See Amazon.de or Amazon.com for more information. The price is about 12$ or 16€
- GPS Smart Antenna VK-172 NEW USB GPS Receiver Ublox7 for PC laptop Windows AU
- Support NMEA 0183 and ublox binary protocol
- Chip:U-Blox (G-7020)
- C / A code, 1.023 yards stream
- Receive frequency: L1 [1575.42MHz]
- Receive Channel: 56CH
- Support DGPS [WAAS,EGNOS & MSAS]
- Positioning performance
- Less than 2.5m [Autonomous][50%]
- Rate : Less than 0.02m/s
- Direction: Less than 0.5 Degrees
- Timing accuracy:1us
- Reference coordinate system:WGS-84
- Max Altitude:18000 m
- Max Speed :500 m/s
- Acceleration: Less than 4g
- Electrical properties
- Other parameters
- Tracking sensitivity: -162 dBm
- Standard clock pulse : 0.25Hz ~1 KHz
- Acquisition Sensitivity: -160dBm
- Positioning update rate :1Hz ~ 5Hz (Default 1Hz)
- Acquisition time (average)
- USB port interface
- Cold Start: 29seconds
- Data Rate: 9600bps
- Warm Start: 28seconds
- Operating temperature : -30 Celsius ~ +85 Celsius
- Hot Start: 1 seconds
- AGPS :3 seconds
- Tested on Ubuntu 18.04.5 LTS.
- Plug USB GPS dongle into your linux server
- git clone https://github.com/bohnelang/gps_ntp_timeserver.git
- cd gps_ntp_timeserver
- chmod 755 ./make_all.sh
- ./make_all.sh
-
Best place for receiving the GPS signal is outside the house. I use a water proof glass jar.

-
Further I use a USB ribbon cable to go through the windows frame from inside to outside.

Type on bash dmesg and look for u-blox
[176233.876141] usb 1-3.1: new full-speed USB device number 18 using ehci-pci
[176233.985443] usb 1-3.1: New USB device found, idVendor=1546, idProduct=01a7
[176233.985456] usb 1-3.1: New USB device strings: Mfr=1, Product=2, SerialNumber=0
[176233.985465] usb 1-3.1: Product: u-blox 7 - GPS/GNSS Receiver
[176233.985474] usb 1-3.1: Manufacturer: u-blox AG - www.u-blox.com
[176233.986584] cdc_acm 1-3.1:1.0: ttyACM0: USB ACM device
or lsusb and look for u-blox
Bus 001 Device 018: ID 1546:01a7 U-Blox AG
Enter the cgps as root in a bash
You could see something like this:
x Time: 2021-03-04T07:58:15.000Z xxPRN: Elev: Azim: SNR: Used: x
x Latitude: 49.20894250 N xx 5 44 211 25 Y x
x Longitude: 8.35006849 E xx 7 13 068 28 Y x
x Altitude: 148.600 m xx 8 11 035 20 Y x
x Speed: 0.05 kph xx 13 75 304 26 Y x
x Heading: 0.0 deg (true) xx 14 57 113 31 Y x
x Climb: 0.00 m/minn xx 15 38 297 34 Y x
x Status: 3D0FIX (5 secs) xx 18 11 302 30 Y x
x Longitude Err: +/- 7 m xx 20 08 327 23 Y x
x Latitude Err: +/- 11 m xx 23 07 327 25 Y x
x Altitude Err: +/- 28 m xx 24 10 253 25 Y x
x Course Err: n/a xx 28 56 123 42 Y x
x Speed Err: n/a xx 30 48 067 42 Y x
x Time offset: 0.078 xx x
x Grid Square: JN49hv xx x
You can use this command on bash:
watch ntpq -p
You can see something like this:
remote refid st t when poll reach delay offset jitter
==============================================================================
*SHM(0) .GPS. 0 l 14 16 377 0.000 -0.284 1.638
LOCAL(0) .LOCL. 12 l - 16 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
START_DAEMON="true"
USBAUTO="true"
DEVICES="/dev/ttyACM0"
GPSD_OPTIONS="-n"
