Read this in other languages: 한국어.
In this Code Pattern we will use a Jupyter notebook to showcase an example of machine learning with time series on IBM Power8 systems. The notebook will focus on evalulating the predictability of future financial market values in the "renewable energy" sector by examining related markets and sentiment detected in New York Times news articles.
When the reader has completed this Code Pattern, they will understand how to:
- Extract and format structured data from various external sources.
- Extract and format unstructured data and use IBM Watson cognitive services to extract data sentiment.
- Build and train Neural Networks.
- Display and share results in Jupyter notebooks.
The intended audience for this Code Pattern is application developers who need to efficiently build powerful deep learning applications, but who may not have an abundance of time or data science experience.
- The developer loads the provided notebook, which is run on a PowerAI system.
- As the notebook is run, it uses data from The New York Times and market data.
- The notebook uses the IBM Watson Natural Language Understanding service to analyze the text.
- The notebook uses TensorFlow and machine learning to develop models and predictions.
- IBM Watson Natural Language Understanding: An IBM Cloud service that can analyze text to extract meta-data from content such as concepts, entities, keywords, categories, sentiment, emotion, relations, semantic roles, using natural language understanding.
- IBM Power AI: A software platform that includes the most popular machine learning frameworks with IBM Power Systems.
- IBM Power Systems: IBM Power Systems is IBM's Power Architecture-based server line, built with open technologies and designed for mission-critical applications.
- Nimbix Cloud Computing Platform: An HPC & Cloud Supercomputing platform enabling engineers, scientists & developers, to build, compute, analyze, and scale simulations in the cloud
- Data Science: An open-source web application that allows you to create and share documents that contain live code, equations, visualizations and explanatory text.
- Tensorflow: An open source software library for numerical computation using data flow graphs.
Follow these steps to setup and run this Code Pattern. The steps are described in detail below.
- Get 24-hours of free access to the PowerAI platform
- Access and start the Jupyter notebook
- Run the notebook
- Analyze the results
- Save and share
- End your trial
IBM has partnered with Nimbix to provide cognitive developers a trial account that provides 24-hours of free processing time on the PowerAI platform. Follow these steps to register for access to Nimbix to try the PowerAI Cognitive Code Patterns and explore the platform.
Go to the IBM Marketplace PowerAI Portal, and click Request Trial.
On the IBM PowerAI Trial page, shown below, enter the required information to sign up for an IBM account and click Continue. If you already have an IBM ID, click Already have an account? Log in, enter your credentials and click Continue.
On the Almost there… page, shown below, enter the required information and click Continue to complete the registration and launch the IBM Marketplace Products and Services page.
Your IBM Marketplace Products and Services page displays all offerings that are available to you; the PowerAI Trial should now be one of them. From the PowerAI Trial section, click Launch, as shown below, to launch the IBM PowerAI trial page.
The Welcome to IBM PowerAI Trial page provides instructions for accessing the trial, as shown below. Alternatively, you will receive an email confirming your registration with similar instructions that you can follow to start the trial.
Summary of steps for starting the trial:
-
Start a terminal session from your local machine and issue the following command where
{IP Address}is the IP Address (or host name) shown on the welcome page (or in the confirmation email).ssh -L 8888:localhost:8888 nimbix@{IP Address} -
Enter the password shown on the welcome page (or in the confirmation email) when prompted.
-
From your local browser, go to the following URL to get started: http://localhost:8888/tree/.
Use git clone to download the example notebook and data with a single command.
- Get a new terminal window by clicking on the
Newpull-down and selectingTerminal.
- Run the following command to clone the git repo:
git clone https://github.com/IBM/powerai-notebook
- Once done, you can exit the terminal and return to the notebook browser. Use the
Filestab and click onpowerai-notebookthennotebooksand thenClean_Energy_Watson_V1.0.ipynbto open the notebook.
When a notebook is executed, what is actually happening is that each code cell in the notebook is executed, in order, from top to bottom.
Each code cell is selectable and is preceded by a tag in the left margin. The tag
format is In [x]:. Depending on the state of the notebook, the x can be:
- A blank, this indicates that the cell has never been executed.
- A number, this number represents the relative order this code step was executed.
- A
*, this indicates that the cell is currently executing.
There are several ways to execute the code cells in your notebook:
- One cell at a time.
- Select the cell, and then press the
Playbutton in the toolbar.
- Select the cell, and then press the
- Batch mode, in sequential order.
- From the
Cellmenu bar, there are several options available. For example, you canRun Allcells in your notebook, or you canRun All Below, that will start executing from the first cell under the currently selected cell, and then continue executing all cells that follow.
