“Many men of course became extremely rich, but this was perfectly natural and nothing to be ashamed of because no one was really poor – at least no one worth speaking of.” Douglas Adams, The Ultimate Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy
This software is a basic implementation of the defined yard sales models in the papers:
An H Theorem for Boltzmann’s Equation for the Yard-Sale Model of Asset Exchange.[1]
Oligarchy as a Phase Transition: The effect of wealth-attained advantage in a Fokker-Planck description of asset exchange.[2]
The sim uses the ascape api for agent based simulations. (http://ascape.sourceforge.net/)
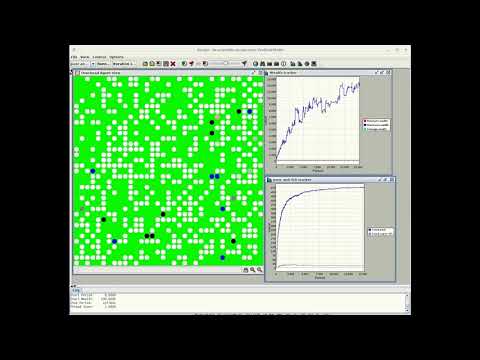
The agents move on the plane (a discrete 2D VonNeumann space) and interact with each other defined by the corresponding algorithm. They all started out with the same amount of wealth, so the Gini coefficient is 0 at the beginning. All models share the same basic data and structures defined by the abstract class de.urszeidler.ascape.AbstractYardSaleModel. These are nAgents , startWealth and the dimensions ( latticeHeight , latticeWidth ) of the space. The basic agent behavior is defined by the abstract class de.urszeidler.ascape.AbstractYardSaleAgent and includes the wealth of the agent also the behavior set, like moving in the plane and interact and some style definition (color) depending on the individual wealth. The system is stable in any way, the wealth is constant over time, no agent leaves.
As agents need to move to change interaction parters, so the space occupation factor starts to impact the original equations when it get crowdy. For example, when the spaceocc. is 100% and there is no movement, the system tends to build local oligarchies. This might be interesting when moving to a more historical perspective, where moving of the capital was some how restricted. The same deviation from the original equations are true for the near oligarchie state, as the 'enviorment' is sucked dry, the few ultra rich wanders the parched scape, in hope to find another victim to swallow, and in the constant fear of being swallowed, so the convergence of the Gini coefficient diverges in the late state of the system.
The predefined values are:
nAgent: 500
startWealth: 100
latticeHeight: 35
latticeWidth: 35
space: 1225 = latticeHeight * latticeWidth
spaceOcc: 40.82% = space / nAgent
completeWealth: 50.000 = nAgents * startWealth
- de.urszeidler.ascape.ysae.YardSaleModel
- de.urszeidler.ascape.ysae1.YardSaleModel
- de.urszeidler.ascape.ysae_distubution.YardSaleModel
All model collect some basic statistic about the economics of the system.
- number of poor agents
- number of super rich agents
- maximum, minimum and average wealth
An agent is counted as rich if it wealth is greater than richfactor * startWealth and as poor when the wealth is lower than poorfactor * startWealth . The default value are 1.000, ten times the average,and 10 ten times less than average.
You can tweak these values between model runs. For details see http://ascape.sourceforge.net/index.html#Exploring
A simple run of the different model can be found here
Also a run with about 40.000 iterations, compressed to 2 and a half minutes. (about 2 hours in original)
You will find some more specific notes in the math. Or the corresponding wxMaxima (http://wxmaxima-developers.github.io/wxmaxima/) file YardSaleSim/doc/yard-sale.wxmx .
This is the implementation of the proposed model in [1].
This is the implementation of the proposed model in [2] without redistribution function.
This is the implementation of the proposed model in [2] with redistribution function.
To use and try the sim, use the eclipse installer and the SimYardSale.setup Oohmp setup, which will install and configure a eclipse installation, and checkout the code and import it.
- download the installer, get the setup file and install.
Switch to advanced mode. On the first page (product selection), choose whatever product your eclipse should be based upon. On the second page, you can drag your SimYardSale.setup file from the system explorer onto the “eclipse.org” top node. Double click it, so that it is shown in the three lists below.
A detailed description is here
other yard sale model projects:
http://www.physics.umd.edu/hep/drew/math_general/yard_sale.html https://www.compadre.org/osp/items/detail.cfm?ID=13337 https://www.wealthinequality.info/
These are the main papers the sim is based on.
[1] Boghosian, B.M., Johnson, M. & Marcq, J.A. An H Theorem for Boltzmann’s Equation for the Yard-Sale Model of Asset Exchange. J Stat Phys 161, 1339–1350 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10955-015-1316-8
[2] Bruce M. Boghosian, Adrian Devitt-Lee, Merek Johnson, Jeremy A. Marcq, Hongyan Wang Oligarchy as a Phase Transition: The effect of wealth-attained advantage in a Fokker-Planck description of asset exchange. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, Volume 476, 2017, Pages 15-37, ISSN 0378-4371, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2017.01.071. (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S037843711730081X) https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.00770v2
Jie Li, Bruce M. Boghosian, Chengli Li, The Affine Wealth Model: An agent-based model of asset exchange that allows for negative-wealth agents and its empirical validation, Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, Volume 516, 2019, Pages 423-442, ISSN 0378-4371,https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2018.10.042.(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378437118313906) https://arxiv.org/pdf/1604.02370.pdf
Some other references
https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/is-inequality-inevitable/
The code is published under the terms of the BSD license see "etc/license.txt".