This is a sample application to demonstrate how you can combine Hosuto and YaNco to build a reliable and scaleable service with SAP backend integration.
Beside of cloning this repo please consider following requirements:
-
Visual Studio 2019
It is strongly recommended to use at least Visual Studio 2019 16.8.4 to build/run the applications.
If you would like to try the docker or azure integration also the docker/azure tools have to be installed. -
.NET SDK 8.0 (x64)
If you have no Visual Studio installed you will need at least a standalone .NET 8.0 SDK. You can obtain the .NET SDK 8.0 x64 from here:
https://dotnet.microsoft.com/en-us/download/dotnet/8.0 -
SAP RFC SDK
Please note that to build and run this project you have to download the SAP Netweaver RFC SDK from the SAP Support Portal. We recommend to use the Setup Script to download the SDK.See the requirements section of YaNco how to obtain the SDK manually:
https://github.com/dbosoft/YaNco#platforms--prerequisites
You have to download both the Windows_X64 and Linux_x64 Netweaver RFC SDK binaries. Copy them to repos nwrfcsdk directory. -
Azure account
To run only locally no azure account is required. However to scale out API module with CosmosDB or to use Azure Service Bus or Azure Storage account you require a azure account (free accounts available for dev purposes).
This sample uses Hosuto for building microservices that can be either combined in one process or run standalone.
So the application can be either be fully distributed (and scaled) or run as a single process.
Hosuto calls the implementation part Module, and the host of modules ModulesHost. We will here use App as name for the application that runs the ModulesHost.
For getting started with SAPHub we recommend to run the automatic setup script after cloning this repository.
git clone https://github.com/dbosoft/SAPHub.git
cd SAPHub
PowerShell -Command .\setup.ps1The script will guide you through the steps to download the SAP NW RFC SDK and to configure the connection to the SAP System.
This video shows how to use the script: https://youtu.be/FG2KOWbJ42c
Update: Due to changes SAP has made to the logon process, it is no longer possible to download the SDK automatically with the setup script. The script has been updated to guide you through the download but the video is outdated for this part.
The SAPHub comes with 4 pre-build applications.
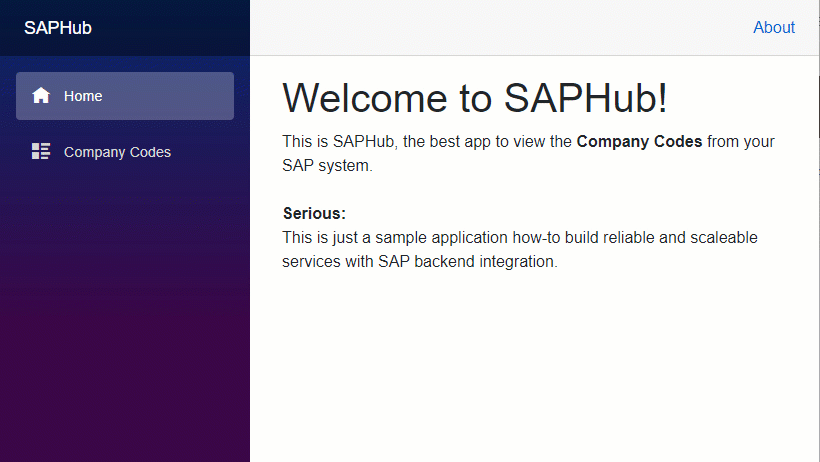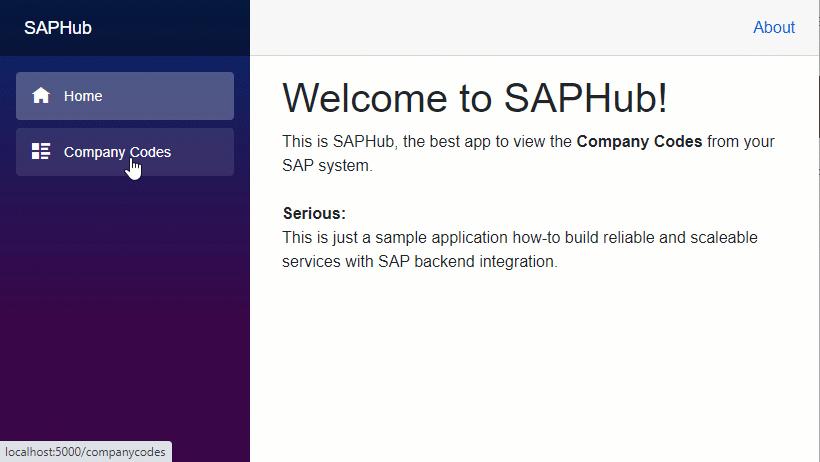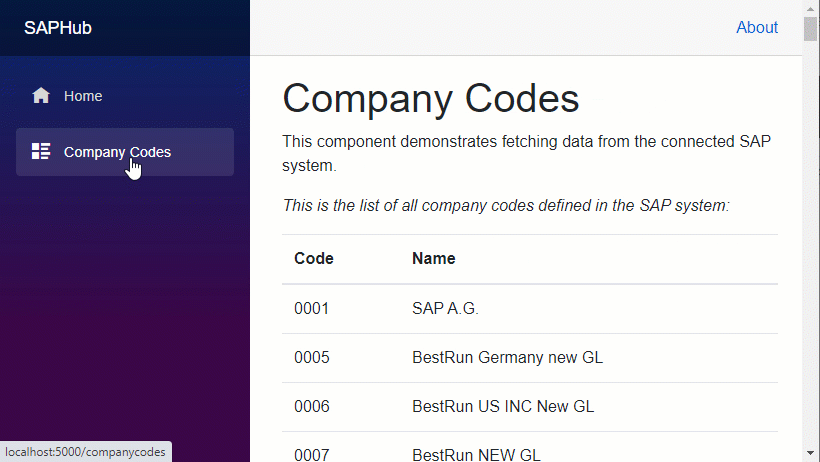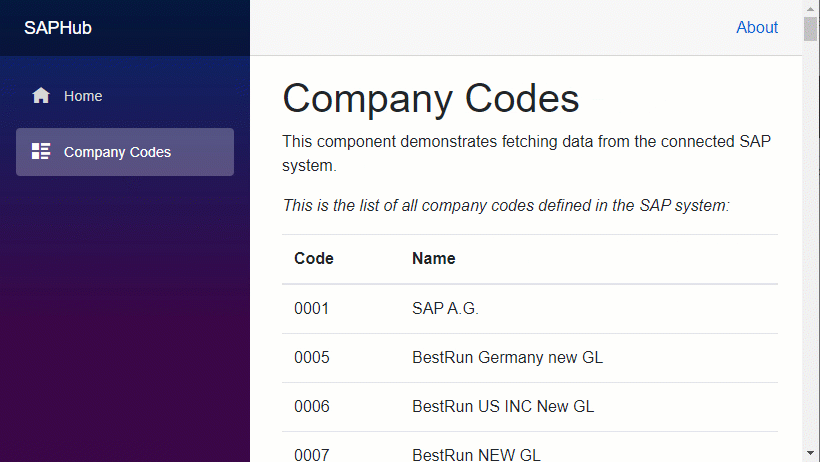
They can be used to read a SAP systems company codes (if this is not exciting enough for you just imagine that you could also place a sales order instead).
This is the "all-in-one" server, that runs the UI Module, API Module and SAP Connector Module in one process.
It requires no additional message exchange system and runs as a console app (only Windows).
Quickstart:
After running the setup script (see Quickstart you can run script Start-SAPHubServer to build and run this app.
To run this application from Visual Studio first configure the SAP connection settings in your user secrets (see below) on project SAPHub.Server.
Then start SAPHub.Server project - a browser should be opened automatically on http://localhost:5000 where you can see the UI.
For swagger UI open http://localhost:5000/api/swagger.
The API Endpoint runs only the API Module in a aspnetcore environment. You can host it in a container or on a hyperscaler like AWS/Azure. To communicate with the SAP Connector Module it requires a message exchange system to be set up. To scale horizontally you have to set up a Cosmos DB (see below).
Quickstart:
You can start this app together with SAPHub.Connector and RabbitMq as message exchange using docker compose. See Quickstart for SAPHub.SAPConnector.
For other setups please check configuration section below.
The SAPConnector Service runs only the SAPConnector Module. It can run separated from all other components and needs only network access to the message exchange and to the SAP system. To communicate with the API Module it requires a message exchange to be set up (see below).
Quickstart:
You can start this app together with SAPHub.UI, SAPHub.ApiEndpoint and RabbitMq as message exchange using docker compose.
- Configure the SAP connection settings in your user secrets (see below) on project SAPHub.SAPConnector.
- Open a command prompt in project directory.
- Run command
docker-compose up.
This will automatically start docker containers running rabbitmq, SAPHub.ApiEndpoint and SAPHub.SAPConnector.
For other setups please check configuration section below.
The standalone UI application is work-in-progress. It can be started, but will not work in docker currently. Please check later again.
The UI module implements a Blazor based application that demonstrates how the API could be used to request data asynchronously from the SAP System.
Scaling
The UI module can be scaled freely. However you have to consider CORS and load balancing the endpoint address for users and the API endpoint addresses.
Therefore, if you scale out the UI, place it behind a load balancer and configure endpoint addresses to the load balancer.
The sample provides a REST API to read company code records from the SAP backend asynchronously.
Requests / Responses
A request of /companycode will not directly return the company code data, but responds with a Operation record. The record contains the operation id.
This operation id can be used to query the status of operation on /operation/<operationId>.
Query response:
{
"id": "49d017f5-4a1b-4d32-aee2-5986daa7f211",
"status":0
}Once it is finished the data can be requested with /companycode/result/<operationId>
Message Flow
- For each request the API module first creates a record for the operation in it's state store.
