Lernd stands for Learning Explanatory Rules from Noisy Data. It is my implementation of the algorithm in the linked paper.
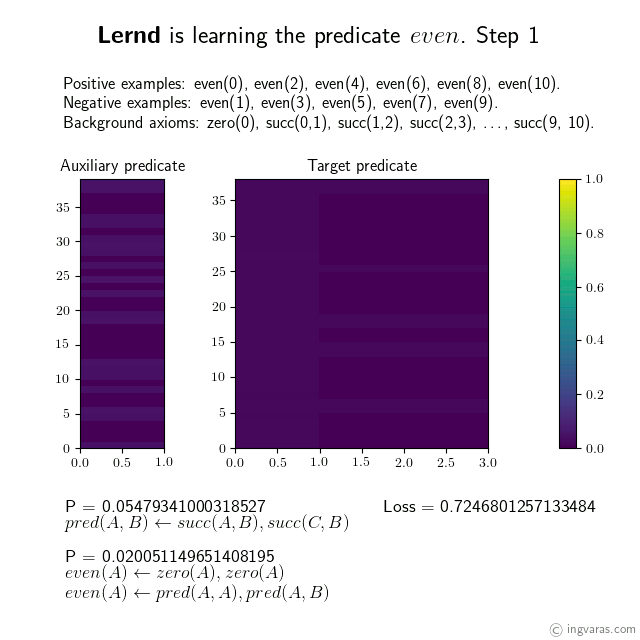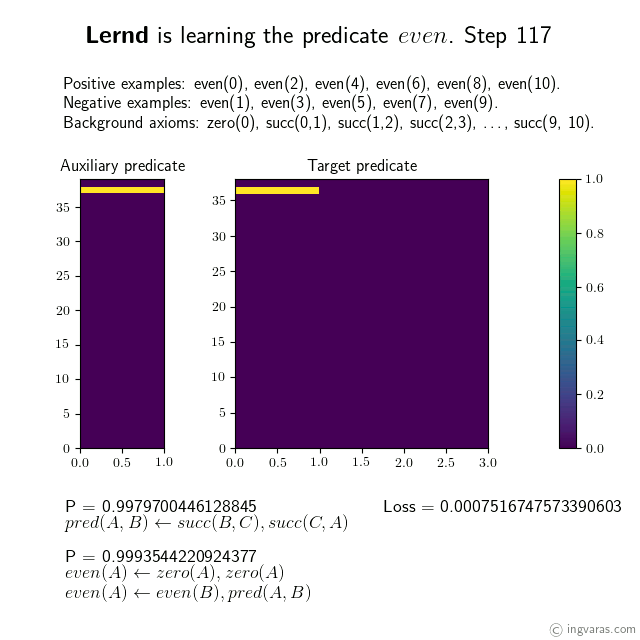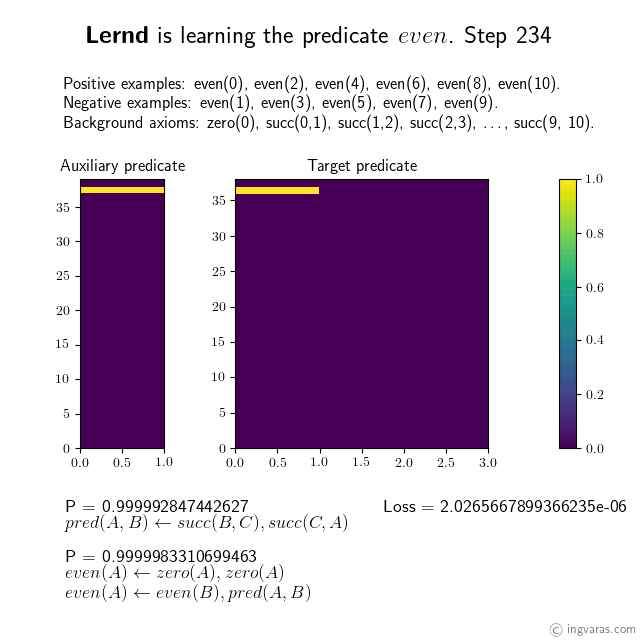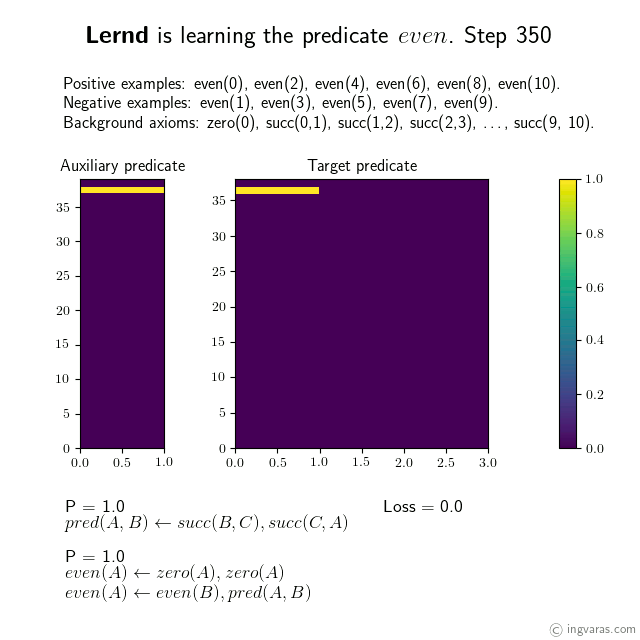
Learning the concept of even numbers from scratch*
If you found this code useful for your research please cite in your work:
@software{ingvaras_merkys_2020_4294059,
author = {Ingvaras Merkys},
title = {crunchiness/lernd: LERND - implementation of $\partial$ILP},
month = nov,
year = 2020,
publisher = {Zenodo},
version = {v1.1-alpha},
doi = {10.5281/zenodo.4294059},
url = {https://github.com/crunchiness/lernd}
}
Demo Jupyter notebooks are available online on Kaggle for a quick look into how it works:
Notebook files for local use can be found on https://github.com/crunchiness/lernd-notebooks
Run Lernd on Python 3.8+
You may create a conda environment (here named "lernd"):
conda create -n lernd python=3.8(Follow instructions at anaconda.com to get and install the conda package manager.)
Activate the environment:
conda activate lerndInstall requirements:
pip install -r requirements.txtRun experiments.
Some benchmark problems are defined in file lernd/experiments.py.
You may run lernd on them:
conda activate lernd # activate environment if using conda
python -m lernd.experiments <problem> # problems: predecessor, even Do a 100 runs at once, saving the output:
python -m lernd.run_many <problem> 100Unit tests are in lernd/test.py.
Run them:
conda activate lernd # activate environment if using conda
python -m lernd.test