www.dpdl.io
developed by SEE Solutions © 2003
Dpdl is a rapid development programming language and constrained device framework with built-in database technology. Dpdl enables access to Java platform API's and to external native libraries and supports the embedding and on-the-fly execution of multiple programming languages like ANSI C, C++, Python, Julia, JavaScript, Lua, Ruby, Java and Clojure directly embedded within Dpdl code.
Further programming languages and natural language interpreters can be added as extensions and embedded via a dedicated plug-in interface and configuration. For example the ROOT C++ Data Analysis framework from Cern is also available as Dpdl language plug-in.
Dpdl is self contained, portable and highly customizable via an extensible interface.
A dedicated AI Dpdl language plug-in (DAN) allows to automatically generate and embed programming language code or content in Dpdl code via generative AI code
Dpdl = ( Java Api's + Embedded C + 'C++' + Python + Julia + JavaScript + Lua + Ruby + Java + Clojure) = Powerful and Versatile
These features make Dpdl a powerful development platform for rapid prototyping, in particular also due to the fact that software written with Dpdl will be enabled to access thousands of existing high-quality software libraries. Dpdl is not intended to replace, but to enable integration of different technologies seamlessly to leverage fast prototyping and foster research and development.
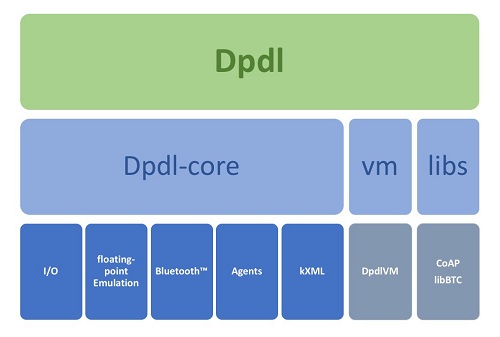
DpdlEngine stack overview
By combining the portability and vast API availability of Java and Python, the computational power of Julia, the expressiveness of Lua and Clojure, the simplicity of Ruby, the web-enablement of JavaScript, the power of C/C++ programming language and a simple acess to native libraries, Dpdl provides a powerful development platform for industrial applications, education and research.
The Dpdl language constructs and syntax is kept simple and follows an object oriented paradigm interoperable with the java platform API and any external java libraries.
Common IoT protocol stacks such as Bluetooth(tm) and CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol) are integrated by default and third party libraries and functions can be added as extensions.
The included Dpdl language plug-in 'DpdlAINerd' (DAN) makes use of AI generative code to enable to automatically generate and embedded executable code and content or data by natural language descriptions contained in Dpdl code.
int status = DPDLAPI_searchClientsOnServer()
int status_discovery = dpdlFalse
int service_discovery = dpdlFalse
int counter = 0
if(status == dpdlTrue)
while (status_discovery != dpdlTrue) && (service_discovery != dpdlTrue)
status_discovery = DPDLAPI_discoveryServerFinished()
service_discovery = DPDLAPI_serviceDiscoveryServerFinished()
print(".")
counter = counter+1
sleep(3000)
endwhile
string dev = "n"
int dev_found = 0
while(dev != "null")
dev = DPDLAPI_getServerVisibleBTAddr()
if(dev != "null")
println("bluetooth device visible: " + dev)
saveData(dev)
dev_found = dev_found + 1
fi
endwhile
else
println("No working Bluetooth stack found")
fiDpdl comes with a very compact and portable scripting engine and an extensible API interface for the development of applications and embedded system software and in particular is ideal to foster rapid application development and rapid prototyping. Embedded ANSI C code and Clojure can also be dynamically compiled in memory at runtime in order to achieve faster execution performance.
Further, Dpdl can be used to encode, store, control and query data efficiently also on small memory footprint devices via a custom data container, a 'DpdlPacket'.
This makes Dpdl suitable for a wide range of use-cases and applications in particular also for Hardware programming.
-
DpdlEngine core (full configuration)
372 Kb -
DpdlNative library with (Embedded C interpreter/compiler)
278 Kb -
Total size of DpdlEngine (Dpdl + C compiler/interpreter) =
650 KbOnly
The size of the DpdlEngine core can be stripped down to 60 Kb with a basic configuration if needed.
