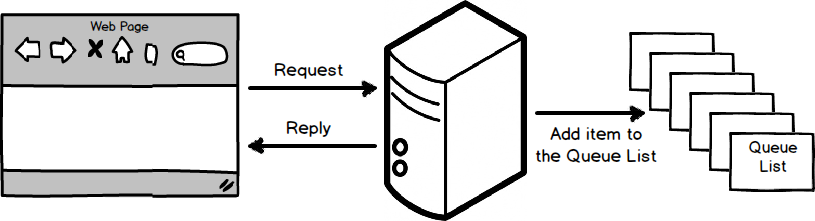
#An example of a Queue System in PHP Optimise the performances of a server for a better user experience is always an important factor. Sometimes users have to wait for an answer from the server because of long processes that are happening all at once in the back end. In order to avoid this is important to consider that not all of them have to be executed at the same time before the server replies to each request. Certainly we can postpone some of them, especially the ones that have job tasks with longer loading time, and put them on hold into a processes queue list that will be executed later on.
The Queue List can be executed whenever we think it's better for the web site. For example it could be at night if the tasks require long time and we'd like to affect as less users as possible in case the website performances slow down.
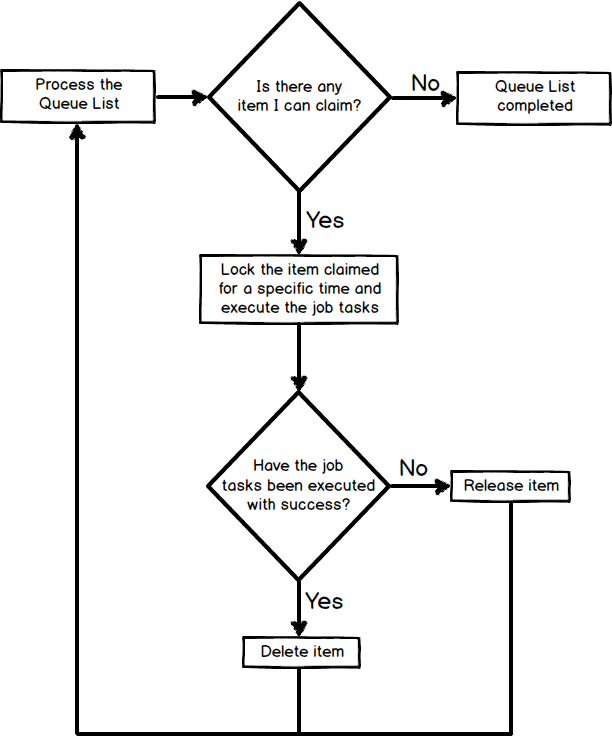
The structure of a workflow that represents the execution of a queue list looks like the following:
Translating in PHP code the above flowchart we'll get something like this:
<?php
/**
* Example of a Queue System.
*/
function queue_system_example() {
require_once(dirname(__FILE__) . '/lib/QueueClass.php');
$queue = new QueueClass();
// Populate the queue.
for ($i = 0; $i < 100; $i++) {
$data = range(0, $i + 1);
$queue->createItem($data);
}
$jobs_to_do = TRUE;
$start = microtime(true);
try {
while ($jobs_to_do) {
$item = $queue->claimItem();
if ($item) {
echo 'Processing the item ' . $item->item_id . '...' . PHP_EOL;
// Execute the job task in a different function.
if (execute_the_job_task($item)) {
// Delete the item.
$queue->deleteItem($item);
echo 'Item ' . $item->item_id . ' processed.' . PHP_EOL;
}
else {
// Release the item to execute the job task again later.
$queue->releaseItem($item);
echo 'Item ' . $item->item_id . ' NOT processed.' . PHP_EOL;
$jobs_to_do = FALSE;
echo 'Queue not completed. Job task not executed.' . PHP_EOL;
}
}
else {
$jobs_to_do = FALSE;
$time_elapsed = microtime(true) - $start;
$number_of_items = $queue->numberOfItems();
if ($number_of_items == 0) {
echo 'Queue completed in ' . $time_elapsed . ' seconds.' . PHP_EOL;
}
else {
echo 'Queue not completed, there are ' . $number_of_items . ' items left.' . PHP_EOL;
}
}
}
}
catch (Exception $e) {
echo $e->getMessage();
}
}
/**
* Execute the job task.
*/
function execute_the_job_task($item) {
// Do something with the item.
return TRUE;
}
For this example the QueueClass created and used is:
<?php
/**
* @file
* QueueClass Class.
*/
/**
* Static queue implementation.
*/
class QueueClass {
/**
* The queue data.
*
* @var array
*/
protected $queue;
/**
* Counter for item ids.
*
* @var int
*/
protected $id_sequence;
/**
* Start working with a queue.
*/
public function __construct() {
$this->queue = array();
$this->id_sequence = 0;
}
/**
* Add a queue item and store it directly to the queue.
*/
public function createItem($data) {
$item = new stdClass();
$item->item_id = $this->id_sequence++;
$item->data = $data;
$item->created = time();
$item->expire = 0;
$this->queue[$item->item_id] = $item;
}
/**
* Retrieve the number of items in the queue.
*/
public function numberOfItems() {
return count($this->queue);
}
/**
* Claim an item of the queue for a specific time.
*/
public function claimItem($lease_time = 3600) {
foreach ($this->queue as $key => $item) {
if ($item->expire == 0) {
$item->expire = time() + $lease_time;
$this->queue[$key] = $item;
return $item;
}
}
return FALSE;
}
/**
* Delete a finished item from the queue.
*/
public function deleteItem($item) {
unset($this->queue[$item->item_id]);
}
/**
* Release an item that the worker could not process, so another
* worker can come in and process it before the timeout expires.
*/
public function releaseItem($item) {
if (isset($this->queue[$item->item_id]) && $this->queue[$item->item_id]->expire != 0) {
$this->queue[$item->item_id]->expire = 0;
return TRUE;
}
return FALSE;
}
/**
* Create a queue.
*/
public function createQueue() {
// Nothing needed here.
}
/**
* Delete a queue.
*/
public function deleteQueue() {
$this->queue = array();
$this->id_sequence = 0;
}
}
This queue class (that implements the interface DrupalQueueInterface) is useful for static implementation, for a dynamic implementation instead is necessary to store the queue list in a database.
The full example could be found here.