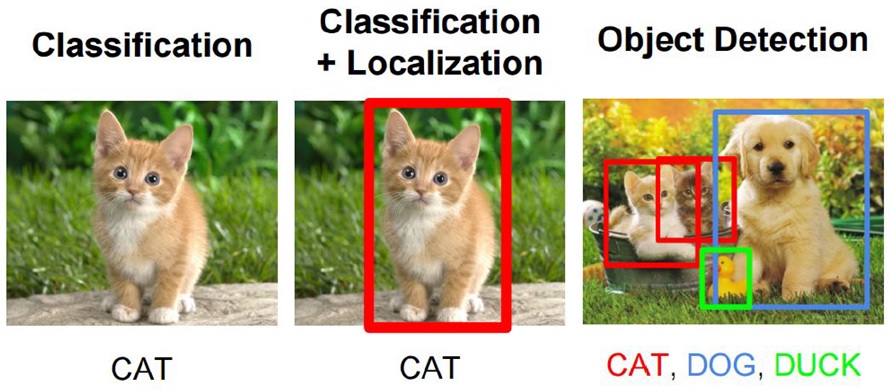
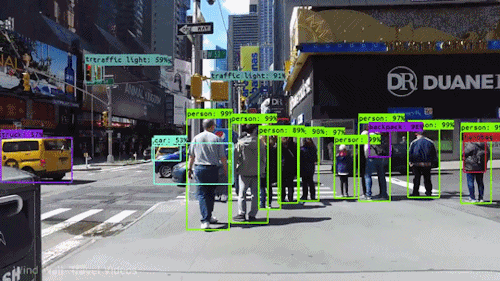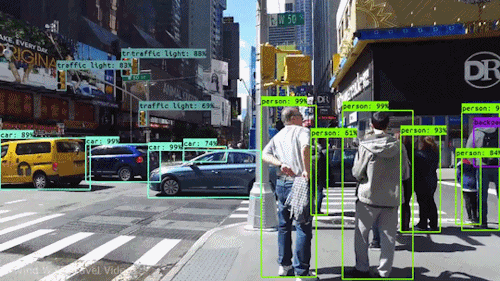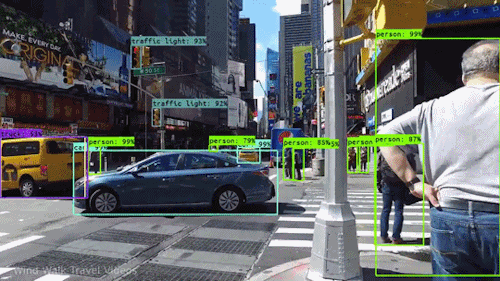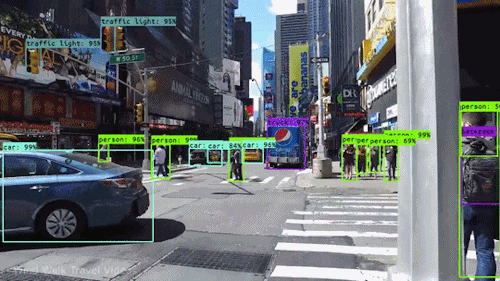
Object Detection: is a computer technology related to Computer vision and Image Processing that deals with detecting instances of semantic objects of a certain class (such as humans, buildings, or cars) in digital images and videos.
Classification: is a process related to categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated and understood.
Localization: Placing a rectangular box for classified objects.
classification is used to find out the label of the image and localization gives an rectangle box after finding the label and Detection used for tracting or detecting the labels in images or in videos . For the object detection we are using YOLOV4 architecture with darknet and OpenCV framework. We used an model where it was developed on 80 labels and data set called coco dataset.
The YOLO algorithm was developed in 2015, and it involves one neuron that is trained and takes an image as input and gives a prediction of a bounding box and the class labels as output.