Here you can find full featured working applications written with Dpdl:
This is a small sample app written with Dpdl that gets the top 10 news stories via http get in json format:
Note: The example 'app/getnews/dpdlGetNews2.h' is identical, but data is decoded in a java object instead of a struct
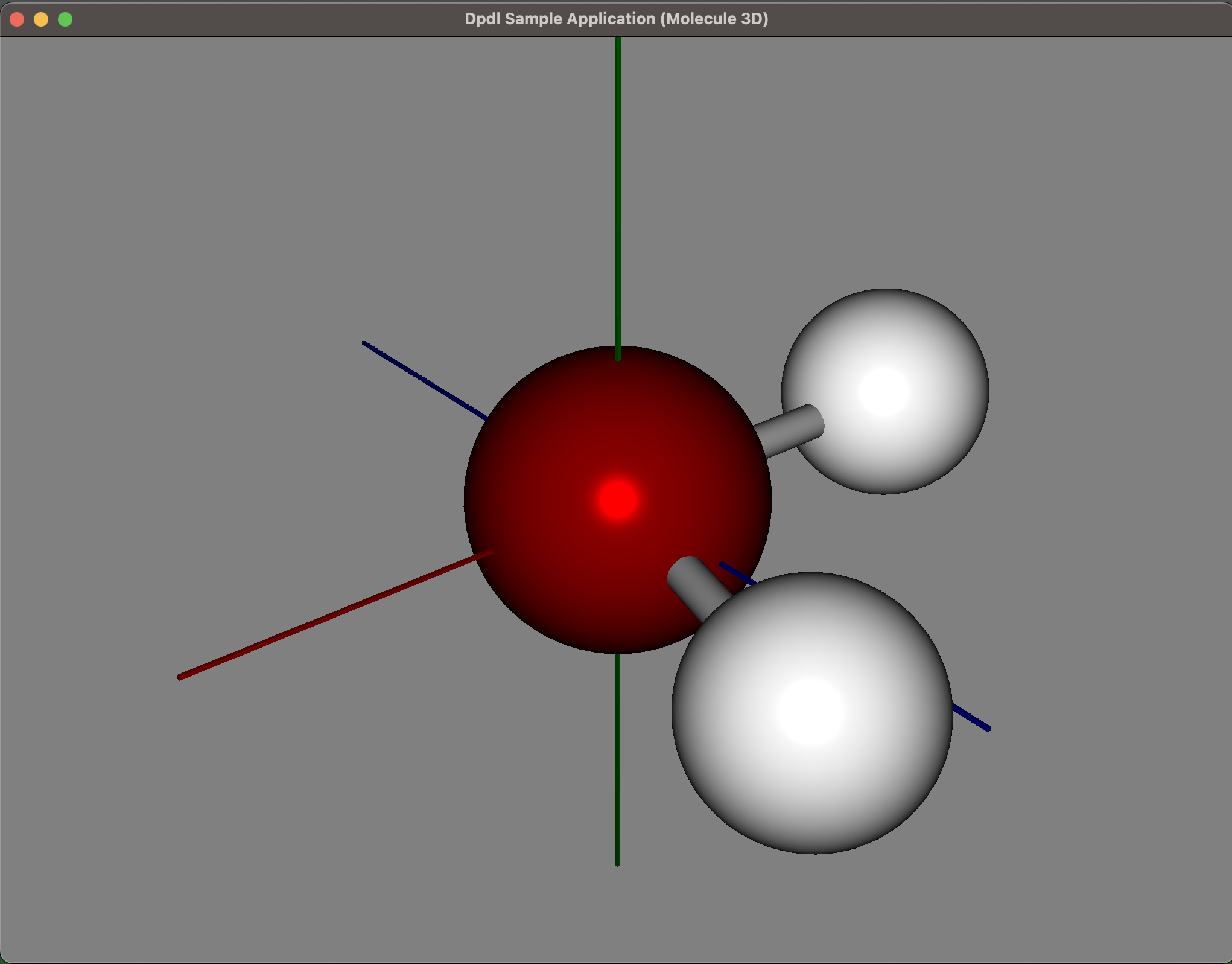
This is a 3D model visualization of chemical molecules (in this case hydrogen) using the JavaFX library. The model can be rotated freely with mouse events (ported to Dpdl from javafx examples)
graphics/dpdl3DJavaFX_molecule.h
VIDEO of Dpdl sample 3D application
Simple Dpdl example that executes an embedded 'Java' code and an embedded 'C' code directly within Dpdl
app/simple/dpdlSimpleJavaAndC.h
Dpdl example that uses the 'sql' Dpdl language plug-in to retrieve data from a database and handle the result set
The Dpdl script connects to the database and performs a query, retrieves and prints out the result set, encodes the result set to a json string, and than decodes the json string to an object that can be accessed as a HashMap
You can find more Dpdl examples on the following page: Dpdl_Examples.md
Or full featured Applications written with Dpdl in the following repository:
Dpdl is suitable for rapid application development in various domains, in particular also for small development of applications on small memory footprint devices, and can be used as embedded scripting engine for various applications.
