📦 DNS cache server on k8s with query statistics visualization using EFK stack for @wide-camp-1909
- Unbound: DNS cache server (only for IPv4 clients)
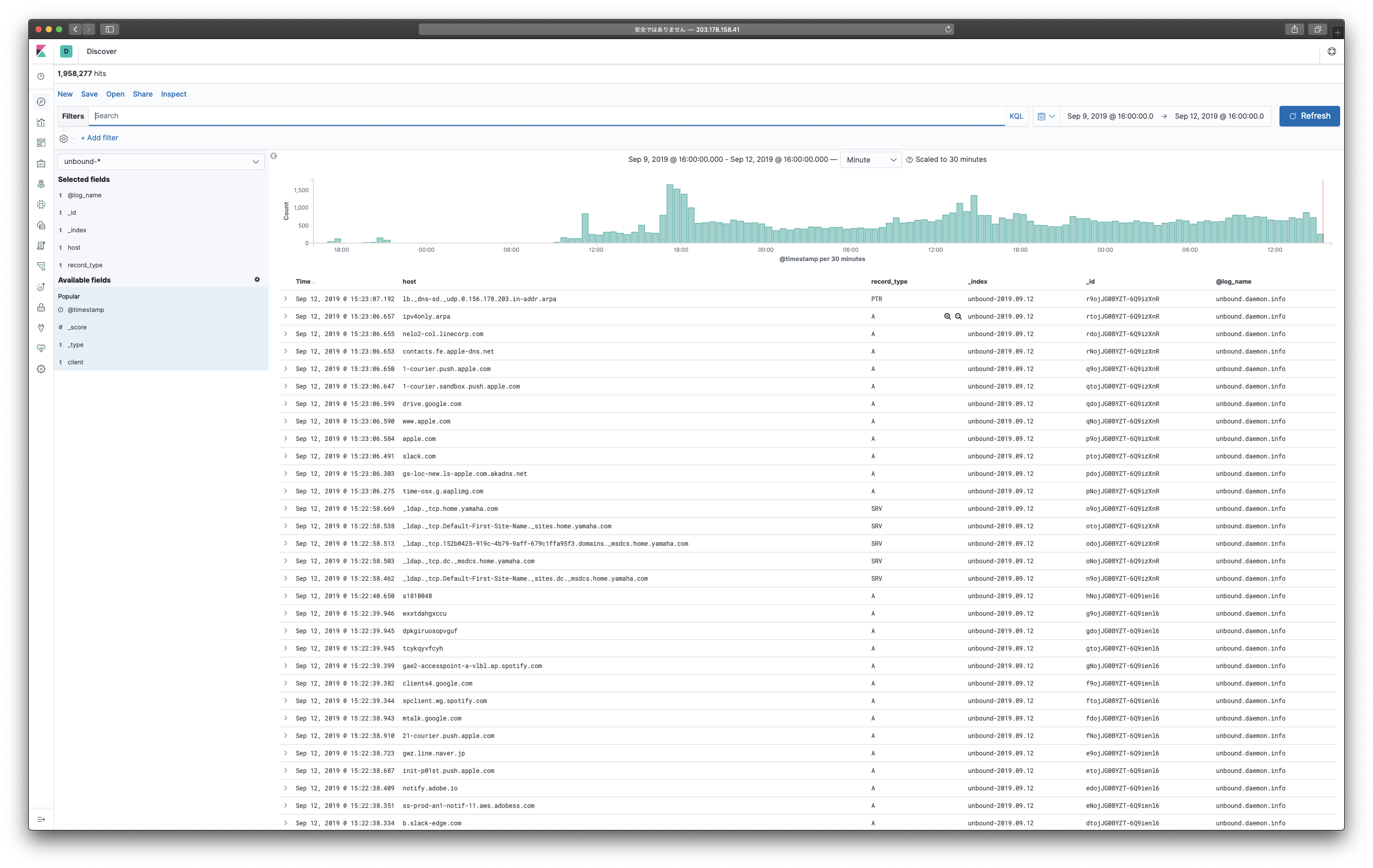
- Elasticsearch: Storing, indexing, and searching DNS logs
- Fluentd: Filtering raw logs from DNS and passing them to ES
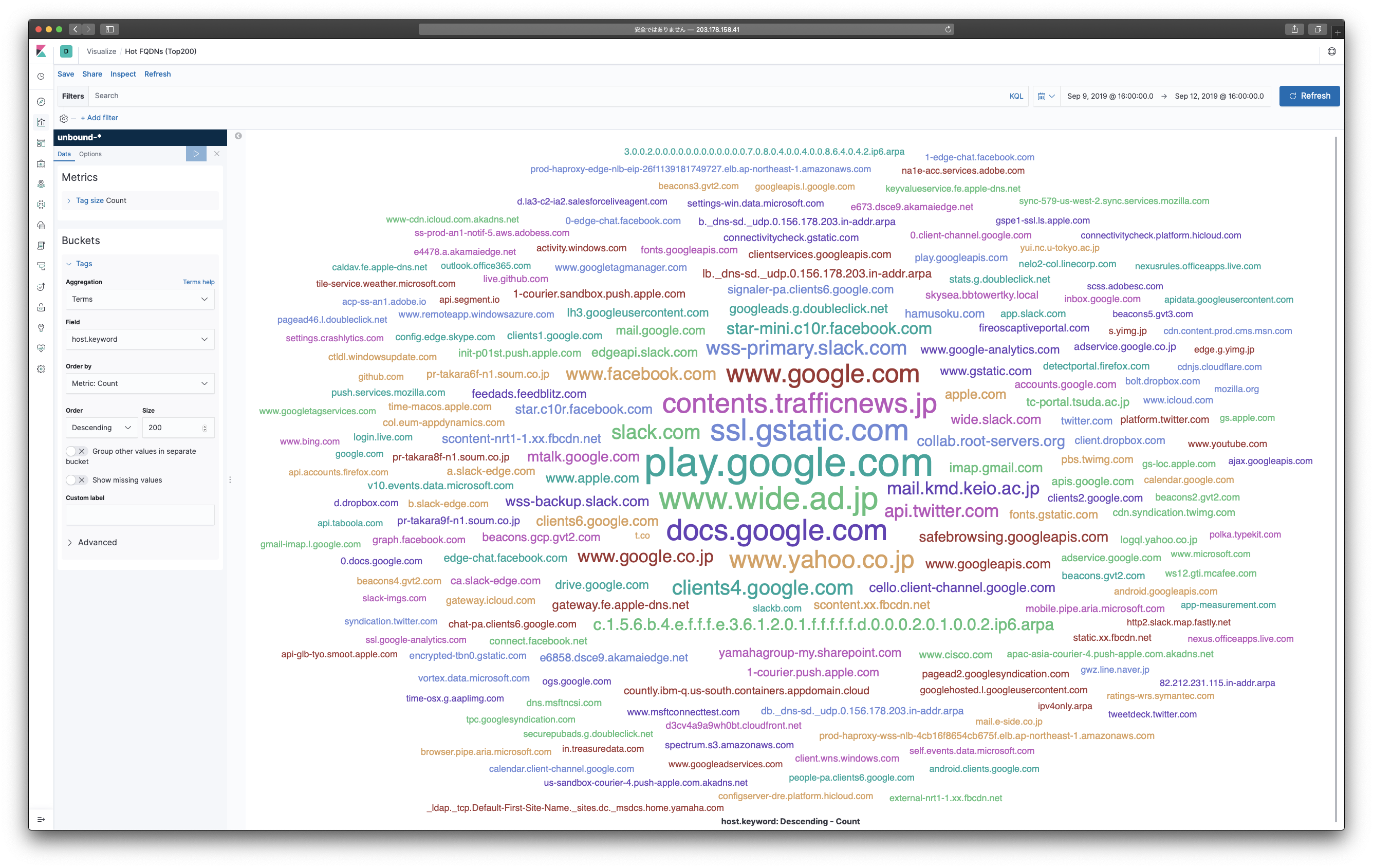
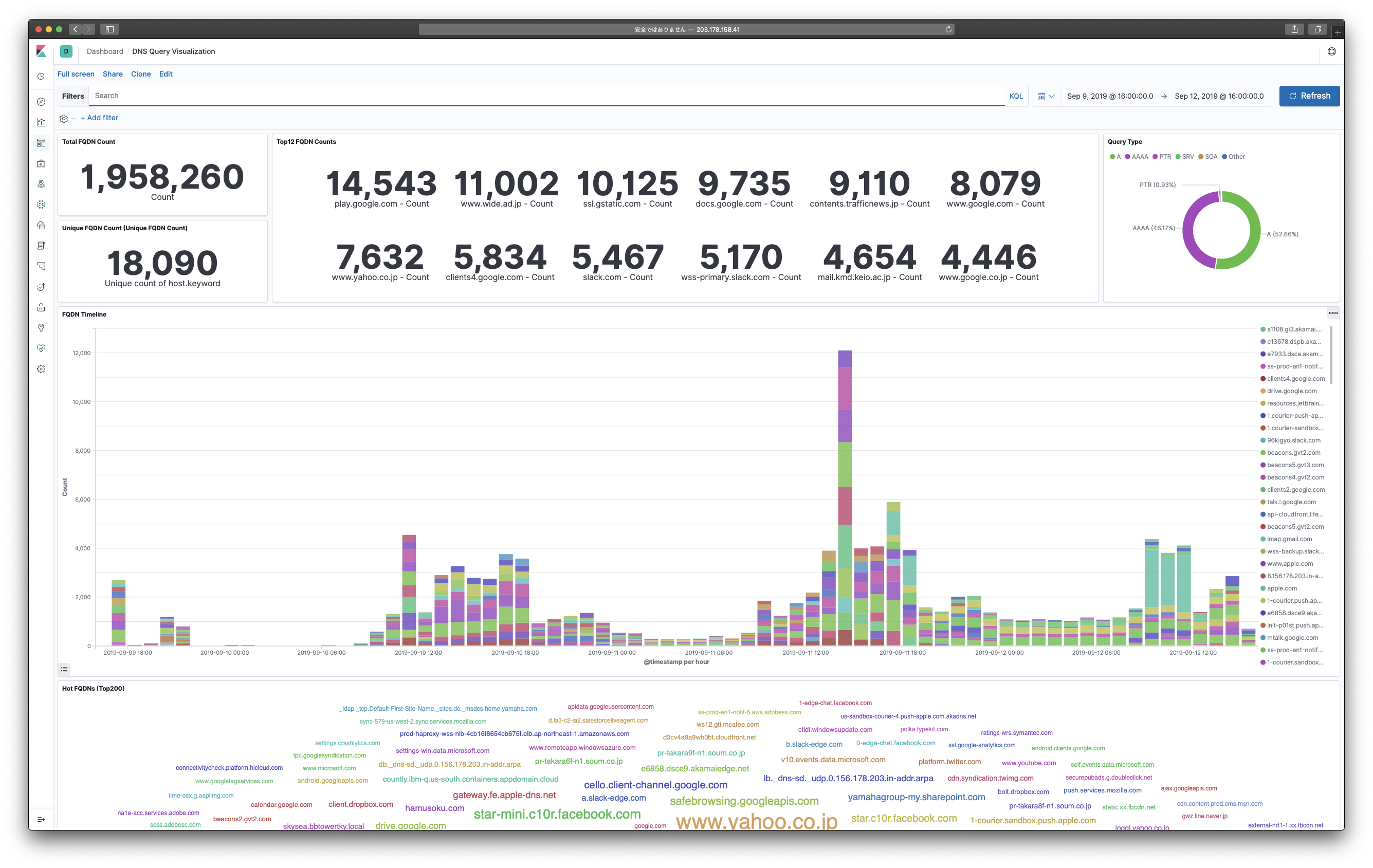
- Kibana: Visualizing query statistics information
These instructions will get you a copy of this project up and running on your Kubernentes environment for production purpose. If you want to use this for development or testing, you should try using docker-compose:
% docker-compose up -d --build
% docker-compose logs -f
NOTE: docker-compose 1.22.0 and higher is necessary for running
At least 10 CPU cores, 8GB of RAM, and 32GB of storage are required for physical or virtual server hardware. Kubernetes ecosystem on it should be:
- docker-engine: 18.06.0 and higher
- Kubernetes: 1.15.0 and higher
- Helm: 2.14.3 and higher
Also you need to prepare the Persistent Volume Storage for Elasticsearch (this must be larger than 32GB). A distributed storage platform Ceph managed by Rook which is one of the cloud-native storage orchestrators is well-known design for this kind of situation.
