Image similarity tasks involve determining how similar two or more images are to each other. In these tasks, it's crucial to learn feature representations that can capture relevant patterns and structures from the images. One common approach to enhancing the performance of image similarity tasks is by leveraging loss functions like Center Loss and Triplet Loss.
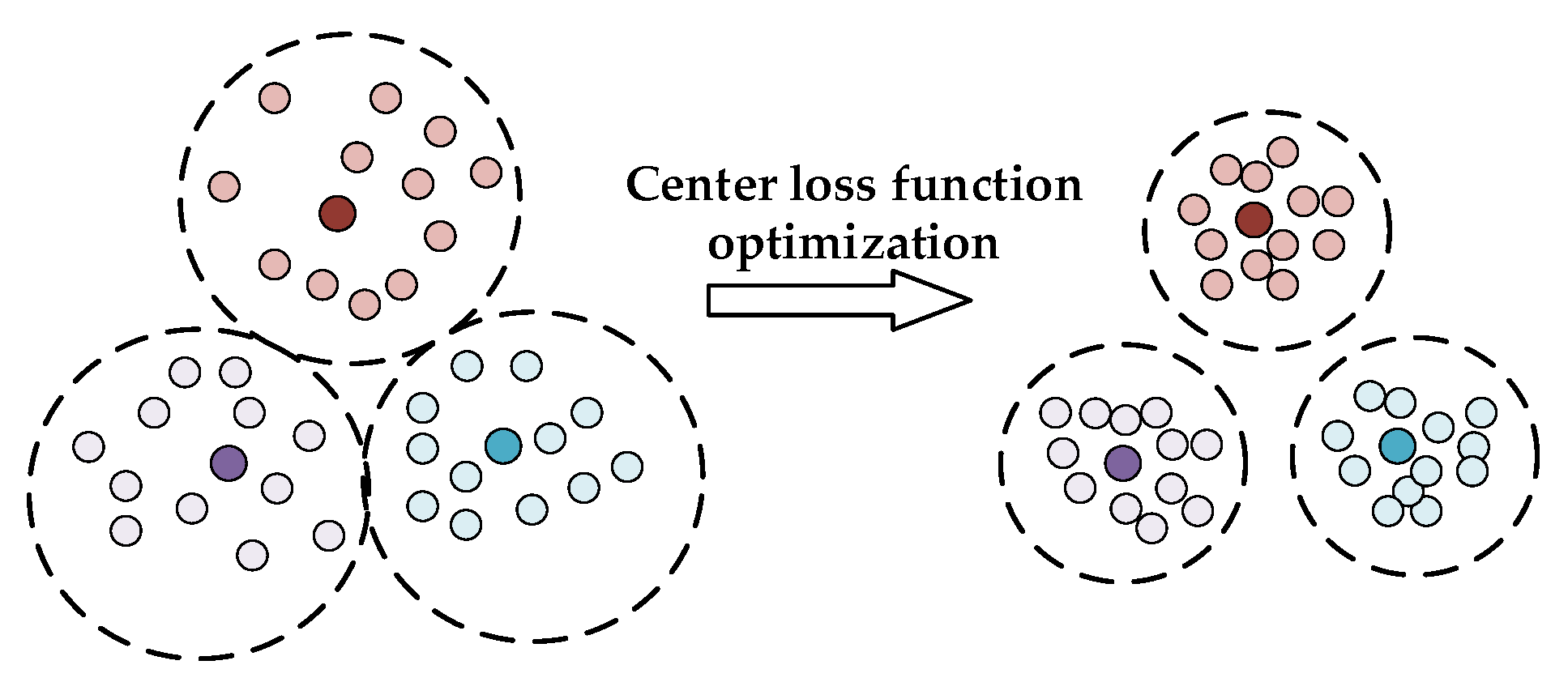
Center Loss is a loss function that aims to improve the intra-class compactness and inter-class separability of feature embeddings. It is calculated as follows:
L_center = ∑ (||f_i - c_yi||^2)Where:
- L_center is the Center Loss.
- f_i represents the feature embedding of the i-th image.
- c_yi is the center of the class to which the i-th image belongs.
Center Loss encourages the feature embeddings of images from the same class to be close to their corresponding class centers, making the feature space more compact and well-separated.
Triplet Loss is another technique used in image similarity tasks. It involves training the model using triplets of images: an anchor image (A), a positive image (P, similar to the anchor), and a negative image (N, dissimilar to the anchor).
The loss is defined as:
L_triplet = max(0, ||f_A - f_P||^2 - ||f_A - f_N||^2 + α)Where:
- L_triplet is the Triplet Loss.
- f_A, f_P, and f_N are the feature embeddings of the anchor, positive, and negative images, respectively.
- α is the margin that enforces a gap between the distances of anchor-positive and anchor-negative pairs.
Triplet Loss encourages the feature embeddings of similar images (anchor and positive) to be closer together in the embedding space than dissimilar images (anchor and negative) by at least the margin α.
Both Center Loss and Triplet Loss contribute to improving image similarity tasks by enhancing the discriminative power of the learned feature embeddings. Center Loss focuses on clustering similar images around class centers, while Triplet Loss enforces a structured distance between anchor-positive and anchor-negative pairs in the feature space.
In this implementation, we focus on the Center Loss technique to enhance the discriminability of feature embeddings. The combination of a feature extraction backbone with Center Loss allows us to learn more informative representations for image similarity tasks.
- Preprocesses images from the Oxford Flowers 102 dataset.
- Uses an EfficientNet-based neural network as the feature extraction backbone.
- Implements the Center Loss technique to enhance feature discriminability.
- Performs training and validation loops.
- Updates centers for each class using exponential moving average (EMA).
- Evaluates the model's performance on the validation set.
The dataset used in this project is the Oxford Flowers 102 dataset, provided by TensorFlow Datasets.