The main nature of Dpdl is for enabling rapid prototyping, rapid development, code reuse and allow a high degree of portability while being simple, extensible and compact. Further, developers can benefit from the possibility to use multiple programming languages due to the fact that a vaster set of APIs are available for a given platform.
Dpdl has also built-in constructs that enable dynamic code generation for generative AI code and provides a dedicated plug-in interface for developing and embedding custom language interpreter plug-ins of all sorts.
The DpdlPacket data container is a highly optimized way to store, query and access data
on devices that have limited memory and storage capabilities.
The AI Dpdl language plug-in 'DpdlAINerd' (DAN) can be used to speed-up the prototyping and development process by leveraging generative AI code for embedded code and data within Dpdl.
Dpdl can be used as:
- Rapid application development platform
- Embedded scripting engine
- Library module
- Utility tool
- Data handling on memory constrained devices
- Development of Domain Specific Languages (DSL)
- Generative AI code
- DpdlEngine is optimized to run on a wide range of platforms (J2ME, JavaME, J2SE, any other JVM >= 1.4 Spec, and all platforms where the open source virtual machine 'miniJVM' can be compiled for the target platform)
- Dpdl API provides access to the complete underlying Java JRE platform API's and to external java and Native libraries
- Multiple embeddable Dpdl language plug-ins available: ANSI C code, C++, Python, Julia, JavaScript, Lua , Ruby, Java and Clojure programming languages can be embedded and executed directly within Dpdl code (interpreted/compiled code)
- Other programming languages can be embedded via a dedicated kernel execution interface (see 'DpdlCustom' tag in DpdlEngine.ini)
- Includes embedded C compiler: On-the-fly compilation of embedded ANSI C code in memory at runtime (via option 'dpdl:compile') for different platforms (i386, RISC-V, ARM and TMS320C67xx) -> very fast compile time
- Built-in Dpdl scripting engine with support for custom extensions (DpdlExtension interface) -> allows to dynamically add language features
- Support for common IoT protocol stacks such as Bluetooth(tm) (JSR-82) and CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol) (IETF standard RFC 7252)
- Packing data in a 'DpdlPacket' is a convenient way to optimize and speedup access to data. The speedup is x 25 times faster compared to a standard record store access
- Virtual record store filesystem
- Double precision floating point emulation layer
- XML with XPath parser
- JSON
- Fast Prototyping
- Small footprint, Only
372 Kbfor core DpdlEngine -> can be stripped down to60 Kbfor minimal setup - Tools for automatically converting Dpdl code to Java , C/C++ and V code
- Allows to automatically generate and embed generative AI programming code within Dpdl using the 'DpdlAINerd' (DAN) Dpdl language plug-in
- Open Source programming language plug-ins
Dpdl embedded minimal C library Documentation
The Dpdl language API allows to access all classes and methods of the underlying Java Platform (JRE) and external java libraries.
Example: using a java HashMap (which interfaces to java.util.HashMap)
object map, s
map=loadObj("HashMap")
map.put(1,"Dpdl")
map.put(2,"Packet")
map.put(3,"Definition")
map.put(4,"Language")
s=map.get(1)
println(s)
s=map.get(4)
println(s)Iterate over the obove HashMap using the same objects and methods as provided by the java API:
object es = map.entrySet()
object iter = es.iterator()
object ep
while(iter.hasNext())
ep = iter.next()
println("key=" + ep.getKey() + " value=" + ep.getValue())
endwhileIn this way all java libraries defined in class definition configuration file (./DpdlLibs/libs/classes.txt) can be loaded and accessed.
The default configuration currently includes Java Platform API, the JavaFX API and bluecove Bluetooth JSR-82.
The default configuration can be easily extended or updated to resolve additional java APIs by editing the class definition configuration file.
The set of classes accessible with Dpdl (default) is defined to be the following set. The methods of the classes that are accessible are referred to the current JRE instance on which Dpdl is running.
NOTE: Additional classes and API's can be added to the class definition file as needed.
It's worth mentioning here that 'Java' code can also be embedded directly within Dpdl as described below.
