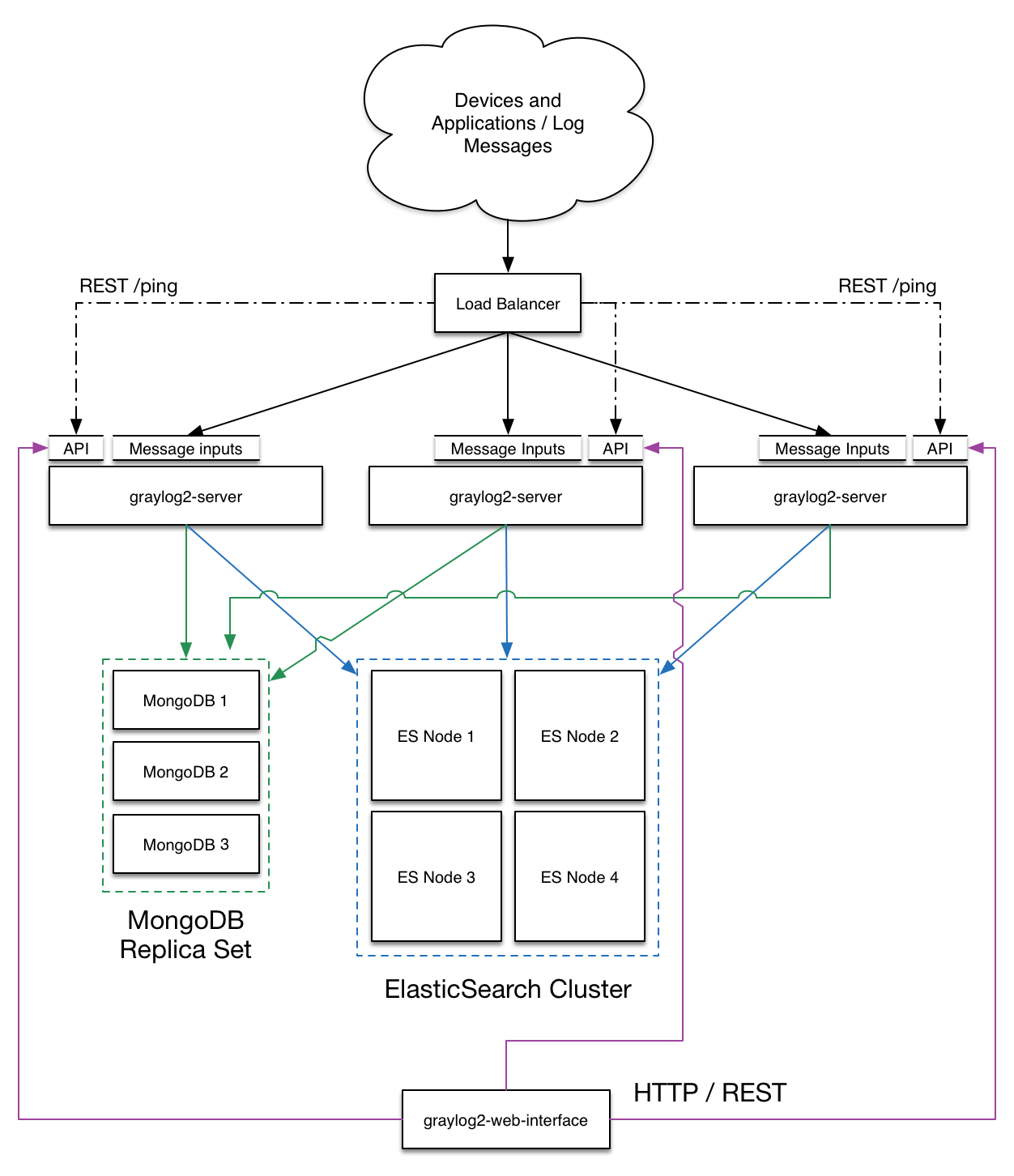
Please note that the original design goal of this role was more concerned with the initial installation and bootstrapping environment, which currently does not involve performing continuous maintenance, and therefore are only suitable for testing and development purposes, should not be used in production environments. The author does not guarantee the accuracy, completeness, reliability, and availability of the role content. Under no circumstances will the author be held responsible or liable in any way for any claims, damages, losses, expenses, costs or liabilities whatsoever, including, without limitation, any direct or indirect damages for loss of profits, business interruption or loss of information.
