Pushing my leetcode solution daily. Have fun
54 - https://leetcode.com/problems/spiral-matrix/
125 - https://leetcode.com/problems/valid-palindrome/
https://leetcode.com/problems/count-odd-numbers-in-an-interval-range/
724 - https://leetcode.com/problems/find-pivot-index/?envType=study-plan&id=level-1
392 - https://leetcode.com/problems/is-subsequence/?envType=study-plan&id=level-1
21 Merge Two Sorted Lists - https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/description/?envType=study-plan&id=level-1
2 - Add Two Number - https://leetcode.com/problems/add-two-numbers/
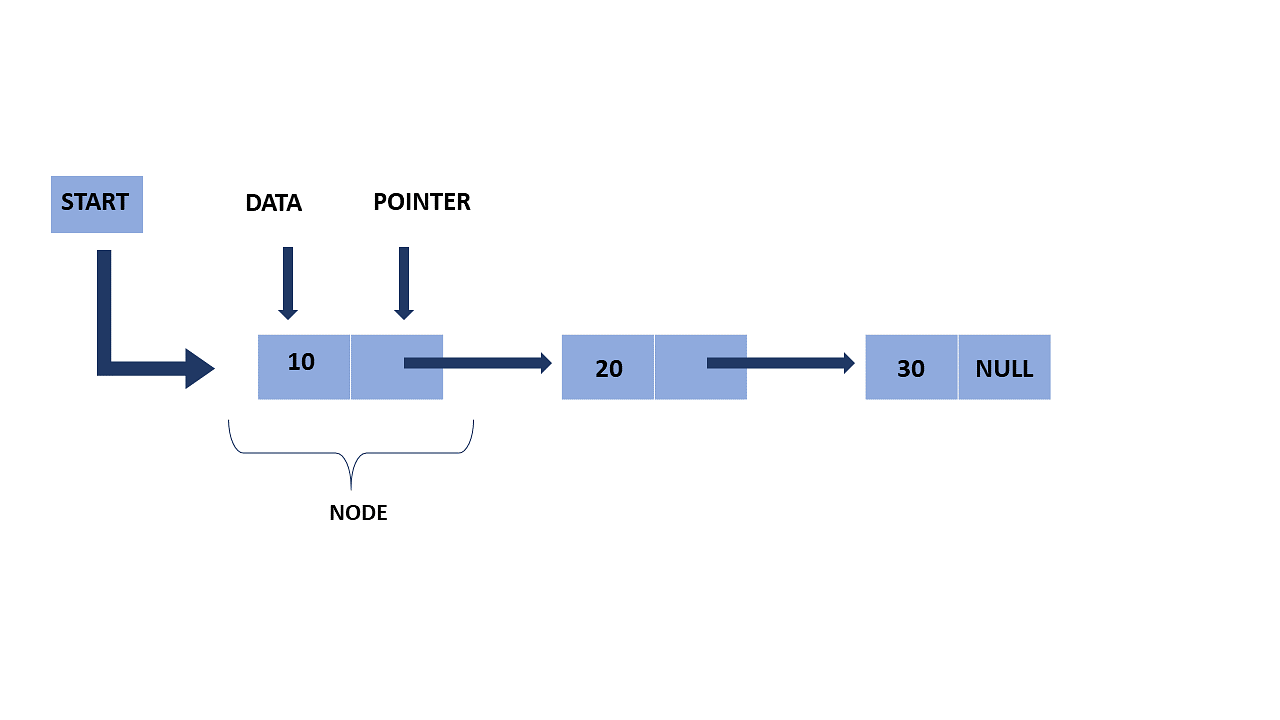
A linked list is the most sought-after data structure when it comes to handling dynamic data elements. A linked list consists of a data element known as a node. And each node consists of two fields: one field has data, and in the second field, the node has an address that keeps a reference to the next node.- What is a Linked List? A linked list is a linear data structure that stores a collection of data elements dynamically. Nodes represent those data elements, and links or pointers connect each node. Each node consists of two fields, the information stored in a linked list and a pointer that stores the address of its next node. The last node contains null in its second field because it will point to no node. A linked list can grow and shrink its size, as per the requirement. It does not waste memory space.
- Hashmap is a popular data structure used in many programming languages. It is a key-value pair data structure that allows for efficient insertion, deletion, and retrieval of values based on their associated keys.
- 1.What is a HashMap? A HashMap is a data structure that allows for the efficient storage and retrieval of key-value pairs. It is implemented as an array of linked lists, where each index of the array corresponds to a hash code generated from the key. The hash code is used to quickly locate the linked list that contains the key-value pair.
- 2.How does a HashMap work? When a key-value pair is added to a HashMap, the key is first hashed to generate an index into the array. If there are no collisions at that index, the key-value pair is added to the linked list at that index. If there are already key-value pairs in the linked list, the new pair is added to the end of the list. When retrieving a value from the HashMap, the key is hashed again to find the index, and then the linked list at that index is searched for the key.
- 3.What is the time complexity of operations in a HashMap? The time complexity of adding, retrieving, and deleting a key-value pair in a HashMap is O(1) on average. In the worst case, where all keys generate the same hash code and end up in the same linked list, the time complexity can be O(n), where n is the number of key-value pairs in the map.
- 4.How do you handle collisions in a HashMap? Collisions can occur when two or more keys generate the same hash code and end up in the same linked list. To handle collisions, each node in the linked list contains both the key and the value. When retrieving a value, the key is searched for in the linked list. When adding a new key-value pair, the new pair is added to the end of the linked list. HashMap handles collision by using a linked list to store map entries ended up in same array location or bucket location or use Chaining collision resolution
- It does not allow to store duplicate value
The stream method return you a stream
Pull requests are welcome. For major changes, please open an issue first to discuss what you would like to change.
Please make sure to update tests as appropriate.