Here just a quick example:
println("Dpdl can also embed native java code...")
object mystr = loadObj("String", "this is a Dpdl object mapped to java api, a str parameter")
int x = 23
dpdl_stack_push(mystr, "./Test/TestRead.txt", x)
>>java
System.out.println("Parameters: ");
System.out.println(" arg0: " + arg0);
System.out.println(" arg1: " + arg1);
System.out.println(" arg2: " + arg2);
static void myMethod1(){
System.out.println("myMethod1: " + 1);
}
myMethod1();
for(int x = 0; x < arg2; x++){
System.out.println("x: " + x);
}
File myfile = new File(arg1);
return 1;
<<
int exit_code = dpdl_exit_code()
println("embedded java exit code: " + exit_code)Multiple programming languages can be embedded and executed within the same Dpdl code via the keyword >>.
Further programming languages can be developed and integrated via a dedicated plug-in interface and configuration. This enables basically every sort of
programming language or natural language interpreter to be embedded directly in Dpdl code.
This features is very useful for rapid development and rapid prototyping and is also a key feature for generative software.
C interpretedcode (minimal subset of C90 with standard C libs included)ANSI C(full ISO C99 standard) compiled in memory and dynamically executed at runtime (see 'dpdl:compile')PythonJuliaJavaScriptLuaRubyOCamlJavaROOT C++Clojure
available Add-on plug-ins:
SqlAi-> see doc/DpdlAINerd.md
See this doc for more details: Dpdl_embedded_languages.md
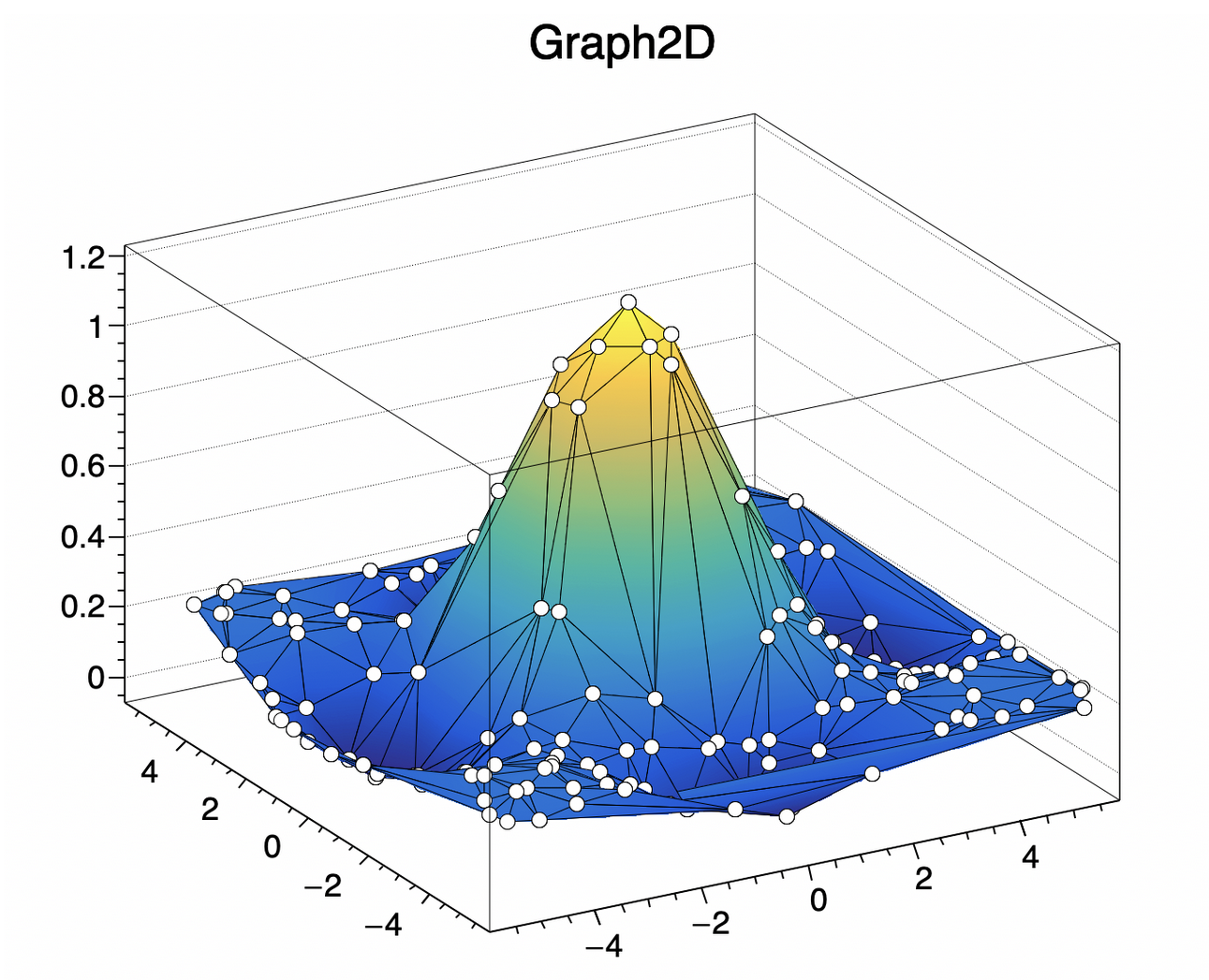
ROOT is a powerful Data Analysis Framework developed by CERN (https://root.cern/) .
