Kushagra, a top class astronomer, lives in Betaverse, a universe parallel to ours with the same physical laws. Kushagra lives on Zirca, a planet similar to earth in Betaverse. Zirca completes one revolution around its star in 365 days. The only difference in the betaverse is that it initially was expanding like our universe, but later started to obey the steady state theory of the universe and the galaxies which were moving, started moving at the speed it was when the transition happened. Kushagra and his team find a galaxy about 3.26 million light years away. They also find some interesting properties in that galaxy and want to study it more. He also finds that the scale factor for this galaxy is 10. The size of the observable betaverse w.r.t zirca is 3.3 million light years. Find the time-period, the zircans have to know more about this galaxy. Write a general program to find the time for any galaxy and use the given values as a test case.
The code.py file contains code for the given problem statement
The code&result file contains code and results for the given test data
!pip install astropy
Astropy is a collection of software packages written in the Python programming language and designed for use in astronomy.
The astropy.cosmology sub-package contains classes for representing cosmologies and utility functions for calculating commonly used quantities that depend on a cosmological model.
The Steady-State Theory suggests that the over appearance and density of the Universe do not change over time even if the Universe is continuously expanding.In simple words it means that the universe is always expanding but maintaining a constant average density, with matter being continuously created to form new stars and galaxies at the same rate that old ones become unobservable as a consequence of their increasing distance and velocity of recession.A steady-state universe has no beginning or end in time, and from any point within it the view on the grand scale—i.e., the average density and arrangement of galaxies—is the same. Galaxies of all possible ages are intermingled.This idea is supported by the red shift evidence.A redshift reveals how an object in space (star/planet/galaxy) is moving compared to us. It lets astronomers measure a distance for the most distant (and therefore oldest) objects in our universe. The redshift depends upon the scale factor at the time of transmission (as compared to the present) Scale factor basically tells us about how the universe is expanding or contracting.
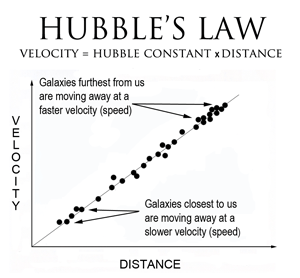
For calculations we use Hubble's Laws:Hubble's laws states that the velocity of recession between our galaxy and the other galaxies are directly proportional to the distance between them and Hubble constant in cosmology is constant of proportionality in the relation between the velocities of remote galaxies and their distances.The Hubble constant is a unit that describes how fast the universe is expanding at different distances from a particular point in space.
https://docs.astropy.org/en/stable/cosmology/index.html
https://earthsky.org/astronomy-essentials/what-is-a-redshift/