and /etc/systemd/system/sockets.target.wants/gpsd.socket (with only IPv4 enabeld)
[Unit]
Description=GPS (Global Positioning System) Daemon Sockets
[Install]
WantedBy=sockets.target
[Socket]
ListenStream=/var/run/gpsd.sock
SocketMode=0600
ListenStream=127.0.0.1:2947
driftfile /var/lib/ntp/ntp.drift
logfile /var/log/ntp.log
leapfile /usr/share/zoneinfo/leap-seconds.list
statistics loopstats peerstats clockstats
filegen loopstats file loopstats type day enable
filegen peerstats file peerstats type day enable
filegen clockstats file clockstats type day enable
#pool 0.de.pool.ntp.org iburst minpoll 5 maxpoll 5
#pool 1.de.pool.ntp.org iburst minpoll 5 maxpoll 5
#pool 2.de.pool.ntp.org iburst minpoll 5 maxpoll 5
#pool 3.de.pool.ntp.org iburst minpoll 5 maxpoll 5
#pool de.pool.ntp.org iburst minpoll 10 maxpoll 10
restrict source notrap nomodify noquery
restrict -4 default kod notrap nomodify nopeer noquery notrust
restrict -6 default kod notrap nomodify nopeer noquery notrust
restrict 10.0.0.0 mask 255.0.0.0 nomodify noquery
restrict 172.16.0.0 mask 255.240.0.0 nomodify noquery
restrict 169.254.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0 nomodify noquery
restrict 192.168.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0 nomodify noquery
restrict 127.0.0.0 mask 255.0.0.0 nomodify noquery
restrict 192.0.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0 ignore
restrict 192.0.0.0 mask 255.255.255.248 ignore
restrict 240.0.0.0 mask 240.0.0.0 ignore
restrict 0.0.0.0 mask 255.0.0.0 ignore
restrict 127.0.0.1
restrict ::1
broadcast 192.168.0.255 autokey ttl 3
broadcast 224.0.1.1 autokey ttl 3
broadcast 169.254.255.255 autokey ttl 3
multicastclient 224.0.1.1
disable auth
enable bclient
manycastclient 224.0.1.1
manycastserver 224.0.1.1
#see http://doc.ntp.org/4.2.6/refclock.html
server 127.127.28.0 minpoll 4 maxpoll 4 prefer
fudge 127.127.28.0 time1 0.063 refid GPS
server 127.127.1.0 minpoll 4 maxpoll 4
fudge 127.127.1.0 stratum 12
- Do not be confused by NTP communications IPs (127.127.28.x and 127.127.1.x) - this is NOT localhost.
- This configuration do not use PPS (pulse per second) interface of linux & GPS dongle .
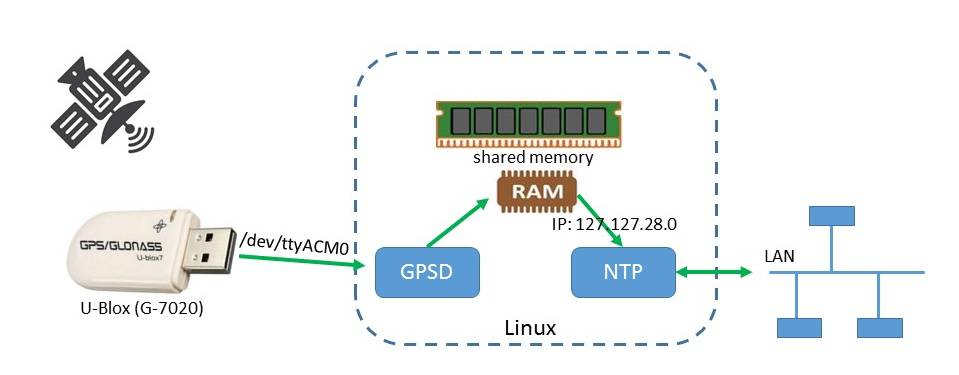
We can use the IP 127.127.28.0 for the 1th USB-device that pushed its data to the shared memory. The NTP configuration lines for this are:
server 127.127.28.0 minpoll 4 maxpoll 4 prefer
fudge 127.127.28.0 time1 0.07 refid GPS
Second we can use the local hardware clock of the server as a fallback (with very low priotity). This device can be found at IP 127.127.1.0. The NTP configuration lines for this are:
server 127.127.1.0 minpoll 4 maxpoll 4
fudge 127.127.1.0 stratum 12
Shared memory IP: 127.127.<TYPE>.<DeviceNo>
- Type 1 Undisciplined Local Clock (LOCAL) <----#####
- Type 2 Trak 8820 GPS Receiver (GPS_TRAK)
- Type 3 PSTI/Traconex 1020 WWV/WWVH Receiver (WWV_PST)
- Type 4 Spectracom WWVB/GPS Receivers (WWVB_SPEC)
- Type 5 TrueTime GPS/GOES/OMEGA Receivers (TRUETIME)
- Type 6 IRIG Audio Decoder (IRIG_AUDIO)
- Type 7 Radio CHU Audio Demodulator/Decoder (CHU)
- Type 8 Generic Reference Driver (PARSE)