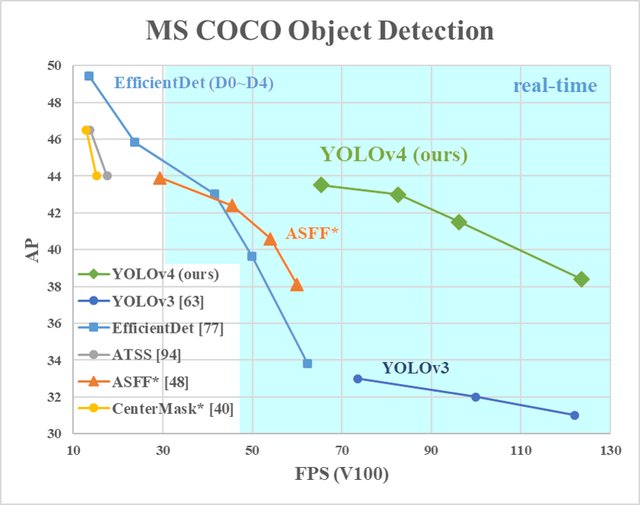
Yolov4 is an improvement on the Yolov3 algorithm by having an improvement in the mean average precision(mAP) by as much as 10% and the number of frames per second by 12%. The Yolov4 architecture has 4 distinct blocks as shown in the image above, The backbone, the neck, the dense prediction, and the sparse prediction.
The R CNN family of techniques used to localize the objects within the image. The network does not look at the entire image, only at the parts of the images which have a higher chance of containing an object.
The yolo framework, on the other hand, deals with object detection in a different way. It takes the entire image in a single instance and predicts the bounding box coordinates and class probabilities for these boxes. The biggest advantage using yolo is its superb speed – it’s incredibly fast and can process 45 frames per second. yolo also understands generalized object representation. This is one of the best algorithms for object detection and has shown a comparatively similar performance to the R CNN algorithms. So for better results we are using yolov4 for developing custom object detection.
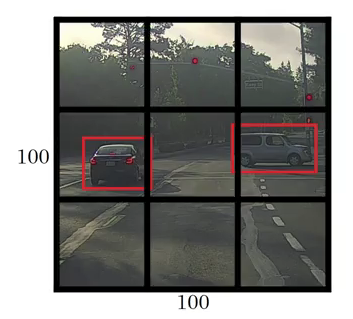
After reading an Image YOLO splits the Image into 19 * 19 grids. For better understanding will take 3 * 3 grid image example
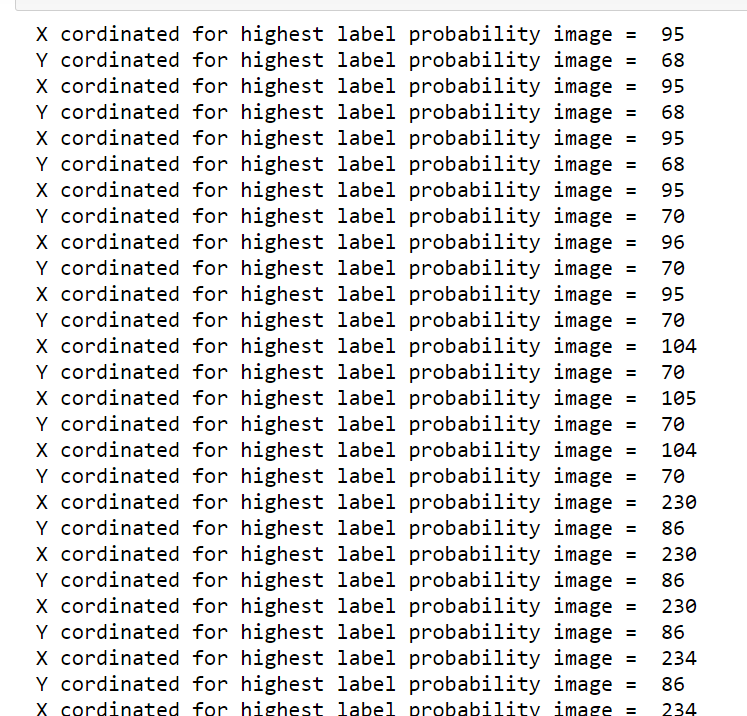
From the above Image 3 * 3 grid each grid will be considered as an individual image and sent to the Neural Network. If the Images label founds in the grid will collect the 4 Parameters from the grid
- Height
- Width
- X_Coordinates from the mid Point of the label
- Y_Coor dinates from the mid Point of the label
We can find the label using the normal CNN method and when there is any label, find the coordinates of the label and its shape of it from the mid location. In this way, we can find out the detection for images and each frame of a video
The cordinates for the labels inside the videos are
The Yolov3 and Yolov4 algorithms are both excellent at object detection, but as pointed out earlier, there are several other algorithms for object detection. Below are the results obtained using yolov3 and yolov4 on the coco dataset for object detection, and some other detection algorithms.