请注意,此角色的最初设计目标更关注初始安装和引导环境,目前不涉及执行连续维护,因此仅适用于测试和开发目的,不应在生产环境中使用。作者不对角色内容之准确性、完整性、可靠性、可用性做保证。在任何情况下,作者均不对任何索赔,损害,损失,费用,成本或负债承担任何责任,包括但不限于因利润损失,业务中断或信息丢失而造成的任何直接或间接损害。
Table of Contents
- Overview
- Requirements
- Role variables
- Dependencies
- Example Playbook
- License
- Author Information
- Contributors
Graylog is a leading centralized log management solution built to open standards for capturing, storing, and enabling real-time analysis of terabytes of machine data. Graylog deliver a better user experience by making analysis ridiculously fast and efficient using a more cost-effective and flexible architecture. Many of IT professionals rely on Graylog’s scalability, comprehensive access to complete data, and exceptional user experience to solve security, compliance, operational, and DevOps issues every day. Purpose-built for modern log analytics, Graylog removes complexity from data exploration, compliance audits, and threat hunting so you can quickly and easily find meaning in data and take action faster.
Every SIEM(Security information and event management) solution should have a clear and a straightforward way to present gathered data and make your life (and the lives of your security analysts) that much simpler. SIEMs should do the following:
-
Correlate security events. It will link events based on common attributes and present that set of information as a bundle. This functionality is one of the most important features of SIEM, since security breach attempts are usually characterized by repetitive actions.
-
Long-term log storage. Having access to long-term data is crucial in forensic security breach investigations. Catching someone in the act just as they try to make an attempt on your network is highly unlikely.
-
Forensic search capabilities. Inputting certain criteria should be sufficient for you to get what are you looking for.
-
Sound the alarm when necessary. The solution should recognize suspicious activity (for example, a huge number of unsuccessful login attempts from the same IP address) and notify your team through a dashboard, email, or even via text message.
-
Reporting. All security information should be presented in easy-to-understand format. This visualization allows for easy data interpretation. Also, through reporting, you will gain access to compliance data and thus the compliance reports. These reports are crucial in existing security, governance, and auditing processes.
Graylog server combined with MongoDB and Elasticsearch, is often compared to the ELK stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana). Though both solutions are pretty similar in terms of feature-set, there are a few differences to consider, Both the tools have their own pros and cons, Everyone has different specifications, selecting a tool is completely based on the system environment and its requirements, It is up to the users to decide which suits them better. Graylog is very powerful and its GUI is very user friendly whereas ELK stack is modularized and flexible. ELK stack and Graylog are both open-source tools to a certain extent for the users to get hands-on experience, continuous support and all the premium features are licensed. Be sure to keep cost in mind, as well as maintenance requirements.
-
ELK is a stack, it collects, indexes and stores data using elastic search, Logstash is the tool to analyze all the information that is stored in elastic search, this information could be log data, All the inferences and observations made by them are visualized by Kibana using its interactive dashboard. Graylog is positioned as a powerful logging solution, while ELK is a Big Data solution. Graylog can receive structured logs and standard Syslog directly from an application through the network protocol. On the contrary, ELK is the solution that analyzes already collected plain text logs using Logstash and then parses them to ElasticSearch.
-
Visualization is done by Kibana in ELK, Kibana has to be set up separately along with the others. Graylog is the whole package of processing and visualization, Its GUI is far more interactive and user friendly than that of Kibana.In ELK, Kibana plays the role of a dashboard and displays the data received from Logstash. Graylog in this sense is more convenient as it offers a single-application solution (excluding ElasticSearch as a flexible data storage) with almost the same functionality, So the time needed to deploy a usable solution is shorter. Moreover, Graylog has a friendlier GUI right out of the box and a more superior permissions system compared to ELK.
-
Being an advanced suite of products, ELK has a fairly steep learning curve, Additionally, it is difficult to maintain. With that said, though, it allows you to do almost everything you need from a single tool, Once you get over the learning curve, it can be a great solution, Logs, metrics, and visualizations are good, and if you want additional functionality, you can search the wide ecosystem of available plugins. But Even though it’s “free,” ELK stack has hidden costs that add up quickly. Graylog has a pretty simple learning curve, which allows you to have an almost fully functional set up in a relatively small amount of time, Another feature that makes Graylog a pleasure to use is that all-important items are easy to find in the GUI, but for anything else out of its scope, you will have to add other tools.
