A disciplined way to manage FluentMigration project and track change of stored procedures, sql function...
Install-Package DatabaseMigrateExt
When we use Fluent Migrator or even EF Migration, it will be very hard to check history of a sql function/stored procedure,
DatabaseMigrateExt can help you resolve the problem using ChangeScript/RefScript pattern.
That means sql function/ stored procedure will be keeped separately in each file (ref-script) and every times we want to change we will create a command (change-script) and point to ref-script, for example:
- We have a ref-script stored proc
dbo.GetProducts - Migration 01 - update
dbo.GetProductsand commit - Migration 02 - update
dbo.GetProductsand commit again - ...
By using source control like Git we know history of stored
dbo.GetProducts
Next, using RefScript/ChangeScript pattern means your stored dbo.GetProducts is only one file, so what happen if someday we want to re-run all migrations for a new empty database.
Normally this will cause a lot errors because file dbo.GetProducts is latest state, every times migrator runs it will apply the latest state of the stored procedure,
in above sample, Migration 01 and Migration 02 will call same file dbo.GetProducts.
There is a high possibility that migratior can not execute your stored procedure because some tables have not created yet.
To hanlde it, we will need to classify type of change-scripts by using ExtMigration Attributes, all migrations relate to schema like Create Database, Alter Column, Created Index, Function... should be run
before Stored Procedure alter migration. Then when you re-run, you will have newest tables, newest schema and Stored Procedure will work.
So that is what DatabaseMigrateExt does.
See Sample Project at https://github.com/minhhungit/DatabaseMigrateExt/tree/master/Samples
<add key="mgr:DatabaseKeys" value="MovieStore"/>
<add key="mgr:RootNamespace" value="DatabaseMigrateRunner.Migrations"/>
<add key="mgr:MovieStore_ConnString" value="Your_ConnectionString_For_MovieStore_At_Here"/>Note:
mgr:MovieStore_ConnString = 'mgr:' + [DatabaseKey] + '_ConnString'
Anytime you want to add new database, just need to add new database name into mgr:DatabaseKeys and add new connection key for it.
Make sure that name of DatabaseKey setting must match with ConnString setting.
For example:
<add key="mgr:DatabaseKeys" value="MovieStore, InventoryDb, MyNewDatabase"/>
<add key="mgr:MovieStore_ConnString" value="ConnectionString_For_MovieStore"/>
<add key="mgr:InventoryDb_ConnString" value="ConnectionString_For_InventoryDb"/>
<add key="mgr:MyNewDatabase_ConnString" value="ConnectionString_For_MyNewDatabase"/>Of course, you also need a child folder for that database to store migration scripts in Migrations folder, like InvenetoryDb and MovieStore folders (match name with DatabaseKey)
ExtMigration Attributes:
There are 2 attributes:
- Use
[ExtMgrDataStructureAndFunctions]for marking the migration as aSTRUCTURE, aDATAor aFUNCTIONtype. - Use