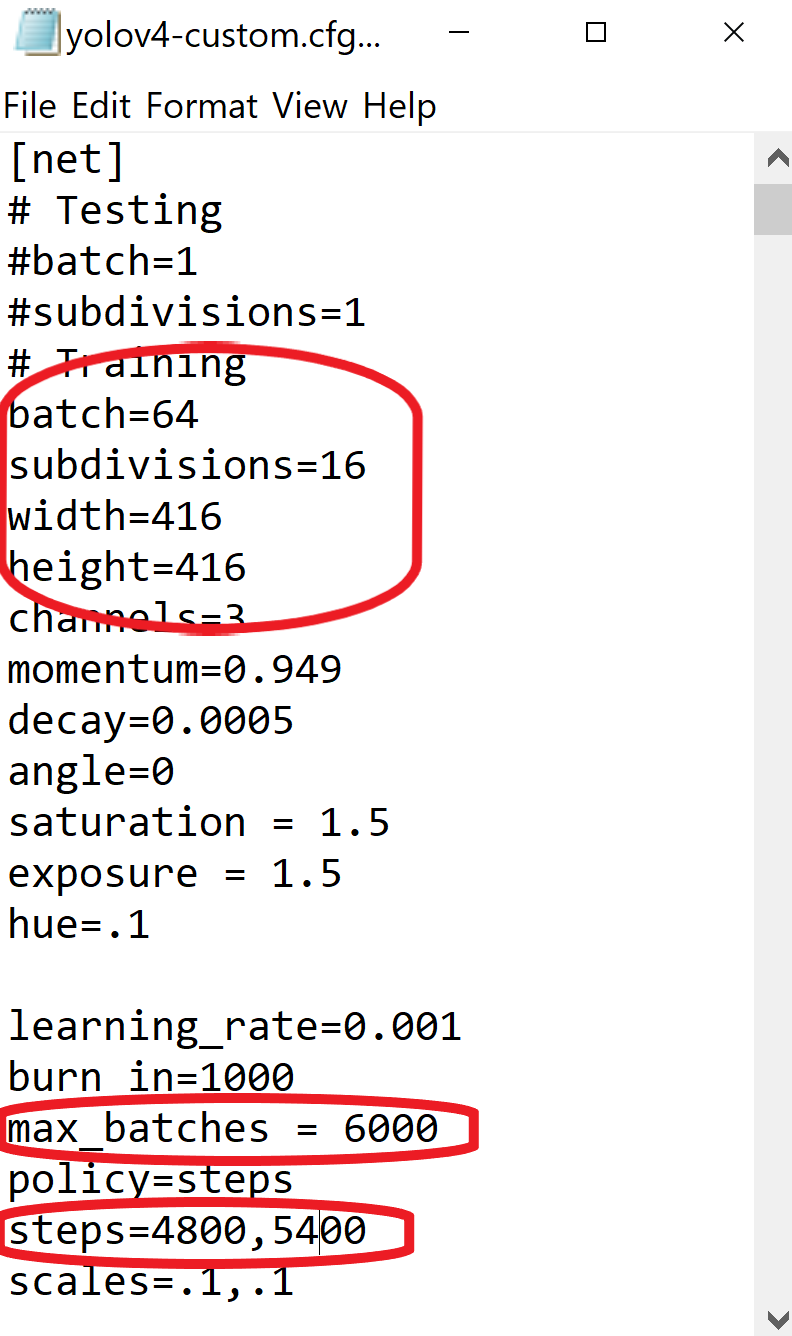
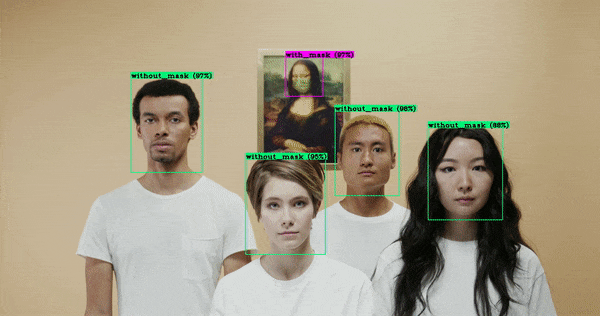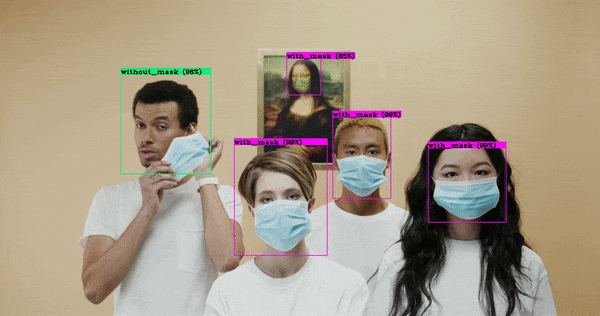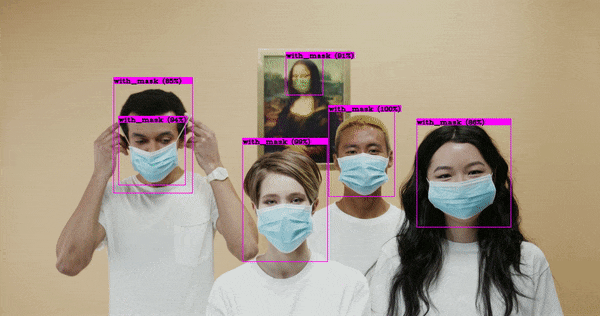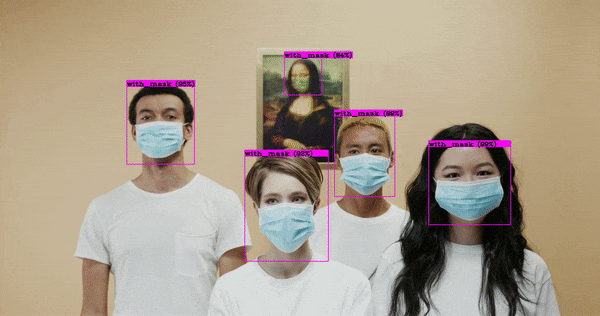
After making use of pretrained weights from coc dataset, we trained our own object detection model that is used to find whether the person wearing the mask or not. For making an custom object detection we used data around 15,000 images, where 7000 with masks and 7000 without masks. For developing this model used yolov4 custom configuration file which we can get from source = 'git clone https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet' .