ROOT C++ code can be embedded within Dpdl via the keyord >>root
Example Dpdl code embedding 'ROOT C++':
# main
println("test embedded ROOT C++...")
>>root
auto canvas = new TCanvas("c","Graph2D example",0,0,700,600);
double x, y, z, P = 6.;
int np = 200;
auto dt = new TGraph2D();
auto r = new TRandom();
for (int N=0; N<np; N++) {
x = 2*P*(r->Rndm(N))-P;
y = 2*P*(r->Rndm(N))-P;
z = (sin(x)/x)*(sin(y)/y)+0.2;
dt->SetPoint(N,x,y,z);
}
dt->Draw("tri1 p0");
canvas->Modified(); canvas->Update();
<<
int exit_code = dpdl_exit_code()
println("embedded ROOT exit code: " + exit_code)NOTE: The native Dpdl library 'dpdlroot' needs to be downloaded and deployed separately (see Download section below)
Dpdl allows the embedding and on-the-fly execution of ANSI C code directly within Dpdl code with the keyword >>c
The C code can be embedded with 2 different Modes:
- Interpreted
- Compiled in memory at runtime (if option 'dpdl:compile' is enabled)
Example Dpdl code with embedded C code (Mode 1):
# main
# starting with Dpdl, pushing parameters on the stack and embedding C code
println("testing embedded C code in Dpdl")
int n = 6
double x = 10.0
string a = "test"
dpdl_stack_push(n, x, a)
>>c
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv){
printf("Hello C from Dpdl!\n");
printf("\n");
printf("num params: %d\n", argc);
int cnt;
for (cnt = 0; cnt < argc; cnt++){
printf(" param %d: %s\n", cnt, argv[cnt]);
}
return 0;
}
<<
int exit_code = dpdl_exit_code()
println("embedded C exit code: " + exit_code);
# again Dpdl code...
object str = loadObj("String", "Dpdl embedded C")
bool b = str.contains("C")
println("Dpdl contains C: " + b)Other programming languages or natural language interpreters can be easily integrated in Dpdl via a dedicated plug-in interface and configuration. Please feel free to suggest your opinion on the 'Discussion' section on the DpdlEngine GitHub repository
The Dpdl language plug-in 'DpdlAINerd' (DAN) allows to generate and embed code via popular AI engine (eg. OpenAI, Google Vertex AI, etc..)
see here for more info: doc/DpdlAINerd.md
Dpdl runs on a wide range of platforms and provides also a small footprint java virtual machine, released as open-source, that can be compiled for almost every platform as soon as an ANSI C compiler is available for the target platform.
- J2ME MIDP (Mobile Information Device Profile) -> MIDP 1.0 and MIDP 2.0 (CLDC 1.0, CLDC 2.0)
- Java ME CLDC & GCF (JSR 360)
- Java ME Embedded Profile (JSR 361)
- Java versions >= 1.4 and later
- Java > 1.1 (but without 'loadObj' and 'getClass' methods)
- All Platforms where the included Open Source virtual machine (miniJVM) can be compiled
DpdlEngine V1.0 has been tested on:
* MacOS aarch64
* Linux x86_64
* Raspberry PI 3 (armv7l)
* Windows 64-bit
* Android
* JavaME
* J2ME (MIDP 2.0)
Note: The DpdlEngine needs to be re-packaged for running on Android, JavaME and J2ME
(X + version) Supported
(*) available soon
| Platform | Embedded ANSI C | Python | Julia | Js | Clojure | Lua | ROOT C++ | Ruby | Java | SQL | OCaml |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linux x86_64 | X | X v3.2 | X v1.9.3 | X | X v1.12.0 | X v5.4 | X v6.28 | * | X | X | X v4.01 |
| Mac OS X (aarch64) | X | X v3.12 | X v1.9.3 | X | X v1.12.0 | X v5.4 | X v6.28 | X 3.2.2 | X | X | X v4.01 |
| Raspberry PI 3 (armv7) | X | X v3.2 | X v1.9.3 | X | X v1.12.0 | X v5.4 | * | * | X | X | X v4.01 |
| Windows64 | X | * | * | X | X v1.12.0 | * | * | * | X | X | X v4.01 |
The Dpdl framework and API documentation are available via the following links:
Dpdl embedded minimal C library Documentation
Dpdl Java API Documentation (available only for the registered version of DpdlEngine)
See 'Download' page for more details:
Dpdl is currently developed by SEE Solutions and the following integrations has been defined:
- Front-End compiler based on LLVM for compiling Dpdl code to IR
Python code can be embedded within Dpdl code by using the keyword >>python.
