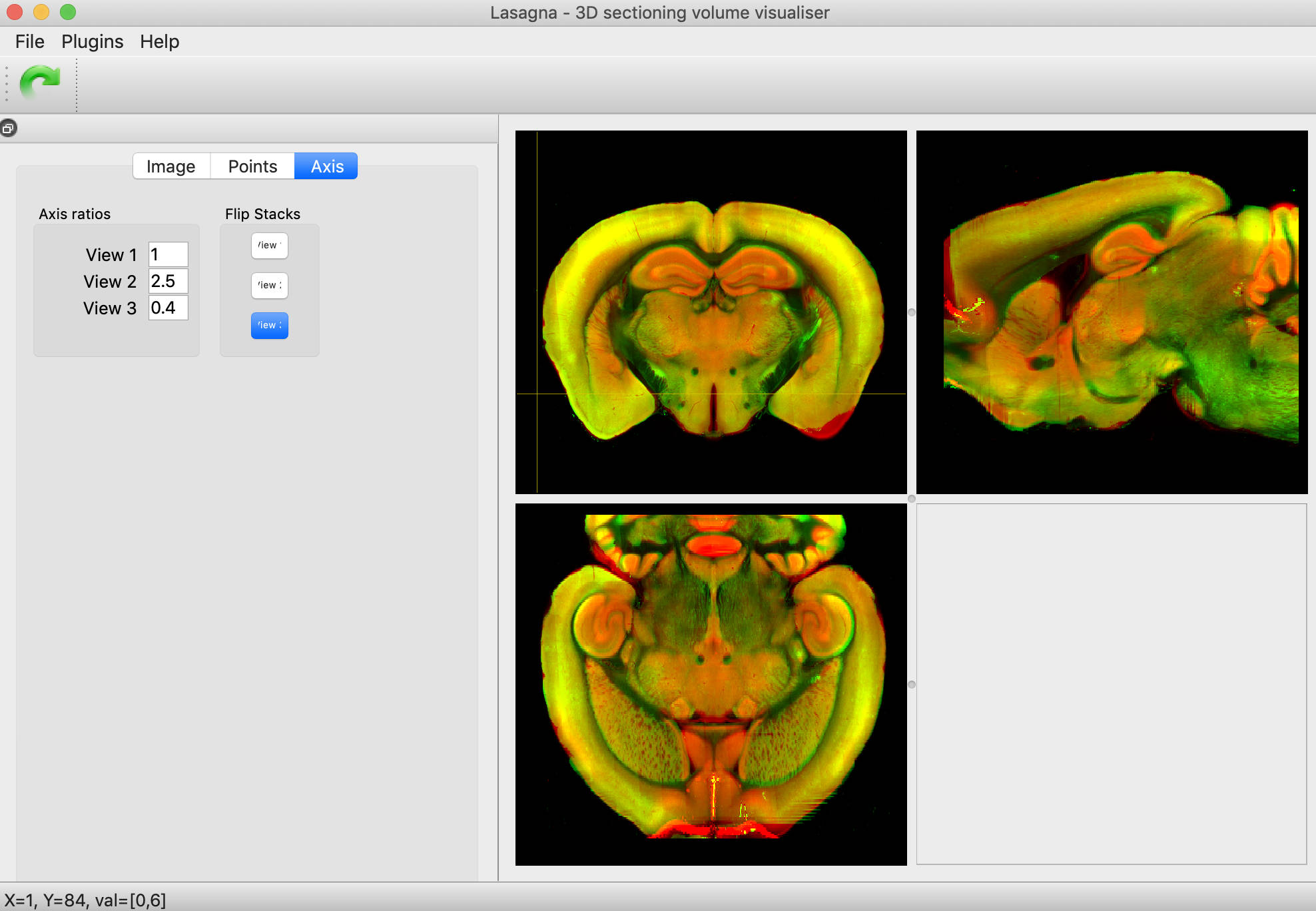
Lasagna a lightweight platform for visualising for 3D volume data developed for the OpenSerialSection project. Lasagna features a flexible plugin system, allowing it to be easily extended using Python and PyQt. Visualisation is peformed via three linked 2D views. Lasagna was written to explore registration accuracy of 3D data, guide registration, and overlay point data onto images. For more information see the wiki. The above image shows a mouse brain (green) registered to the Allen Atlas template brain (red).