- Type 9 Magnavox MX4200 GPS Receiver (GPS_MX4200)
- Type 10 Austron 2200A/2201A GPS Receivers (GPS_AS2201)
- Type 11 Arbiter 1088A/B GPS Receiver (GPS_ARBITER)
- Type 12 KSI/Odetics TPRO/S IRIG Interface (IRIG_TPRO)
- Type 13 Leitch CSD 5300 Master Clock Controller (ATOM_LEITCH)
- Type 14 EES M201 MSF Receiver (MSF_EES)
- Type 15 reserved
- Type 16 Bancomm GPS/IRIG Receiver (GPS_BANCOMM)
- Type 17 Datum Precision Time System (GPS_DATUM)
- Type 18 NIST/USNO/PTB Modem Time Services (ACTS_MODEM)
- Type 19 Heath WWV/WWVH Receiver (WWV_HEATH)
- Type 20 Generic NMEA GPS Receiver (NMEA)
- Type 21 TrueTime GPS-VME Interface (GPS_VME)
- Type 22 PPS Clock Discipline (PPS)
- Type 23 reserved
- Type 24 reserved
- Type 25 reserved
- Type 26 Hewlett Packard 58503A GPS Receiver (GPS_HP)
- Type 27 Arcron MSF Receiver (MSF_ARCRON)
- Type 28 Shared Memory Driver (SHM) <----#####
- Type 29 Trimble Navigation Palisade GPS (GPS_PALISADE)
- Type 30 Motorola UT Oncore GPS GPS_ONCORE)
- Type 31 Rockwell Jupiter GPS (GPS_JUPITER)
- Type 32 Chrono-log K-series WWVB receiver (CHRONOLOG)
- Type 33 Dumb Clock (DUMBCLOCK)
- Type 34 Ultralink WWVB Receivers (ULINK)
- Type 35 Conrad Parallel Port Radio Clock (PCF)
- Type 36 Radio WWV/H Audio Demodulator/Decoder (WWV)
- Type 37 Forum Graphic GPS Dating station (FG)
- Type 38 hopf GPS/DCF77 6021/komp for Serial Line (HOPF_S)
- Type 39 hopf GPS/DCF77 6039 for PCI-Bus (HOPF_P)
- Type 40 JJY Receivers (JJY)
- Type 41 TrueTime 560 IRIG-B Decoder
- Type 42 Zyfer GPStarplus Receiver
- Type 43 RIPE NCC interface for Trimble Palisade
- Type 44 NeoClock4X - DCF77 / TDF serial line
http://doc.ntp.org/4.2.6/refclock.html
An IP address – The IP address of a remote peer or server;
.LOCL. – This local host (a place marker at the lowest stratum included in case there are no remote peers or servers available);
.PPS. – “Pulse Per Second” from a time standard;
.IRIG. – Inter-Range Instrumentation Group time code;
.ACTS. – American NIST time standard telephone modem;
.NIST. – American NIST time standard telephone modem;
.PTB. – German PTB time standard telephone modem;
.USNO. – American USNO time standard telephone modem;
.CHU. – CHU (HF, Ottawa, ON, Canada) time standard radio receiver;
.DCFa. – DCF77 (LF, Mainflingen, Germany) time standard radio receiver;
.HBG. – HBG (LF Prangins, Switzerland) time standard radio receiver;
.JJY. – JJY (LF Fukushima, Japan) time standard radio receiver;
.LORC. – LORAN-C station (MF) time standard radio receiver. Note, no longer operational;
.MSF. – MSF (LF, Anthorn, Great Britain) time standard radio receiver;
.TDF. – TDF (MF, Allouis, France) time standard radio receiver;
.WWV. – WWV (HF, Ft. Collins, CO, America) time standard radio receiver;
.WWVB. – WWVB (LF, Ft. Collins, CO, America) time standard radio receiver;
.WWVH. – WWVH (HF, Kauai, HI, America) time standard radio receiver;
.GOES. – American Geosynchronous Orbit Environment Satellite;
.GPS. – American GPS;
.GAL. – Galileo European GNSS;
.ACST. – manycast server;
.AUTH. – authentication error;
.AUTO. – Autokey sequence error;
.BCST. – broadcast server;
