This repository is the result of my final year dissertation project at the University of the West of England, Bristol.
This project is aimed at helping people and researchers understand audio signals and its classification by visualising the signal, as well as evaluating state of the art audio feature extraction and classification methods.
- Research into existing methods of audio feature extraction.
- Research into neural networks for audio classification
- Identify a good performing neural network architecture for audio classification
- Design, build and, implement a cross platform interface program to visualize audio signals with at least 2 of the latest feature extraction methods (MFCC, Spectrograms, Mel Spectrograms).
- Train Existing Neural Network Architectures on the Kaggle2018 Dataset.
- Compare and analyse different neural network architectures (with the same dataset) in conjunction with different feature extraction methods.
- Identify the best hyper parameters for different neural network architectures that yield best accuracy for audio classification.
- Identify the advantages and limitations of each feature extraction method used.
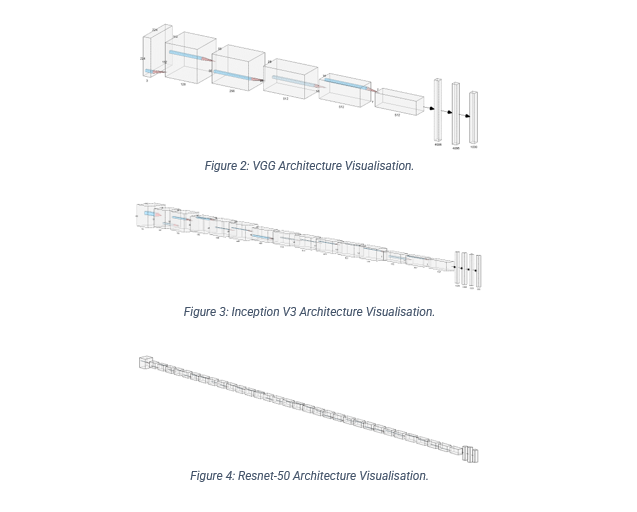
This research project compares each of the following convolution neural network architectures:
Brief directory summary
project
│ README.md
│ requirements.txt
└───app:
│ │ execute.pyw -> runs the interface program
│ │ config.py -> configures the audio related settings
│ └─── tf_models:
│ │ this folder contains old redacted trained models that are not good at all
│ │ You may find the fully trained example models on Google Drive
└───documents:
│ │
│ └─── designs: (designs related to the research project)
│ │
│ └─── research: (related pdfs, some may be missing)
└───notebooks:
│ │ Data_Normalizer_Cacher.ipynb (normalizes to npy and inspects dataset)
│ │ Data_Feature_Extractor.ipynb (handles feature extraction and caches them as npy files)
│ │ helper.py (contains helper functions used by notebooks)
│ └─── MEL: (mel spectrogram based CNN training notebooks)
│ │
│ └─── MFCC: (MFCC based CNN training notebooks)
└───redacted_notebooks:
contains all the redacted notebooks that where essential to the learning of tensorflow 2.0 but may be incomplete or in disarray as they where retired.
H5 Model Attributes to work with interface program
└───h5:
│ │
│ └─── metadata: (array of strings that are properly in encoding order to match softmax layer)
│ │
│ └─── dfe: the desired feature extraction method the model wants
The attributes are attached with the h5 model, refer to the helper.py load & save ext functions, they instruct the interface program what the model expects.
