This project is based on this paper
-
Point Cloud Data
Point clouds are sets of 3D points that represent the shape and structure of objects or scenes in the form of unordered point sets. Due to the unordered property of the point cloud, traditional network can not directly use the point cloud data to train.
-
Point Net
PointNet was introduced by Charles R. Qi et al. in a 2017 paper titled "PointNet: Deep Learning on Point Sets for 3D Classification and Segmentation." It is a neural network architecture that directly takes raw point clouds as input and processes them without any pre-processing or feature extraction steps. PointNet is capable of learning meaningful features from point clouds, such as local and global geometric information, and can be used for tasks such as 3D object classification, semantic segmentation, and point cloud generation.
-
Adding Permutation Invariance
The idea of extracting a global feature is essential when doing classification and segmentation tasks because the input data cannot reflect the global information. The main challenge with processing point cloud data is that it is unordered. We want the same output features regardless of the order of the input point cloud. To have a permutation-invariant network, we need a symmetric function for unordered input. To handle the above problem, we apply MLPs on the individual points in the input point cloud to expand the dimension of input. And we achieve permutation-invariant by applying max-pooling operations to aggregate information across the points.
-
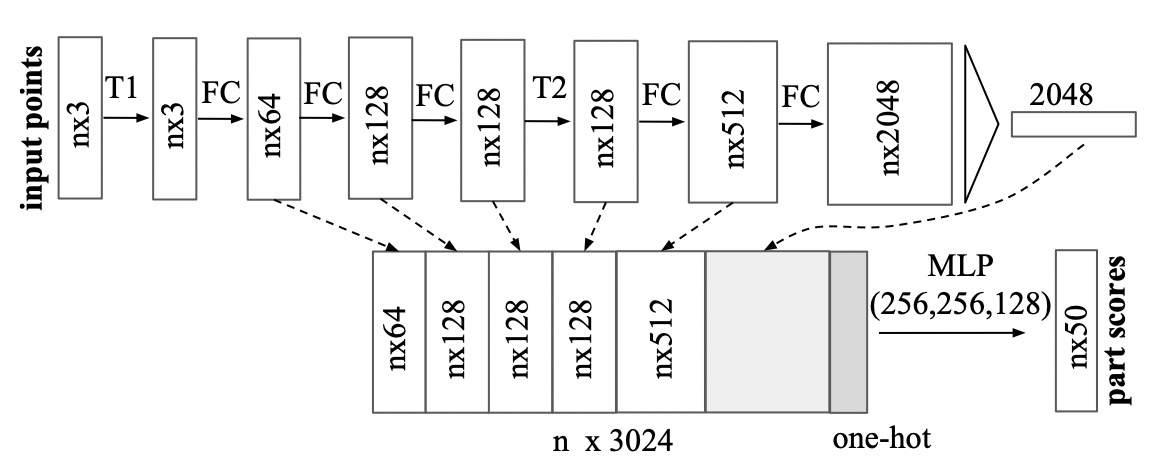
Joint Alignment Network
 The Joint Alignment Network (T-Net) can eliminate the influence of translation, rotation, and other factors on point cloud classification and segmentation. The input point cloud passes through this network to obtain an affine transformation matrix. Then, this matrix is multiplied by the original point cloud to obtain a new nx3 point cloud. The same method is applied to the feature space to ensure the invariance of features.
The Joint Alignment Network (T-Net) can eliminate the influence of translation, rotation, and other factors on point cloud classification and segmentation. The input point cloud passes through this network to obtain an affine transformation matrix. Then, this matrix is multiplied by the original point cloud to obtain a new nx3 point cloud. The same method is applied to the feature space to ensure the invariance of features. -
Concatenating data and global feature during segmentation
 Different from object classification which just needs global feature information, part segmentation needs both global and local feature. To do local and global information aggregation, we use a method similar to U- Net. PointNet aggregate local and global features simply by concentrating the global feature and local feature of each point in the hidden layer of MLP. With this modification, the network can predict each point category relying on global semantics and local geometry.
Different from object classification which just needs global feature information, part segmentation needs both global and local feature. To do local and global information aggregation, we use a method similar to U- Net. PointNet aggregate local and global features simply by concentrating the global feature and local feature of each point in the hidden layer of MLP. With this modification, the network can predict each point category relying on global semantics and local geometry.
-
Adding Permutation Invariance
Let students achieve forward pass of MLPs with shared weights and max-pooling across the points.
-
Joint Alignment Network Let students implement t-net module in the notebook to understand the architecture of t-net.
In order to constrain the matrix learned by t-net to be rotaion matrix, a penalty term is added to the loss of the module and have a coeficient alpha. Let student tune the alpha value and observe the accuracy change due to the alpha. This can help student understand the loss deisgn and the intuition for the proposal of t-net in PointNet.
Open classifier.ipynb and segmentation.ipynb will show you the model structure and how we train.