Using informed and uninfromed search algorithms to solve the 8-Puzzle game. This team work (me and @Rami)was developed as assignment 1 for AI Course Fall 2019/2020 offering at CCE Department, Faculty of Engineering, Alexandria University.
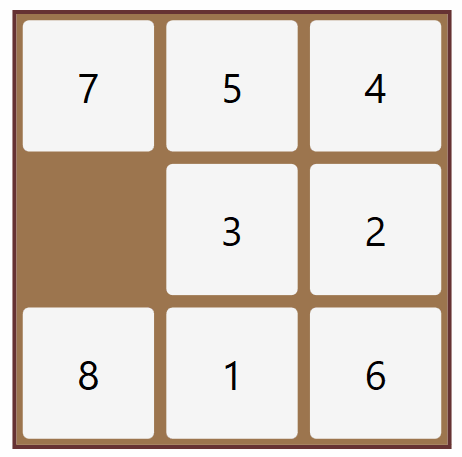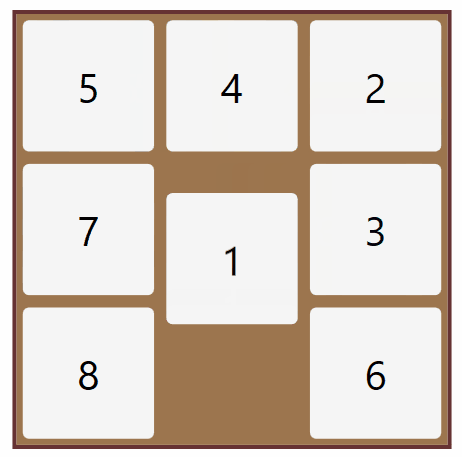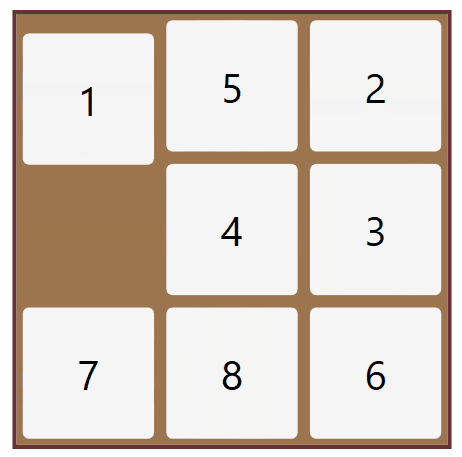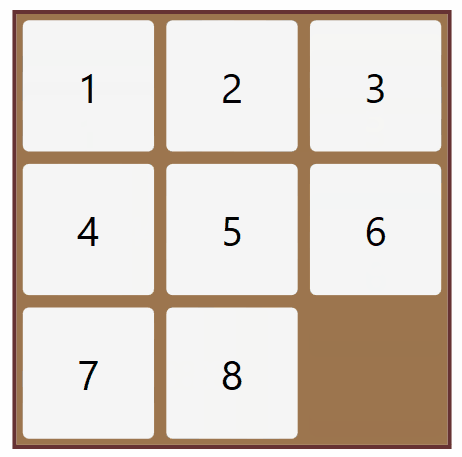
An instance of the 8-puzzle game consists of a board holding 8 distinct movable tiles, plusan empty space. For any such board, the empty space may be legally swapped with any tile horizontally or vertically adjacent to it. In this assignment, the blank space is going to be represented by the number 0. Given an initial state of the board, the search problem is to find a sequence of moves that tran-sitions this state to the goal state; that is, the configuration with all tiles arranged in ascending order 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8 .
We followed OOP (Object Oriented Paradigm) concepts to construct our code structure. With each object in the list below representing an object in the game world.
-
Puzzle State: This class represents the puzzle state at a certain time, it includes: configuration, cost, parent node, children nodes, the actions a state can do and whether this state is a goal or not.
-
Puzzle Solver: It is responsible of solving the input puzzle, and calculating total estimated cost to solve.
-
Search Algorithms: This module includes the required search algorithms: BFS, DFS and A* written in an abstract way to allow re-use.
-
Distance Metrics: Again, an abstarct module to allow re-use, it includes the required distance metrics: Euclidean distance and Manhattan distance
-
Priority Queue: This class has the priority queue data structure used to implement A* search. It is a wrapper over the standard "heapq" module in Python to add support for delete items.
-
Breadth First Search (BFS): It is a traversing algorithm where you should start traversing from a selected node (source or starting node) and traverse the graph layerwise thus exploring the neighbour nodes (nodes which are directly connected to source node).
-
Depth First Search (DFS): It is an algorithm for traversing or searching tree or graph data structures. The algorithm starts at the root node (selecting some arbitrary node as the root node in the case of a graph) and explores as far as possible along each branch before backtracking.
-
A Star Search (A*): It is a graph traversal and path search algorithm, which is often used in computer science due to its completeness, optimality, and optimal efficiency. One major practical drawback is its. space complexity, as it stores all generated nodes in memory.
Tried out both Eculidean and Manhattan distance metrics for heuristics for A* search. Manhattan distance is found out to be more admissible than Euclidean distance because Euclidean distance underestimates the cost as it is shorter than Manhattan distance.
- Intend to implement more search algorithms (e.g. Real Time A* Search) and apply on this work.
- Intend to make a web-based GUI for the game.
Made with ❤️ by Amr Elzawawy and Rami Khafagi