-
Graylog is used in many security applications and it is centralized. Data in huge scales (Terabytes) can be analyzed from multiple log sources as well as multiple geographic locations as all the data is centralized and therefore it can be accessed anywhere. DevOps engineers and SREs mostly care about speed, reliability, and flexibility in queries and visualizations. For this, the ELK stack is a better choice. Additional elements to consider are alerting, proactivity, live tail, automatic insights and integration with their workflow.
This Ansible role installs Graylog on linux operating system, including establishing a filesystem structure and server configuration with some common operational features, Will work on the following operating systems:
- CentOS 7
The following list of supported the graylog releases:
- 3.x, 4.x
There are some variables in defaults/main.yml which can (Or needs to) be overridden:
graylog_cluster: Cluster name of servers that implements distribution performance.graylog_heap_size: Specify the maximum memory allocation pool for a Java virtual machine.graylog_path: This directory is used to store Graylog server state.graylog_root_email: The email address of the root user.graylog_root_pass: The password for root user.graylog_root_timezone: The time zone setting of the root user.graylog_root_user: The default root username.graylog_https: A boolean value, whether Encrypting HTTP client communications.graylog_version: Specify the Graylog version.
graylog_elastic_dept: A boolean value, whether ElasticSearch use the same environment.graylog_mongod_dept: A boolean value, whether MongoDB database use the same environment.graylog_ngx_dept: A boolean value, whether proxy web interface and API traffic using NGinx.
graylog_ngx_domain: Defines domain name.graylog_ngx_port_http: NGinx HTTP listen port.graylog_ngx_port_https: NGinx HTTPs listen port.graylog_ngx_block_agents: Enables or disables block unsafe User Agents.graylog_ngx_block_string: Enables or disables block includes Exploits / File injections / Spam / SQL injections.
graylog_elastic_auth: A boolean value, Enable or Disable Elasticsearch authentication.graylog_elastic_https: A boolean value, whether Encrypting HTTP client communications.graylog_elastic_cluster: Specify name for your Elastic cluster name.graylog_elastic_heap_size: Specify the maximum memory allocation pool for a Java virtual machine.graylog_elastic_hosts: List of Elasticsearch hosts Graylog should connect to.graylog_elastic_path: Specify the ElasticSearch data directory.graylog_elastic_port_rest: Elasticsearch REST port.graylog_elastic_user: Elasticsearch authenticated user.graylog_elastic_pass: Elasticsearch authenticated password.graylog_elastic_version: Specify the Elasticsearch version.graylog_elastic_memory_lock: A boolean value, whether lock the process address space into memory on startup.
graylog_mongod_auth: A boolean value, Enable or Disable MongoDB authentication.graylog_mongod_ssl: A boolean value, whether Encrypting client and cluster communications.graylog_mongod_encryption: A boolean value, whether enabled the WiredTiger storage Data at Rest Encryption.graylog_mongod_encryptionKey: The encryptionKey character string.graylog_mongod_hosts: Group of MongoDB hosts Graylog should connect to.graylog_mongod_node_role: Member role for ReplicaSet.graylog_mongod_path: Specify the MongoDB data directory.graylog_mongod_port: The MongoDB instance port.graylog_mongod_replset: MongoDB ReplicaSet name.graylog_mongod_sa_user: MongoDB Superuser name.graylog_mongod_sa_pass: MongoDB Superuser password.graylog_mongod_user: MongoDB Graylog database authenticate username.graylog_mongod_pass: MongoDB Graylog database authenticate password.graylog_mongod_version: Specify the MongoDB version, minimum 34.graylog_mongod_backupset_arg.keep: Backup retention cycle in days.graylog_mongod_backupset_arg.encryptkey: BackupSet encryption key.graylog_mongod_backupset_arg.cloud_rsync: Whether rsync for cloud storage.graylog_mongod_backupset_arg.cloud_drive: Specify the cloud storage providers.graylog_mongod_backupset_arg.cloud_bwlimit: Controls the bandwidth limit.graylog_mongod_backupset_arg.cloud_event: Define transfer events.graylog_mongod_backupset_arg.cloud_config: Specify the cloud storage configuration.
graylog_port_arg.api: WEB / API network communication ports.