CAUTION: You should not create PV from NFS. Running Elasticsearch on NFS is not supported officially and known to be problematic, also performance will be very low. If you really need to use NFS, no_root_squash option must be available and enabled at NFS server, or Elasticsearch cannot run due to the permission problem. (See: wide-camp-1909/sandbox)
It is desirable that either public or private Docker registry is available for image pulling.
If not, you have to run docker build command at each of the Kubernetes worker nodes.
(Building private registry guide: wide-camp-1909/sandbox)
Finally, you may deploy Kubernetes Metrics Server in namespace kube-system.
If there is no metrics-server available on your Kubernetes cluster, Horizontal Pod Autoscaling of unbound DNS will not work.
(Check and follow the instructions: wide-camp-1909/metrics-server)
Install this repository on your Kubernetes environment:
% helm repo add wide-camp https://wide-camp-1909.github.io/camp-dns-efk/chartIf the above installation was successful, you can search packages via:
% helm repo list
% helm search camp-dns-efkTo deploy the chart with release name camp-dns in namespace camp-dns, run the following:
% helm install wide-camp/camp-dns-efk --name camp-dns --namespace camp-dns --debug --dry-run | bat -l yaml
% helm install wide-camp/camp-dns-efk --name camp-dns --namespace camp-dnsCheck the release status with:
% helm status camp-dns
% helm get camp-dnsOpen your favorite browser and go http://203.178.158.41:5601/ to see Kibana dashboard.
You can setup dashboard quickly by uploading kibana-dashboard.json via Import Dashboard API.
To delete the release, type:
% helm delete --purge camp-dnsThis command removes all components associated with the chart and delete the release completely.
If you did not set the Reclaim Policy of Persistent Volume as Retain, all data would be lost.
The following table lists the configurable parameters and their default values.
| Parameter | Description | Default (for wide-camp-1909) |
|---|---|---|
unbound.image.repository |
unbound image repository |
203.178.158.5:30500/wide-camp-1909/camp-dns-unbound |
unbound.image.tag |
unbound image tag |
latest |
unbound.image.pullPolicy |
Image pull policy | IfNotPresent |
unbound.image.pullSecret |
Image pull secret for private registry | camp-reg |
unbound.replicaCountInit |
Number of initial replicas | 3 |
unbound.replicaCountMin |
Number of minimum replicas | 2 |
unbound.replicaCountMax |
Number of maximum replicas | 9 |
unbound.averageUtilization |
Threshold of CPU usage for scale-out | 50 |
unbound.listen |
unbound service endpoint IPs |
[203.178.158.32, 203.178.158.33] |
unbound.allow |
unbound range of recursion request allowance |
[127.0.0.0/8, 10.0.0.0/8, 172.16.0.0/12, 192.168.0.0/16, 203.178.156.0/22] |
elasticsearch.image.repository |
elasticsearch image repository |
elasticsearch |
elasticsearch.image.tag |
elasticsearch image tag |
"7.3.1" |
elasticsearch.image.pullPolicy |
Image pull policy | IfNotPresent |
elasticsearch.memory |
Memory allocation | 32g |
elasticsearch.persistence.data.size |
Size of PV Claim | 300Gi |
elasticsearch.persistence.data.storageClassName |
Name of PV storage class | rook-ceph-block-retain |
fluentd.image.repository |
fluentd image repository |
203.178.158.5:30500/wide-camp-1909/camp-dns-fluentd |
fluentd.image.tag |
fluentd image tag |
latest |
fluentd.image.pullPolicy |
Image pull policy | IfNotPresent |
fluentd.image.pullSecret |
Image pull secret for private registry | camp-reg |
fluentd.listen |
fluentd service endpoint IP |
203.178.158.40 |
kibana.image.repository |
kibana image repository |
kibana |
kibana.image.tag |
kibana image tag |
"7.3.1" |
kibana.image.pullPolicy |
Image pull policy | IfNotPresent |
kibana.listen |
kibana service endpoint IP |
203.178.158.41 |
Below are known issues of this project as of wide-camp-1909.
Currently, Kubernetes does not support Source IP with externalTrafficPolicy: Local when externalIPs are used.
In short, the unbound Pods cannot get clients' source (global) addresses since they are behind NAT.
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.