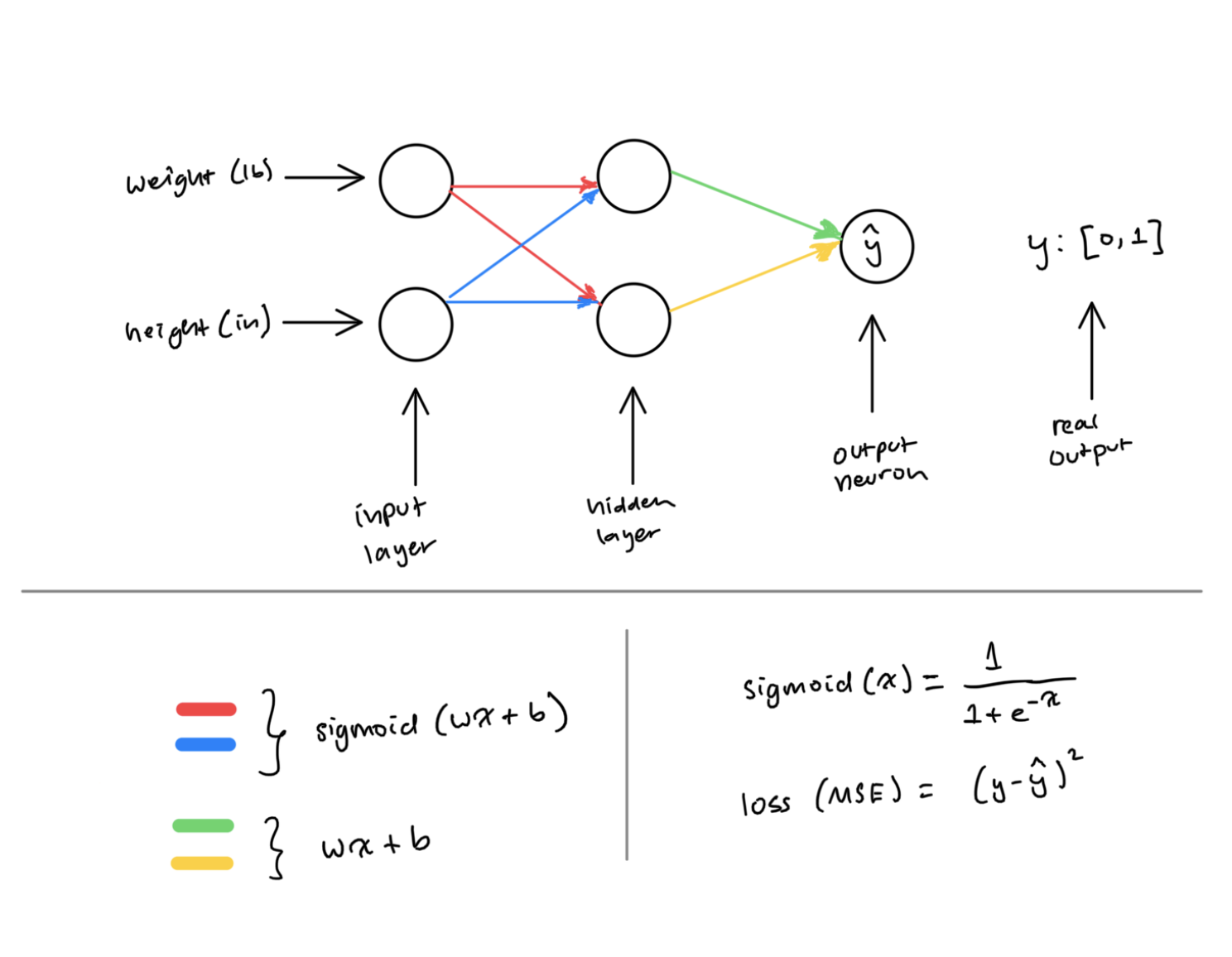
#include "NeuralNetwork.cpp"// input layer with 2 neurons, hidden layer with 2 neurons
vector<int> layers = {2, 2};
NeuralNetwork nn = NeuralNetwork(layers);
// weight (lb), height (in)
// (shifted weight by -135 and height by -65 for data normalization)
vector<vector<double>> x = {
{-2, -1},
{25, 6},
{17, 4},
{-15, -6}
};
// 1 = female, 0 = male
vector<double> y = {1, 0, 0, 1};
// fit network (1000 epochs)
nn.fit(x, y, 1000);
// make predictions
cout << "-------" << endl;
cout << nn.predict({-7, -3}) << endl; // 123 pounds, 62 inches (expected value = 1)
cout << nn.predict({20, 20}) << endl; // 155 pounds, 68 inches (expected value = 0)Output:
0.845303
-0.0957723
NOTE: Normalizing each input feature as done above almost always yields faster loss convergence due to the sigmoid activation function's sensitivity to extreme neuron activations. Typically, this is achieved by subtracting the feature mean from each input value.
// required imports
#include <vector>
#include "NeuralNetwork.cpp"
#include "Dataframe.cpp"// parse csv, shuffle training data, get x and y dataframes
vector<vector<double>> matrix = raw2D("training-data/iris-cleaned.csv");
shuffle2D(matrix);
vector<vector<double>> x = isolateX(matrix);
vector<double> y = isolateY(matrix);
// normalize input data
vector<double> columnMeans = getColumnMeans(x);
normalize2D(x, columnMeans);
// construct fit network (10000 epochs)
vector<int> layers = {4, 3};
NeuralNetwork nn = NeuralNetwork(layers);
nn.fit(x, y, 10000);
// make predictions
cout << "-------" << endl;
vector<double> setosa = {5.1, 3.5, 1.4, 0.2};
normalize1D(setosa, columnMeans);
cout << nn.predict(setosa) << endl;Compiler: Command:
clang++ clang++ -std=c++17 Main.cpp
g++ g++ -std=c++17 Main.cpp