Table of Contents
Documentation of steps taken to setup and use Visual Studio Code for development on a Mac environment
Below are the steps required, with some optional steps , to setup a working VSC environment. These step are typically only performed once.
- Download Visual Studio Code (VSC) from https://code.visualstudio.com/
- Once installed and started you will be welcomed by the
Welcomescreen
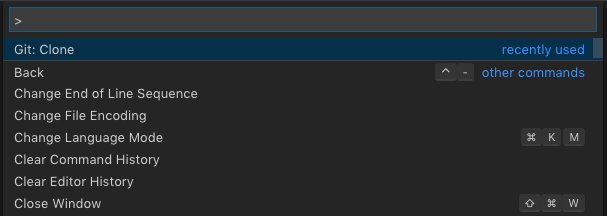
- Launch command prompt with keyboard shortcut
shift+cmd+p
- Inside the cmd prompt, enter the
Git: Clonecmd or select it from the dropdown list of common/recent cmds - This will prompt you for your
repo urle.g.https://github.com/leecardona/vscode-setup.git
- After you provide the url and hit enter, you will be presented with a download save dialog box asking you to designate where on your local machine you wish to place this local copy of the repo
- Once the repo is done downloading, VSC will prompt you on the lower right with post repo download action shorcuts, select
Open repositoryoption
- You should now be navigated to the source control management (SCM) tab in VSC. You can also manually select this tab by clicking on the SCM tab icon
Optional: This is an optional step but I found that VSC on Mac did not always detect file changes done on the local machine via the finder or if your repo is on a cloud drive like Google Drive or Dropbox. Creating a designated Workspace seems to address this issue. Typically a Workspace is used when you want to save the setup of you VSC working environment. For example, if your project is comprised of more than one repo folder or perhaps in addition to your primary repo folder you want to include some additional folders for quick access via the VSC file explorer tree.
- Ensure you're in the desired repo by selecting the
Explorertab
- You should see your repo and it's folder structure in the VSC Explorer
- from the File menu, select
Save Workspace As...
- You will be prompted with a local finder dropdown box to select where on your local machine you wish to save the workspace config file
- Once you have named and saved your workspace, note the updated VSC Explorer as it now will denote that the repo is saved as a
(WORKSPACE)
Optional: Git tags are used to denote key points in code development that signify a milestone, typically a release of some kind like a major or minor release version, or hotfix. Git hosting services like Github will detect tags and auto create releases for you with nice zipped file links for easy release downloading for end-users. VSC support plugins/extentions that add easy to use features to the user interface of VSC that can make activities like tagging easier to manage.
- Go to the VSC Marketplace to search and install available extentions. Enter the keyboard shortcut
cmd + pNote this brings up the quick actions dialog not the VSC cmd prompt - they are not the same.
-
Once presented with the actions dialog enter:
ext install git-tags. I thought this would install the extention but it did not. It only navigated me to the VSC Marketplace and filtered the search for tag related extentions, just be aware. -
You can also select the VSC Marketplace tab to manually navigate and then enter
tagsin the search box.
- From the result of tag related extentions select
git-tagby clicking on theinstallbutton for it.
Below are steps that are performed as part of using VSC on a normal iterative basis.
Commiting code updates is pretty straight forward in VSC as it should auto detect any changes to your local git repo. When it does, VSC will provide a visual indication by placing a badge over the SCM tab icon denoting how many changes it has deteced, like so:
- To commit changes select the SCM tab and you be presented with the commit box as shown below:
- To locally commit your changes simply enter a commit message in the provided box and then click on the
Check Markabove the message box:
- Once your changes have been commited you are able to push or sync your changes with the remote repo or perform other actions by selecting the
More actionsicon, represented by an elipse icon:
- This will result in the actions dropdown dialog appearing. From here simply select the git action you wish to perform for this commit, e.g. push, pull, sync, other...
- To manage tags using the git-tag extention simply navigate to the SCM tab:
- Select the
More actionsicon:
- To add a tag to the current commit, select
Create tagfrom the dropdown menu:
- This will result in a create tag input dialog box opening:
- Enter your desired tag value and press enter. You will then be prompted for syncing your remote repo with this tag at this time or not. Normally select
Yesto complete this operation.
- Git-tag extention also allows to quickly view all your tags and even delete them if you so desire. To view your tags navigate to the SCM tab:
- Select the
More actionsicon:
- To view your tags, select
List tagsfrom the dropdown menu:
- This will result in a tags list window opening as shown below:
- From here you can view all your tags as well as
DELETEany you wish to remove
- Creating branches in VSC is pretty easy and is done via the branch switching dialog. To bring up the branch switching dialog click on the current banch indicator at the bottom left of VSC screen:
- This will result in the branch switching dialog as shown below:
- From here simply click on the
+ Create new branchoption and you'll be presented with an input box to enter your desired branch name:
- VSC also automatically switches you to the new branch once created. You can verify this by noting the current branch indicator at the lower left of the VSC screen:
- After the new branch is created be sure to update the remote repo by publishing this change. Simply click the update cloud icon to the right of the current branch indicator to update the remote repo with the new branch:
- Switching branches in VSC is pretty easy and is done via the branch switching dialog. To bring up the branch switching dialog click on the current banch indicator at the bottom left of VSC screen:
- This will result in the branch switching dialog as shown below:
- From here simply select the desired branch from the list of available branches and VSC will automatically switch you to that branch
- Merging branches to pretty straight forward as well. First ensure you are in the
targetbranch you want to update, not thesourcebranch with the new code and/or files . You can check the current banch by looking at the current branch indicator at the bottom left of VSC screen:
- To initiate a merge use the keyboard shortcut combination
shift+cmd+pto bring up the VSC command prompt:
- Inside the cmd prompt, enter the
Git: Merge Branchcmd or select it from the dropdown list of common/recent cmds. This will result in theSelect a branch to merge fromdialog appearing.
- Select your
sourcebranch from the list of available branches to update thetargetbranch you are currently in.
- To delete a branch in VSC you have to first ensure you are not currently in the branch you wish to delete or you wont be able to select it for deletion. You can check the current banch by looking at the current branch indicator at the bottom left of VSC screen:
- Once you're sure your not in the branch you wish to delete, enter the keyboard shortcut combination
shift+cmd+pto bring up the VSC command prompt:
- Inside the cmd prompt, enter the
Git: Delete Branchcmd or select it from the dropdown list of common/recent cmds. This will result in theSelect a branch to deletedialog appearing.
- Select the branch from the list of available branches you wish to delete.
I welcome and appreciate community contributions. If you have an idea or a question I'd love to hear from you! The easiest ways to contribute is by forking this repo followed by a pull request or raising an issues in this repo's Github.
Copyright 2018 Lee Cardona. @leecardona
The documentation is provided under Apache License 2.0. Contributions to this project are accepted under the same license.