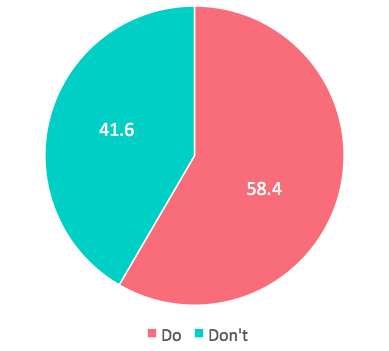
We are ethical hackers. The goal of this project was not to exploit vulnerabilities in the Android apps we analyzed but to determine whether unauthorized access or other malicious activities were possible. This software is not intended for use in any unethical, illicit, or malicious way. If you choose to do so, it is at your own risk and the penalty of the law. >:(
In fact, we even notified people about the security vulnerabilities we found:
Apekit is a pipeline of python tools and modules that downloads a large number of Android apps, decompiles them from APK back to Java source code, then performs static analysis on the source code to detected potential security vulnerabilities. Apekit was built by students at Boston University as a final project for EC521 Cyber Security. Feel free to contribute and improve!
| Module | Description |
|---|---|
| backend | peewee ORM interface to a sqlite database that holds metadata and vulnerability results. |
| crawler | Randomly samples Android apps from the 10-31-2014 snapshot of the Android marketplace on Archive.org. Archive.org deployed PlayDrone in October 2014 to capture 1.4M free apps. |
| androguard | (not in this repo) We use the Androguard decompiler for recovering the source code from each of the apks we sample. Just clone their repo directly into your project to use it. |
| vulns | Modules for testing each of the vulnerabilities listed below. |
| charting | Makes some pretty plots of the results. |
- Clone us!
git clone https://github.com/ksparakis/apekit apekit
cd apekit- Create a virtual environment
virtualenv venv- Install the necessary dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt- Clone Androguard
git clone https://github.com/androguard/androguard androguard- Start downloading apps!
nohup python -u crawl.py &- Decompile and analyze the apps you downloaded
nohup python -u apekit.py &- Gawk at some pretty charts with the results
Use of HTTP instead of HTTPS
Many developers use HTTP instead of HTTPS for communication with APIs. This makes it easy for atttackers to eavesdrop on potentially sensitive communication such as user authentication or monetary transactions.
API and Security Keys in Source Code
Secret keys are used to access a variety of APIs and services. Amazon Web Services, Facebook, Twitter, and Google all rely on secret keys for authentication. Secret keys are meant to be SECRET and should not be present in the source code of an application.
Comments Not Removed from Source Code
Comments can reveal the intended behavior of an app's source code to attackers. This makes it easier for attackers to reverse engineer those applications and steal intellectual property.
A Selection of Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE)
CVE is a dictionary of publicly known information security vulnerabilities and exposures. CVE’s common identifiers enable data exchange between security products and provide a baseline for evaluating security tools and services.
We selected CVE Android vulnerabilities that were easy to identify using static analysis.
| Vulnerability | Description |
|---|---|
| CVE-2014-8610 | AndroidManifest.xml in Android before 5.0.0 does not require the SEND_SMS permission for the SmsReceiver receiver, which allows attackers to send stored SMS messages, and consequently transmit arbitrary new draft SMS messages or trigger additional per-message charges from a network operator for old messages, via a crafted application that broadcasts an intent with the com.android.mms.transaction.MESSAGE_SENT action, aka Bug 17671795. |
| CVE-2014-8507 | Multiple SQL injection vulnerabilities in the queryLastApp method in packages/WAPPushManager/src/com/android/smspush/WapPushManager.java in the WAPPushManager module in Android before 5.0.0 allow remote attackers to execute arbitrary SQL commands, and consequently launch an activity or service, via the (1) wapAppId or (2) contentType field of a PDU for a malformed WAPPush message, aka Bug 17969135. |
| CVE-2014-7911 | luni/src/main/java/java/io/ObjectInputStream.java in the java.io.ObjectInputStream implementation in Android before 5.0.0 does not verify that deserialization will result in an object that met the requirements for serialization, which allows attackers to execute arbitrary code via a crafted finalize method for a serialized object in an ArrayMap Parcel within an intent sent to system_service, as demonstrated by the finalize method of android.os.BinderProxy, aka Bug 15874291. |
| CVE-2012-4222 | drivers/gpu/msm/kgsl.c in the Qualcomm Innovation Center (QuIC) Graphics KGSL kernel-mode driver for Android 2.3 through 4.2 allows attackers to cause a denial of service (NULL pointer dereference) via an application that uses crafted arguments in a local kgsl_ioctl call. |
| CVE-2011-4276 | The Bluetooth service (com/android/phone/BluetoothHeadsetService.java) in Android 2.3 before 2.3.6 allows remote attackers within Bluetooth range to obtain contact data via an AT phonebook transfer. |
| CVE-2011-3874 | Stack-based buffer overflow in libsysutils in Android 2.2.x through 2.2.2 and 2.3.x through 2.3.6 allows user-assisted remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via an application that calls the FrameworkListener::dispatchCommand method with the wrong number of arguments, as demonstrated by zergRush to trigger a use-after-free error. |
| CVE-2013-2597 | The acdb audio driver provides an ioctl system call interface to user space clients for communication. When processing arguments passed to the ioctl handler, a user space supplied size is used to copy as many bytes from user space to a local stack buffer without proper bounds checking. An application with access to the /dev/msm_acdb device file (audio or system group) can use this flaw to, e.g., elevate privileges. |
| CVE-2014-3100 | Stack-based buffer overflow in the encode_key function in /system/bin/keystore in the KeyStore service in Android 4.3 allows attackers to execute arbitrary code, and consequently obtain sensitive key information or bypass intended restrictions on cryptographic operations, via a long key name. |
| Google bug 13678484 | The software does not properly validate an application's certificate chain. An application can supply a specially crafted application identity certificate to impersonate a privileged application and gain access to vendor-specific device administration extensions. The vulnerability resides in the createChain() and findCert() functions of the Android JarUtils class. [securitytracker-1030654] Google bug 13678484 [blackhat-briefing-fakeid] |
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Igor DePaula | igorp@bu.edu |
| Carlton Duffett | cduffett@bu.edu |
| Zach Lister | zlister@bu.edu |
| Petar Ojdrovic | pojdrov@bu.edu |
| Luke Sorenson | lasoren@bu.edu |
| Konstantino Sparakis | sparakis@bu.edu |
Copyright 2015. Code released under the Apache 2.0 license.
Don't make us go apekit...