We have to take GPu permisson which supports cuda version. Because darknet framework was trained on Nvdia cuda Library. And perform the following changes in make file
cd '/content/drive/MyDrive/yolo/darknet'
!sed -i 's/OPENCV=0/OPENCV=1/' Makefile
!sed -i 's/GPU=0/GPU=1/' Makefile
!sed -i 's/CUDNN=0/CUDNN=1/' Makefile
!sed -i 's/CUDNN_HALF=0/CUDNN_HALF=1/' Makefile
!sed -i 's/LIBSO=0/LIBSO=1/' Makefile- change line batch to batch=64
- change line subdivisions to subdivisions=16
- set network size width=416 height=416 or any value multiple of 32
- change line max_batches to (classes*2000 but not less than the number of training images and not less than 6000), f.e. max_batches=6000 if you train for 3 classes
- change line steps to 80% and 90% of max_batches, f.e. steps=4800,5400
It means how many mini-batches you split your batch in. Batch=64 -> loading 64 images for one iteration. Subdivision=8 -> Split batch into 8 mini-batches so 64/8 = 8 images per mini-batch and these 8 images are sent to the GPU for processing. This process will be performed 8 times until the batch is completed and a new iteration will start with 64 new images. If you are using a GPU where the RAM is low, set a higher value for subdivisions ( 32 or 64). This will obviously take longer to train since we are reducing the number of images being loaded and also the number of mini-batches. If you have a GPU with good RAM, set a lower value for subdivisions (16 or 8). This will speed up the training process as this loads more images per iteration.
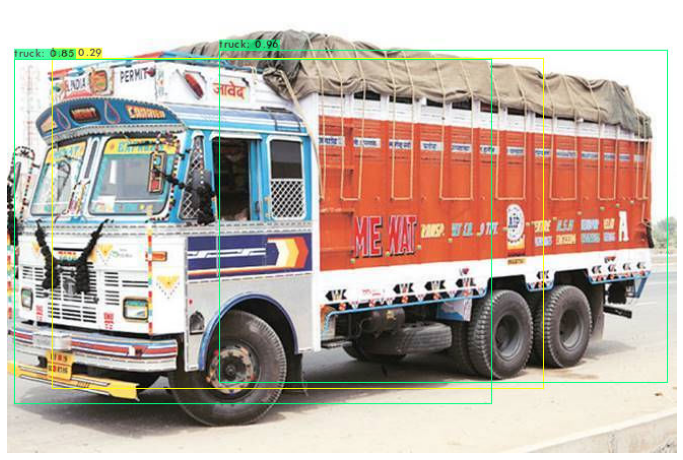
The YOLO implementations are amazing tools to detect common objects in images and videos. However there are many cases,when the object which we want to detect is not part of the popular dataset. In such cases we need to create our own training set and execute our own training. Vehicle and its License plate detection are one such cases. I have used yolov4 to detect the desired classes.
| Vehicle | Label Id |
|---|---|
| Car | 0 |
| Truck | 1 |
| Bus | 2 |
| Motorcycle | 3 |
| Auto | 4 |
| CarLP | 5 |
| TruckLP | 6 |
| BusLP | 7 |
| MotorcycleLP | 8 |
| AutoLP | 9 |
| *License Plate(LP) |
Later split all the dataset in training and validation set and store the path of all the images in file named train.txt and valid.txt
Yolov4 needs certain specific files to know how and what to train.
- obj.data
- obj.names
- obj.cfg
This basically says that we are training 10 classes, what the train and validation files are and which file contains the name of object we want to detect.During training save the weight in backup folder.
classes = 10
train = train.txt
valid = test.txt
names = obj.names
backup = backup
Every new cateogry must be in new line and its category number be same what we have used at the time of annotating data.
Car
Truck
Bus
Motorcycle
Auto
CarLP
TruckLP
BusLP
MotorcycleLP
AutoLP
Just copied the yolov4.cfg files and made few changes in it.
- In line 3, set
batch=24to use 24 images for every training step. - In line 4, set
subdivisions=8to subdivide the batch by 8 to speed up the training process. - In line 127, set
filters=(classes + 5)*3, e.gfilter=45. - In line 135, set
classes=10, number of custom classes. - In line 171, set
filters=(classes + 5)*3, e.gfilter=45. - In line 177, set
classes=10, number of custom classes.
To view all other open source projects visit