.CRYPT. – Autokey protocol error;
.DENY. – access denied by server;
.INIT. – association initialized;
.XFAC. – association changed (IP address changed or lost);
.MCST. – multicast server;
.RATE. – (polling) rate exceeded;
.TIME. – association timeout;
.STEP. – step time change, the offset is less than the panic threshold (1000ms) but greater than the step threshold (125ms).
https://nlug.ml1.co.uk/2012/01/ntpq-p-output/831
From https://nlug.ml1.co.uk/2012/01/ntpq-p-output/831
remote – The remote peer or server being synced to. “LOCAL” is this local host (included in case there are no remote peers or servers available);
refid – Where or what the remote peer or server is itself synchronised to;
st – The remote peer or server Stratum
t – Type (u: unicast or manycast client, b: broadcast or multicast client, l: local reference clock, s: symmetric peer, A: manycast server, B: broadcast server, M: multicast server, see “Automatic Server Discovery“);
when – When last polled (seconds ago, “h” hours ago, or “d” days ago);
poll – Polling frequency: rfc5905 suggests this ranges in NTPv4 from 4 (16s) to 17 (36h) (log2 seconds), however observation suggests the actual displayed value is seconds for a much smaller range of 64 (26) to 1024 (210) seconds;
reach – An 8-bit left-shift shift register value recording polls (bit set = successful, bit reset = fail) displayed in octal;
delay – Round trip communication delay to the remote peer or server (milliseconds);
offset – Mean offset (phase) in the times reported between this local host and the remote peer or server (RMS, positive for ‘remote time’ is ahead of ‘local time’, milliseconds);
jitter – Mean deviation (jitter) in the time reported for that remote peer or server (RMS of difference of multiple time samples, milliseconds);
From https://nlug.ml1.co.uk/2012/01/ntpq-p-output/831
The first character displayed in the table (Select Field tally code) is a state flag (see Peer Status Word) that follows the sequence ” “, “x”, “-“, “#”, “+”, “*”, “o”:
” ” – No state indicated for:
non-communicating remote machines,
“LOCAL” for this local host,
(unutilised) high stratum servers,
remote machines that are themselves using this host as their synchronisation reference;
“x” – Out of tolerance, do not use (discarded by intersection algorithm);
“–” – Out of tolerance, do not use (discarded by the cluster algorithm);
“#” – Good remote peer or server but not utilised (not among the first six peers sorted by synchronization distance, ready as a backup source);
“+” – Good and a preferred remote peer or server (included by the combine algorithm);
“*” – The remote peer or server presently used as the primary reference;
“o” – PPS peer (when the prefer peer is valid). The actual system synchronization is derived from a pulse-per-second (PPS) signal, either indirectly via the PPS reference clock driver or directly via kernel interface.
0: Atom clock, etc
1: Server direct connected to atom clock
...
16: Sun clock :)
- NTP: Network Time Protocol
- GPS: Global Positioning System
- IP: Internet Protocol
- PPS: Pulse per second