- Then it sends the operation to the SAP Connector queue for processing.
- When a SAP Connector reports status change events, it updates the state of operation in it's state store.
Scaling
To scale the API Module horizontally you have to enable the cosmos db storage.
Reason: when a SAP Connector sends a status event update only one API Endpoint will process the changes and update it's state store. Therefore all API Module instances have to use the same state store.
Also you have to place it behind a load balancer and configure endpoint addresses to the load balancer.
The SAP connector module will be used to establish the connection to the SAP system. For development we used our internal ERP EHP 8 IDES system, but it should work with almost any ERP or S/4 system.
Message Flow
- For each operation recieved the SAP Connector will establish a connection to the SAP system to retrieve the data (2 requests max. in parallel).
- Then it sends a operation update event with result or error state.
Scaling
The SAP Connector can be scaled freely.
Keep in mind that each SAP Connector will use up to 3 connections (2 processors, 1 for metadata) at same time to backend, so do not overload the backend SAP system with to many connectors.
The apps are configured by .NET configuration settings. Following methods for setting the config are supported:
-
User Secrets
This is the prefered method, as it will automatically be used in Visual Studio and containers. -
Environment Variables
You can also use environment variables prefixed with SAPHUB_ to set configuration settings. For example the bus type:SAPHUB_BUS__TYPE=rabbitmq
The following settings are required/supported in the apps:
-
SAPHub.Server:
- SAP Connection (required)
- Message Exchange (optional)
- Data Exchange (optional)
- CosmosDb (optional)
- URL endpoints (optional)
-
SAPHub.ApiEndpoint:
- Message Exchange (required)
- Data Exchange (required)
- CosmosDb (optional, required to scale)
- URL endpoints (required)
-
SAPHub.UI:
- URL endpoints (required)
-
SAPHub.SAPConnector:
- Message Exchange (required)
- Data Exchange (required)
- SAP Connection (required)
To configure where the UI module can find the API and to enable CORS from the UI module you have to configure these URLs in both modules.
-
endpoints::default
This is the default (base) url that will be used if a relative path is defined, or path is not definied. -
endpoints::api
URL of API endpoint -
endpoints::ui
URL of UI
This is the default configuration of SAPHub.Server:
{
"endpoints": {
"default": "http://localhost:5000",
"api": "http://localhost:5000/api"
}
}For the SAP Connector Module you have to configure the SAP connection.
Configuration:
{
"saprfc": {
"ashost": "<your SAP system hostname>",
"sysnr": "<SAP system No>",
"client": "<SAP Client No>",
"user": "<UserName>",
"passwd": "<Password>",
"lang": "EN"
}
}The API Module and the SAP Connector module communicate asynchronously via a message exchange. The following messages exchanges are supported:
-
In-Memory
Supports only the communication between modules hosted in same process.The in-memory exchange is automatically used in the SAPHub.Server app and only makes sense if you run one single instance of SAPHub.Server.
Configuration:
{ "bus" : { "type" : "inmemory" } } -
Azure Storage Account
Uses Azure Storage Account Queues as message exchange.Configuration:
{ "bus" : { "type" : "azurestorage", "connectionstring": "" } } -
Azure Service Bus
Uses a Azure Service Bus as message exchange.Configuration:
{ "bus" : { "type" : "azureservicebus", "connectionstring": "" } } -
RabbitMq
Uses RabbitMq as message exchange.Configuration:
{ "bus" : { "type" : "rabbitmq", "connectionstring": "" } }
To transfer large data (results) between the API module and the SAP connector a data exchange is required. The following data exchanges are supported:
-
In-Memory
Supports only the communication between modules hosted in same process.The in-memory exchange is automatically used in the SAPHub.Server app and only makes sense if you run one single instance of SAPHub.Server.
Configuration:
{ "databus" : { "type" : "inmemory" } } -
Azure Storage Account
Uses Azure Storage Account Blobs as data exchange.Configuration:
{ "databus" : { "type" : "azurestorage", "connectionstring": "", "container": "saphub" } } -
File System
Uses a path on the filesystem as data exchange (makes only sense if SAP Connector and API Module could access the path.Configuration:
{ "databus" : { "type" : "filesystem", "path": "\\\\somehost\\some_share" } }
To scale out the API Module (by starting multiple SAPHub.APIEndpoint or SAPHub.Server apps) you have to enable the Azure Cosmos DB as shared DB storage for the API endpoints.
Please note that you can also use the CosmosDB emulator to run this locally.
Configuration:
{ "cosmosdb" : { "databaseName" : "<your_db_name>", "connectionstring": "" } }
Even if this is only a sample implementation we will continue to maintain it as reference architecture. You are welcome to contribute enhancements or to report issues.
The code of this sample is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details. Feel free to use it in any application.
SAP, Netweaver are trademarks of SAP SE