[ExtMgrStoredProcedures]for marking the migration as aSTORED PROCEDURE.
Note: System will just find migration scripts which used ExtMigration Attributes to apply, everything else will be skipped.
For example:
[ExtMgrDataStructureAndFunctions(2017, 9, 22, 02, 08, 01)]
public class InventoryDb_20170922_020801_inital_tables : ExtDataStructureFunctionMigration
{
public override void Up()
{
// do someting
}
public override void Down()
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}Migration structure: You can put migration classes in everywhere in your project as long as it is placed under availabel namespace.
For example: DatabaseMigrateRunner.Migrations.MovieStore
Remember that your ref-scripts must be placed fixed in folder @RefScript inside DatabaseKey folder. You can change children folders's name like DataAndStructure/Function/Stored like anything you want with these settings:
- mgr:SqlDataStructureRefScriptNamespace
- mgr:SqlFunctionRefScriptNamespace
- mgr:SqlStoredRefScriptNamespace
- mgr:SqlGeneralScriptRefScriptNamespace
Order of migrations: DatabaseMigrateExt will executes migration scripts with bellow order:
- Data, Structure or Function (version number start with 1000..., ex: 100020171021194001)
- Stored Procedure (version number start with 3000..., ex: 300020190908032101)
| Version | AppliedOn | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 100020171021194001 | 2020-03-24 16:42:18.000 | MovieStore_20171021_194001_inital_tables |
| 100020171022154501 | 2020-03-24 16:42:18.000 | MovieStore_20171022_154501_inital_function |
| 300020170807140103 | 2020-03-24 16:42:18.000 | MovieStore_20170807_140103_create_stored |
| 300020190908032101 | 2020-03-24 16:42:18.000 | MovieStore_20190908_032101_exec_script |
Ref-Script And Change-Script
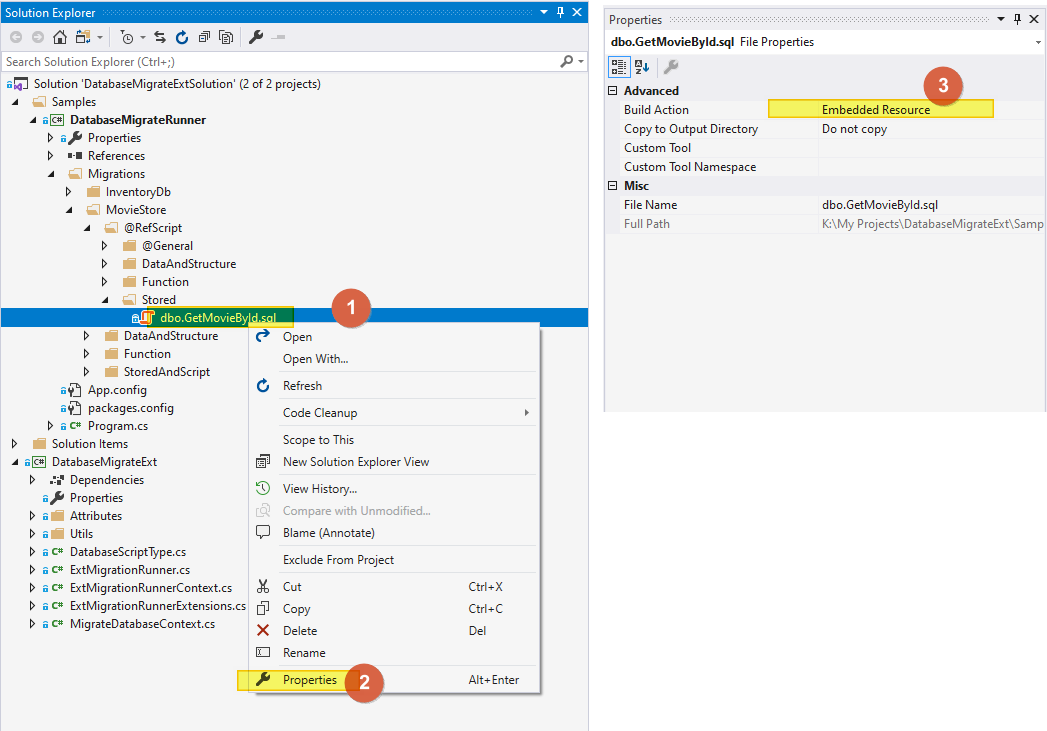
- Your sql scripts (can be strucuture/stored/funtion...) must be marked as 'Embedded Resource' - you normally just do this one time, after that just need to copy old file and rename - see bellow image 👇)
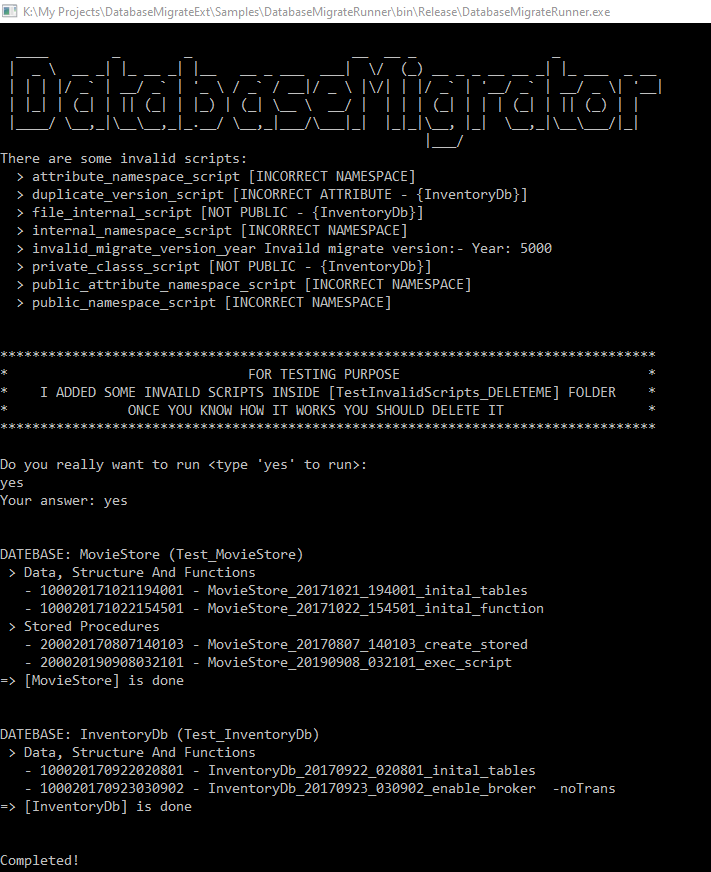
- DatabaseMigrateExt will find and show all invaild migration scripts when application starts, you should check them
- DatabaseMigrateExt will not execute invalid scripts
The idea of change script/ref script is from Nghia Nguyen aka my boss
Sample script:
using DatabaseMigrateExt;
namespace DatabaseMigrateRunner.Migrations.MovieStore
{
[ExtMgrDataStructureAndFunctions(2017, 9, 22, 02, 08, 01)]
public class SqlStructure_20170921_194001_inital_tables : ExtDataStructureFunctionMigration
{
public override void Up()
{
// do something here
}
....
}
}You also can define author on attribute, like this:
[ExtMgrDataStructureAndFunctions("Hung Vo", 2017, 9, 22, 02, 08, 01)]using DatabaseMigrateExt;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Run migration with default settings
ExtMigrationRunner
.Initialize()
.Process();
Console.WriteLine("Completed!");
Console.ReadKey();
}