MicroPython will also be supported as option in the coming release.
Example Dpdl code with embedded 'Python' code:
println("testing embedding python code")
println("")
>>python
languages = ['Dpdl', 'C', 'Python', 'Clojure']
for language in languages:
print(language)
<<
println("")
int exit_code = dpdl_exit_code()
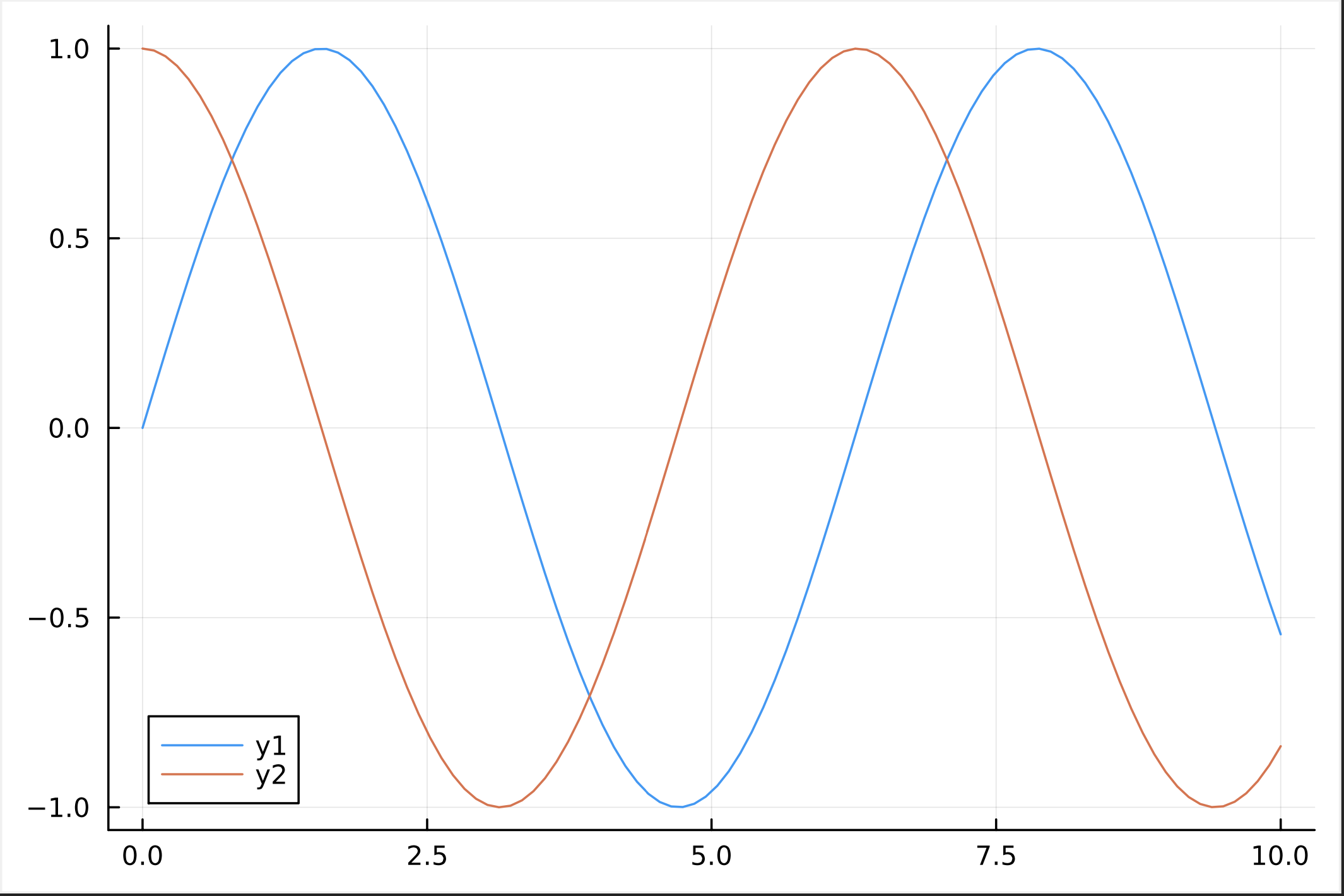
println("embedded python exit code: " + exit_code);Julia is a powerful and performant computational programming language (https://julialang.org)
Julia code can be embedded within Dpdl via the keyord >>julia
Example Dpdl code embedding 'Julia' that generates a Plot and saves the result as PDF file:
#main
println("Testing Plot data with Julia programming language...")