- From the
Notes:
-
Regarding cell
[4]: For the Code Pattern we import already collected stock market data. This can be done inside the notebook, but requires access to private financial websites (such as Bloomberg), which requires a subscription fee. -
Regarding cell
[5]: In an effort to speed up the notebook processing time, the New York Times data has already been collected and stored in a JSON file, and is imported by the notebook. -
The Code Pattern is based on the original Google Cloud Platform example documented at https://cloud.google.com/solutions/machine-learning-with-financial-time-series-data. The difference between this "IBM Demo" and the original "Google Demo" is noted in the following table:
The result of running the notebook is a report which may be shared with or without sharing the code. You can share the code for an audience that wants to see how you came your conclusions. The text, code and output/charts are combined in a single web page. For an audience that does not want to see the code, you can share a web page that only shows text and output/charts.
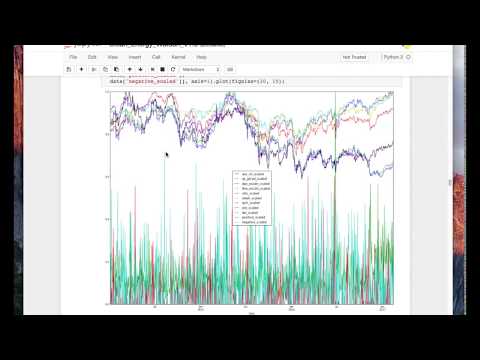
The graphs and charts produced in this Code Pattern attempt to prove that the closing value of the Nasdaq Clean Energy Index can be predicted by examining various input sources, such as the New York Times and other financial markets, both foreign and domestic. These markets include:
- Australian Clean Tech Index (asx_cti)
- Germany DAX (dax_eusdn)
- UK FTSE100 (ftse-eo100)
- UK Credit Suisse (n8wh)
- US First Trust Nasdaq Clean Edge ETF (qcln and cels)
- US S&P Global Clean Energy Index (icln and sp_gtced)
- US Equity Uncertainty Index (dei)
The notebook begins by collecting and formatting data:
-
Collect and merge 3 years of stock market financial data.
-
Collect 3 years of "green energy" articles from the New York Times. This data is then feed into the Watson Natural Language Understanding service to gather sentiment analysis - specifically by assigning a relative positive or negative score to each article.
The notebook then utilizes EDA (exploratory data analysis) methods to find correlations in the data. These findings include:
- Over a 3-year period, there is a correlation between all of the indexes.
- There is a correlation between current values of an index and lagged values of the same index.
- There are 2 US indexes (qcln and icln) that correlate with the closing values of other indexes available on the same day (i.e. non-US indexes).
The final analysis from the EDA are as follows:
- The Australian Index close from the same day is a strong predictor for the close of the Nasdaq Energy Index.
- European indices are a significant predictor for the close of the Nasdaq Energy Index.
- Indices from previous days were not a good predictor for the Nasdaq Energy Index.
After determining this correlation in the data, the notebook then uses TensorFlow and the IBM PowerAI machine learning framework to train and test the data.
After hundreds of thousands of iterations over the data using multiple models, the notebook is able to achieve a 70% success rate for predicting whether the Nasdaq Energy Index would close up or down on any given day.
Because this notebook is running temporarily on a Nimbix Cloud server, the options to saving and sharing the notebook are limited.
Under the File menu, there are options to:
Download as...will download the notebook to your local system.Print Previewwill allow you to print the current state of the notebook.
When you are done with your work, please cancel your subscription by issuing the following command in your ssh session or by visiting the Manage link on the My Products and Services page.
sudo poweroff --force- Demo on Youtube: Watch the video.
- Putting the “AI” in PowerAI: IBM’s latest Power servers, the world’s fastest deep learning servers, come with an AI twist.
- PowerAI Now Includes Newly Announced TensorFlow 1.0: As the TensorFlow ecosystem grows, IBM brings its features to PowerAI to give deep-learning developers a high-performance turnkey system.
- Artificial Intelligence Code Patterns: Enjoyed this Code Pattern? Check out our other AI Code Patterns.
- Data Analytics Code Patterns: Enjoyed this Code Pattern? Check out our other Data Analytics Code Patterns
- AI and Data Code Pattern Playlist: Bookmark our playlist with all of our Code Pattern videos
- With Watson: Want to take your Watson app to the next level? Looking to utilize Watson Brand assets? Join the With Watson program to leverage exclusive brand, marketing, and tech resources to amplify and accelerate your Watson embedded commercial solution.
- Data Science Experience: Master the art of data science with IBM's Data Science Experience
- PowerAI: Get started or get scaling, faster, with a software distribution for machine learning running on the Enterprise Platform for AI: IBM Power Systems
This code pattern is licensed under the Apache Software License, Version 2. Separate third party code objects invoked within this code pattern are licensed by their respective providers pursuant to their own separate licenses. Contributions are subject to the Developer Certificate of Origin, Version 1.1 (DCO) and the Apache Software License, Version 2.