graylog_mail_arg.transport_email_enabled: Enable mail for alert.graylog_mail_arg.transport_email_hostname: The SMTP host address.graylog_mail_arg.transport_email_port: The SMTP host communication port.graylog_mail_arg.transport_email_use_auth: Enable SMTP Authentication.graylog_mail_arg.transport_email_use_tls: Enable SMTP with STARTTLS for encrypted connections.graylog_mail_arg.transport_email_use_ssl: Enable SMTP over SSL (SMTPS) for encrypted connections.graylog_mail_arg.transport_email_auth_username: The SMTP clients AUTH username.graylog_mail_arg.transport_email_auth_password: The SMTP clients AUTH password.graylog_mail_arg.transport_email_subject_prefix: Email subject line.graylog_mail_arg.transport_email_from_email: Specifies the e-mail address of the sender.graylog_mail_arg.transport_email_web_interface_url: Specify this if you want to include links in alert mails.
graylog_arg.alert_check_interval: Length of the interval in seconds in which the alert conditions for all streams should be checked and alarms are being sent.graylog_arg.allow_highlighting: Allow searches to be highlighted.graylog_arg.allow_leading_wildcard_searches: Allow searches with leading wildcards.graylog_arg.async_eventbus_processors: Number of threads used exclusively for dispatching internal events.graylog_arg.versionchecks: Software version check.graylog_arg.disable_sigar: Disable the use of SIGAR for collecting system stats.graylog_arg.http_connect_timeout: The default connect timeout for outgoing HTTP connections.graylog_arg.http_enable_cors: Enable CORS headers for HTTP interface.graylog_arg.http_enable_gzip: This compresses API responses and therefore helps to reduce overall round trip times.graylog_arg.http_max_header_size: The maximum size of the HTTP request headers in bytes.graylog_arg.http_read_timeout: The default read timeout for outgoing HTTP connections.graylog_arg.http_thread_pool_size: The size of the thread pool used exclusively for serving the HTTP interface.graylog_arg.http_write_timeout: The default write timeout for outgoing HTTP connections.graylog_arg.index_ranges_cleanup_interval: Time interval for index range information cleanups.graylog_arg.inputbuffer_processors: The number processors of input ring buffers.graylog_arg.inputbuffer_ring_size: Size of input ring buffers.graylog_arg.inputbuffer_wait_strategy: Wait strategy describing how buffer processors wait on a input sequence.graylog_arg.message_journal_dir: The directory which will be used to store the message journal.graylog_arg.message_journal_enabled: Enable the disk based message journal.graylog_arg.message_journal_flush_age: Specify a time interval at which we will force an fsync of data written to the log.graylog_arg.message_journal_flush_interval: Specify an interval at which we will force an fsync of data written to the log.graylog_arg.message_journal_max_age: The maximum hours for journal hold messages before they could be written.graylog_arg.message_journal_max_size: The maximum size for journal hold messages before they could be written.graylog_arg.message_journal_segment_age: Controls the period of time which Graylog will force the log to roll evengraylog_arg.message_journal_segment_size: The segment size of message journal.graylog_arg.mongod_max_connections: The maximum connections your MongoDB server can handle from a single client.graylog_arg.output_batch_size: Batch size for the Elasticsearch output.graylog_arg.output_flush_interval: Flush interval (in seconds) for the Elasticsearch output.graylog_arg.outputbuffer_processors:Raise this number if your buffers are filling up.graylog_arg.processbuffer_processors: The number of parallel running processors.graylog_arg.processor_wait_strategy: Wait strategy describing how buffer processors wait on a cursor sequence.graylog_arg.ring_size: Size of internal ring buffers.graylog_arg.recvbuffer_sizes: UDP receive buffer size for all message inputs.