>>julia
using Plots
x = range(0, 10, length=100)
y1 = sin.(x)
y2 = cos.(x)
p = plot(x, [y1 y2])
savefig(p, "./Test/myplot.pdf")
dispose_status = @ccall dpdl_julia_dispose()::Int32
return 1
<<
int exit_code = dpdl_exit_code()
println("finished with exit code: " + exit_code)NOTE: The native Dpdl library 'dpdljulia' needs to be downloaded and deployed separately (see Download section below)
JavaScript is the ideal programming language for web applications as it's supported by all popular web browsers.
JavaScript code can be embedded within Dpdl via the keyword >>js or >>qjs
Dpdl allows the embedding of javascript with 2 different Modes:
- Using the 'QuickJS' javascript engine from Fabrice Bellard '>>qjs' (Suggested)
- Using the 'Nashorn' javascript engine embedded in the Java platform '>>js'
Example:
println("testing embedded qjs...")
dpdl_stack_push("my Hello Message!!!")
>>qjs
import { fib } from "./DpdlLibs/js/fib_module.js";
var a_message = "null";
console.log(scriptArgs)
console.log('Dpdl sends a message with QuickJS');
if(scriptArgs.length > 0){
a_message = scriptArgs[0];
}
std.printf("Message = %s %d", a_message, 23);
console.log('');
console.log("fib(10)=", fib(10));
<<
int exit_code = dpdl_exit_code()
println("Dpdl qjs exited with exit code: " + exit_code)QuickJS provides a powerful and complete API to interact with the javascript engine at low level. Custom native functions and objects can be implemented as shared libraries and loaded in javascript. You can find examples in the folder './DpdlLibs/js/'
Lua code can be embedded within Dpdl code by using the keyword >>lua.
Example Dpdl code with embedded 'Lua' code:
println("testing embedding Lua within Dpdl....")
string buffer_key = "dpdlbuf_result"
dpdl_stack_push(buffer_key, "name", "Alexis", "surname", "Kunst")
>>lua
function doSomeAlg()
local home_dir = os.getenv("HOME")
print("user home: ", home_dir)
local x = os.clock()
local s = 0
for i=1,100 do
s = s + i
io.write(".")
end
print("")
print(string.format("elapsed time: %.2f\n", os.clock() - x))
end
function paramLen(T)
local count = 0
for _ in pairs(T) do count = count + 1 end
return count
end
function dpdl_main(params)
local num_params = paramLen(params)
io.write("dpdl_main call with number of params: ")
io.write(num_params)
print()
print("executing my embedded algorithm...")
print("")
doSomeAlg()
print()
print("returning param values in 'uppercase'")
local tab_out = {numfields=1}
for k,v in pairs(params) do
tab_out.numfields = tab_out.numfields + 1
tab_out[tostring(k)] = string.upper(tostring(v))
end
tab_out.numfields = tostring(tab_out.numfields)
return tab_out
end
<<
int exit_code = dpdl_exit_code()
println("embedded lua exit code: " + exit_code)
string resp_buf = dpdl_stack_buf_get(buffer_key)
println("lua response buffer: ")
println(resp_buf)A dedicated Dpdl language plug-in allows to directly inject SQL statements and retrieve the result sets. Connection, query and packing the results are performed directly by the plug-in
Example Dpdl code with embedded 'SQL':
println("testing 'sql' queries with Dpdl...")