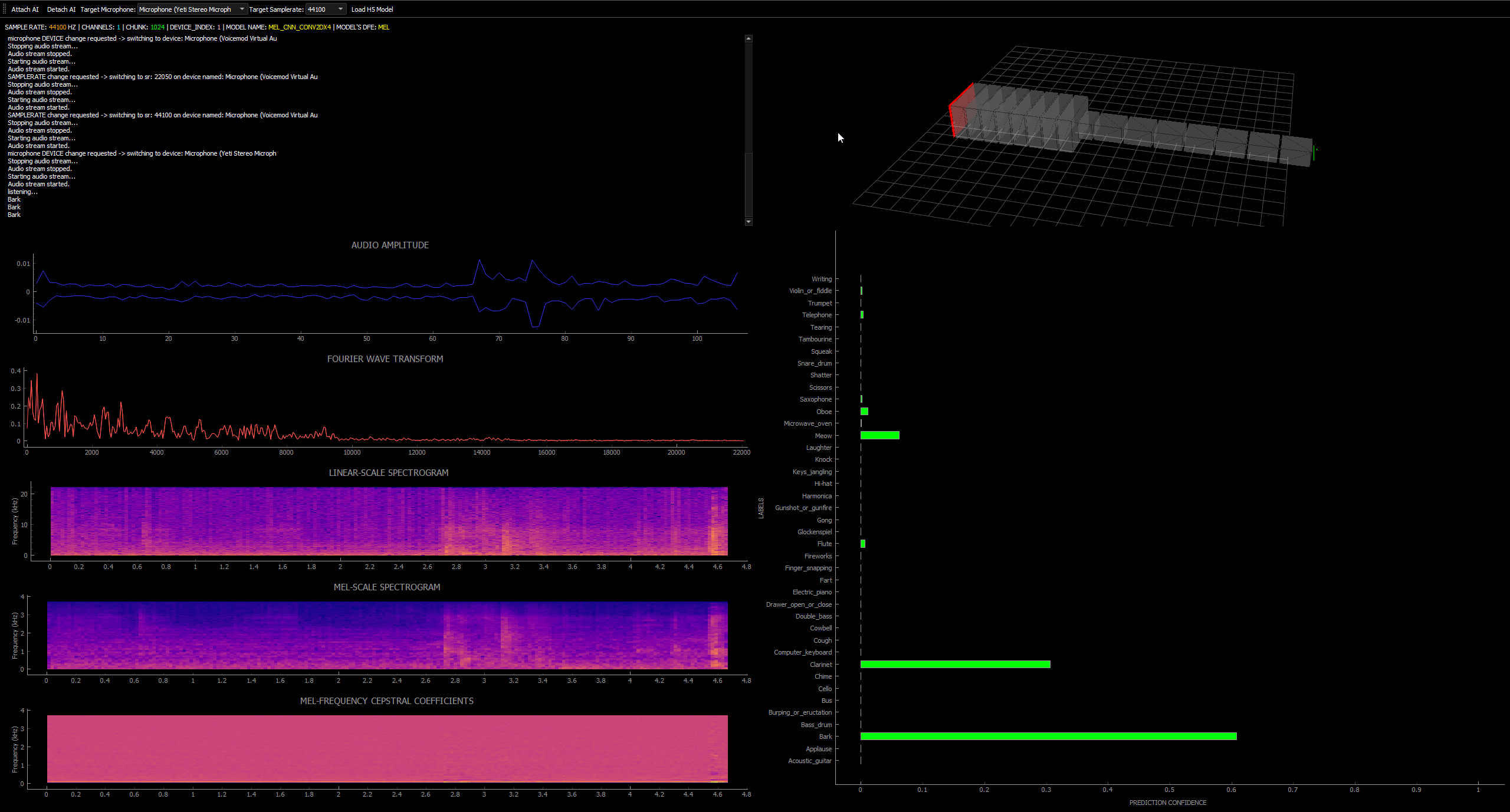
Hereafter is a screenshot of the interface program running a simple CNN model classifying audio sounds. In this example, the interface program is showing a linear-scale spectrogram, a mel scaled variant and a MFCC. The bar chart depicts the multiple labels that can be predicted by the model since the metadata is embedded within it.
The interface program will function and switch input devices on both windows and the Linux distribution Fedora 35(in this case, it was only tested upon that specified linux distribution)
Trained models can be found on Google Drive here:
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1shlnOvHh2BxEb_HjnXWw21mapsjMiknh/view?usp=sharing