Here is a video showing navigation of a three-channel dataset with Lasagna. In this example video the image stack is pretty big (a few GB) which makes the navigation a little laggier than normal.
First clone the repo and cd to it:
git clone https://github.com/SainsburyWellcomeCentre/lasagna.git
cd lasagna
A Conda environment yml file is provided. If you use conda, you can create a virtual environment and download all the dependencies by running:
git clone https://github.com/SainsburyWellcomeCentre/lasagna.git
cd lasagna
conda env create -f lasagna_environment.yml
Now activate the virtual environment with activate lasagna (Windows) or source activate lasagna (Linux/Mac).
You can now install:
pip install -e .
Lasagna is now installed. Try lasagna -D for load with a demo image.
The above ought to work without Conda too if you miss out the conda command.
On systems with a Python 3 install you can try just cloning then running:
pip3 install --user -e .
If you have trouble with a non-Conda install, see the following:
Lasagna runs on Python 3, PyQt5, and uses PyQtGraph for the plotting and requires the following modules:
- PyLibTiff
- pynrrd
- numpy
- pyqtgraph >0.11.0
- MatplotLib
- yaml [and pyyaml]
- Scipy [optional - ARA explorer]
- Scikit-Image [optional - ARA explorer]
- PyQt5
- SIP
- tifffile [optional for importing LSM files]
- vtk [optional, for faster import of MHD files but doesn't work in Python 3]
On Linux you can install most of the above via your package manager
with the remaining packages being installed via pip3 (cd to Lasagna
directory to run the pip3 install line) :
apt-get install python3 python3-pip python3-pyqt5 python3-numpy python3-matplotlib
python3-scipy python3-sip
pip3 install -r requirements.txt --user
This command installs the dependencies in your home folder.
If you add the --upgrade flag, pip3 will also install newer
vesions of packages already in the system path.
There is currently no vtk support in Python 3.
If you run into problems try installing the dependencies separately (see below).
For other platforms, please see here
On Mac you will first need to Install HomeBrew
/usr/bin/ruby -e "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)"
The install Python 3 and a couple of other packages without which you won't be able to install the rest of the dependencies:
brew install freetype pkg-config python3
Now you can install the dependencies in requirements.txt using:
pip3 install -r requirements.txt --user
If for some reason this fails, try installing the dependencies seperately:
pip3 install numpy
pip3 install matplotlib
...
After the first run, Lasagna creates a preferences file in the .lasagna hidden directory in your home directory.
You may need to edit this file to make Lasagna aware of its built in-plugins. i.e. edit the pluginPaths preference.
This step isn't user-friendly, sorry.
To start lasagna, just activate the virtual environment (if you use conda or virtualenv) and enter lasagna. The command line arguments can be listed using lasagna -h
usage: lasagna [-h] [-i IMAGE_STACKS [IMAGE_STACKS ...]]
[-S SPARSE_POINTS [SPARSE_POINTS ...]] [-L LINES [LINES ...]]
[-T TREE [TREE ...]] [-P PLUGIN] [-C] [-D]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i IMAGE_STACKS [IMAGE_STACKS ...], --image-stacks IMAGE_STACKS [IMAGE_STACKS ...]
File name(s) of image stacks to load (default: None)
-S SPARSE_POINTS [SPARSE_POINTS ...], --sparse-points SPARSE_POINTS [SPARSE_POINTS ...]
File names of sparse points file(s) to load (default:
None)
-L LINES [LINES ...], --lines LINES [LINES ...]
File names of lines file(s) to load (default: None)
-T TREE [TREE ...], --tree TREE [TREE ...]
File names of tree file(s) to load (default: None)
-P PLUGIN, --plugin PLUGIN
Start plugin of this name. Use string from plugins
menu as the argument (default: None)
-C, --console Start a ipython console, once the console has started, enter "%gui qt" (default: False)
-D, --demo Load demo images (default: False)
For example, to load Lasagna with demo images and also start the add_line_plugin you should run:
$ lasagna -D -P add_line_plugin
For more information see the wiki.
Lasagna is functional but has lots of small bugs (sorry). Development stalled for a while but has now restarted somewhat. We are looking for contributors.