graylog_elastic_arg.compression_enabled: Enable payload compression for Elasticsearch requests.graylog_elastic_arg.connect_timeout: Maximum amount of time to wait for successfull connection to Elasticsearch HTTP port.graylog_elastic_arg.disable_index_optimization: Disable the optimization of Elasticsearch indices after index cycling.graylog_elastic_arg.disable_version_check: Disable checking the version of Elasticsearch for being compatible with Graylog release.graylog_elastic_arg.discovery_enabled: Enable automatic Elasticsearch node discovery through Nodes Info.graylog_elastic_arg.discovery_filter: Filter for including/excluding Elasticsearch nodes to their custom attributes.graylog_elastic_arg.discovery_frequency: Frequency of the Elasticsearch node discovery.graylog_elastic_arg.idle_timeout: Maximum idle time for an Elasticsearch connection.graylog_elastic_arg.index_optimization_jobs: Maximum number of concurrently running index optimization jobs.graylog_elastic_arg.index_optimization_timeout: Global timeout for index optimization requests.graylog_elastic_arg.max_docs_per_index: Maximum number of documents in an Elasticsearch index before a new index is being createdgraylog_elastic_arg.max_number_of_indices: How many indices do you want to keep.graylog_elastic_arg.max_retries: Maximum number of times Graylog will retry failed requests to Elasticsearch.graylog_elastic_arg.max_size_per_index: Maximum size in bytes per Elasticsearch index on disk before a new index is being created.graylog_elastic_arg.max_time_per_index: Maximum time before a new Elasticsearch index is being created.graylog_elastic_arg.max_total_connections: Maximum number of total connections to Elasticsearch.graylog_elastic_arg.max_total_connections_per_route: Maximum number of total connections per Elasticsearch route.graylog_elastic_arg.replicas: The number of replicas for your indices.graylog_elastic_arg.request_timeout: Global request timeout for Elasticsearch requests.graylog_elastic_arg.retention_strategy: Decide what happens with the oldest indices when the maximum number of indices is reached.graylog_elastic_arg.rotation_strategy: The strategy it uses to determine when to rotate the currently active write index.graylog_elastic_arg.shards: The number of shards for your indices.graylog_elastic_arg.socket_timeout: Maximum amount of time to wait for reading back a response from an Elasticsearch server.
graylog_inputs_arg: Define the global inputs parameters.
graylog_content_packs_arg: Define the Content Packs parameters.
graylog_indexes_arg: Define the customer index parameters.
environments: Define the service environment.datacenter: Define the DataCenter.domain: Define the Domain.customer: Define the customer name.tags: Define the service custom label.exporter_is_install: Whether to install prometheus exporter.consul_public_register: Whether register a exporter service with public consul client.consul_public_exporter_token: Public Consul client ACL token.consul_public_http_prot: The consul Hypertext Transfer Protocol.consul_public_clients: List of public consul clients.consul_public_http_port: The consul HTTP API port.
There are some variables in vars/main.yml:
graylog_kernel_parameters: Operating system variables.
- Ansible versions >= 2.8
- Python >= 2.7.5
- NGinx
- MongoDB
- Elasticsearch
See tests/inventory for an example.
[siem:vars]
graylog_cluster='siem'
[siem]
node01 ansible_host='192.168.1.10'
node02 ansible_host='192.168.1.11'
node03 ansible_host='192.168.1.12'
Including an example of how to use your role (for instance, with variables passed in as parameters) is always nice for users too:
- hosts: all
roles:
- role: ansible-role-linux-graylog
graylog_cluster: 'siem'You can also use the group_vars or the host_vars files for setting the variables needed for this role. File you should change: group_vars/all or host_vars/group_name.
graylog_cluster: 'siem'
graylog_heap_size: '1G'
graylog_path: '/data'
graylog_root_email: 'somebody@domain.com'
graylog_root_timezone: 'Asia/Shanghai'
graylog_root_user: 'admin'
graylog_root_pass: 'changeme'
graylog_https: true
graylog_version: '3.1'
graylog_ngx_dept: false
graylog_elastic_dept: false
graylog_mongod_dept: false
graylog_ngx_block_agents: false