dpdl_stack_var_put("db_url", "jdbc:postgresql://127.0.0.1:5432/mytestdb")
dpdl_stack_var_put("db_user", "testuser")
dpdl_stack_var_put("db_pass", "189923")
dpdl_stack_push("dpdlbuf_res")
>>sql
SELECT id, name, surname, email from mytable
<<
object result = dpdl_stack_obj_get("dpdlbuf_res")
raise(result, "Error: dpdl stack buffer is null")
int rs_size = result.size()
object id, name, surname, email
int c = 0
object entry
for(c < rs_size)
println("-----------------------------------")
entry = result.get(c)
id = entry.get(0)
name = entry.get(1)
surname = entry.get(2)
email = entry.get(3)
println("id: " + id)
println("name: " + name)
println("surname: " + surname)
println("e-mail: " + email)
println("-----------------------------------")
c=c+1
endfor
println("finished")Further Dpdl examples can be found on this page:
A DpdlPacket is a compact, highly compressed executable packet of data with built-in database technology that can be created based on a defined Dpdl code definition. A DpdlPacket can than be allocated and queried efficiently via API interfaces available for Java and for the built-in Dpdl language. In particular Dpdl is very efficient on J2ME and JavaME platforms and has a high degree of backward compatibility.
A DpdlPacket contains 1 - n chunks of compressed data that can be allocated, queried and deallocated when data is not used anymore.
All kind of data can be packed into a DpdlPacket.
The 'DpdlEngine lite' release package includes an encoded DpdlPacket (dpdl_PHONEBOOK.dpdl) and the corresponding Dpdl code definition file dpdl_PHONEBOOK.c used to encode the DpdlPacket. Refer to the Dpdl_documentation for how to allocate, execute and perform queries on a DpdlPacket.
Example of DpdlPacket code definition (dpdl_PHONEBOOK.c)
call(dpdlInterpreter)
::module dpdl_PHONEBOOK
::module_SPEC 23452
::model 836
::dpdlVersion 1.0
OPTIONS {
TARGET = CDC & CLDC
KVM = 1.0
ZIP = true
CHECKSUM = true
SIGNATURE = true
ENCRYPTION(RSA) = false
}
#defineDpdlEncoding UTF-8
#defineDB phone_bz | ./Test/BolzanoPhone.csv | null null
#defineSQL query_ SELECT name, phoneNR, e-mail FROM phone_bz end
#defineProtocol-cHtml phonebook_visual phone_book.html
import extern SystemData
catch DPDL_Script OnInit() {
import("dpdllib.h") nl
println("OnInit()") nl
}
import virtual DATA none {
class BolzanoPhone volatile phonebook_visual {
DATA::string const name;
DATA::string using phoneNR;
DATA::string using e-mail;
#defineGUI Default <PhoneBook> <Enter name and surname:>
catch DPDL_Script OnDecode() {
import("dpdllib.h") nl
import("dpdlRS.h") nl
println("OnDecode()") nl
string time = getTime() nl
println("storing access time..." + time) nl
int rs_id = createRS("AccessStats", AUTHMODE_ANY, dpdlTrue, dpdlTrue) nl
int rec_id = addRecord(rs_id, time) nl
int status = closeRS(rs_id) nl
println("done status: " + status) nl
}
}
}
#defineD BolzanoPhone source phone_bz SQL query {
CHUNK entry [6];
struct BTree DENSE_INDEX hashing *name
entry.content { name , phoneNR , e-mail }
entry.name TAG(0xef) const (string) = 20;
entry.phoneNR TAG(0xefe) (string) = 15;
entry.e-mail TAG(0xefee) (string) = 30;
}This is an example Dpdl sript that show how a 'DpdlPacket' can be allocated and queried:
The database technology in Dpdl has been developed since year 2003 when the first applications where developed for mobile devices.
It started with a BsC thesis by A.Costa:
The DpdlClient console application included in the 'DpdlEngine lite' release is a small console application that exposes some functionalities of Dpdl via a simple command line console. Dpdl code can be executed and DpdlPackets handled. The same functionalities can be accessed via the java or Dpdl API.
These are the console commands available:
Usage:
-l List DpdlPackets installed
-i Install DpdlPacket
-d Uninstall DpdlPacket
-la List DpdlPackets allocated
-a Allocate DpdlPacket
-da Deallocate DpdlPacket
-qp Query DpdlPacket
-c Create DpdlPacket
-libs List Dpdl libraries
-slib Show library
-api List Dpdl API functions
-exec Type && Execute a Dpdl script, between <script>... </script>
-load Load && Execute a Dpdl script file (relative path to./DpdlLibs/ eg. arraylistExample.h)
-bench Run a query benchmark test (on DpdlPacket dpdl_PHONEBOOK)
-h Help
-q quit