graylog_ngx_block_string: false
graylog_ngx_domain: 'siem.example.com'
graylog_ngx_port_http: '80'
graylog_ngx_port_https: '443'
graylog_elastic_auth: true
graylog_elastic_https: true
graylog_elastic_cluster: 'graylog'
graylog_elastic_hosts: 'localhost'
graylog_elastic_heap_size: '3g'
graylog_elastic_memory_lock: false
graylog_elastic_path: '/data'
graylog_elastic_port_rest: '9200'
graylog_elastic_user: 'elastic'
graylog_elastic_pass: 'changeme'
graylog_elastic_version: '6.8.13'
graylog_mongod_auth: true
graylog_mongod_ssl: true
graylog_mongod_encryption: false
graylog_mongod_encryptionKey: 'GvAjQsuMHn/fMyv570tiyFi6kGf3SbSidFDg4KRy6sk='
graylog_mongod_hosts: 'localhost'
graylog_mongod_node_role: 'replica'
graylog_mongod_path: '/data'
graylog_mongod_port: '27017'
graylog_mongod_replset: 'graylog'
graylog_mongod_sa_user: 'sa'
graylog_mongod_sa_pass: 'changeme'
graylog_mongod_user: 'graylog'
graylog_mongod_pass: 'changeme'
graylog_mongod_version: '36'
graylog_mongod_backupset_arg:
keep: '7'
encryptkey: 'Yf3ejyv4kjZf'
cloud_rsync: false
cloud_drive: 'azureblob'
cloud_bwlimit: '10M'
cloud_event: 'sync'
cloud_config:
account: 'blobuser'
key: 'base64encodedkey=='
endpoint: 'blob.core.chinacloudapi.cn'
graylog_port_arg:
api: '9099'
graylog_mail_arg:
transport_email_enabled: false
transport_email_hostname: 'localhost'
transport_email_port: '25'
transport_email_use_auth: false
transport_email_use_tls: false
transport_email_use_ssl: false
transport_email_auth_username: 'somebody@example.com'
transport_email_auth_password: 'changeme'
transport_email_subject_prefix: '[siem]'
transport_email_from_email: 'do-not-reply@example.com'
transport_email_web_interface_url: 'https://{{ graylog_ngx_domain }}'
graylog_arg:
alert_check_interval: '60'
allow_highlighting: true
allow_leading_wildcard_searches: true
async_eventbus_processors: '2'
versionchecks: false
disable_sigar: true
http_connect_timeout: '10s'
http_enable_cors: true
http_enable_gzip: true
http_max_header_size: '8192'
http_read_timeout: '20s'
http_thread_pool_size: '12'
http_write_timeout: '20s'
index_ranges_cleanup_interval: '1h'
inputbuffer_processors: '2'
inputbuffer_ring_size: '65536'
inputbuffer_wait_strategy: 'blocking'
message_journal_dir: '{{ graylog_path }}/graylog/journal'
message_journal_enabled: true
message_journal_flush_age: '1m'
message_journal_flush_interval: '1000000'
message_journal_max_age: '12h'
message_journal_max_size: '10gb'
message_journal_segment_age: '1h'
message_journal_segment_size: '200mb'
mongod_max_connections: '1000'
output_batch_size: '500'
output_flush_interval: '1'
outputbuffer_processors: '2'
processbuffer_processors: '2'
processor_wait_strategy: 'blocking'
ring_size: '65536'
recvbuffer_sizes: '2097152'
graylog_elastic_arg:
compression_enabled: true
connect_timeout: '10s'
disable_index_optimization: false
disable_version_check: true
discovery_enabled: false
discovery_filter: ''
discovery_frequency: '30s'
idle_timeout: '600s'
index_optimization_jobs: '20'
index_optimization_timeout: '1h'
max_docs_per_index: '20000000'
max_number_of_indices: '720'
max_retries: '3'
max_size_per_index: '1073741824'
max_time_per_index: '6h'
max_total_connections: '20'
max_total_connections_per_route: '3'
replicas: '0'
request_timeout: '1m'
retention_strategy: 'delete'
rotation_strategy: 'time'
shards: '1'
socket_timeout: '60s'
graylog_inputs_arg:
- name: 'Syslog UDP'
type: 'org.graylog2.inputs.syslog.udp.SyslogUDPInput'
port: 1514
- name: 'CEF UDP Input'
type: 'org.graylog.plugins.cef.input.CEFUDPInput'
port: 5555
graylog_content_packs_arg:
- name: 'NGinx'
port: '12302-12301'
graylog_indexes_arg:
- refresh_interval: '30s'
translog:
sync_interval: '30s'
durability: 'async'
environments: 'prd'
datacenter: 'dc01'
domain: 'local'
customer: 'demo'
tags:
subscription: 'default'
owner: 'nobody'
department: 'Infrastructure'
organization: 'The Company'
region: 'China'
exporter_is_install: false
consul_public_register: false
consul_public_exporter_token: '00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000'
consul_public_http_prot: 'https'
consul_public_http_port: '8500'
consul_public_clients:
- '127.0.0.1'Please send your suggestions to make this role better.
Special thanks to the Connext Information Technology for their contributions to this role.