These OpenWhisk samples are written in Node.js.
Apache OpenWhisk is a serverless open source cloud platform. It works by executing actions/functions in response to events.
These MQ Samples for OpenWhisk consist of 2 actions, 1 feed, 1 sequence, 2 triggers and 2 trigger-action rules, packaged into a single project mqfunctions.
The samples have been developed following OpenWhisk documentation and samples.
The project is deployed with the openwhisk deploy utility using a single "Package Manifest" YAML file mqfunctions.yml, to describe all the components that make up the OpenWhisk Package.
The project has a dependency on the openwhisk system package for cloudant. This creates a binding (alias) to it with the binding name mqCloudant, allowing the packaged mqfunctions actions to use cloudant functionality, by invoking cloudant actions.
To deploy and run these samples you will need:
- MQ server - You can use IBM MQ in IBM Cloud
- OpenWhisk - You can use IBM Cloud Functions
- OpenWhisk CLI - You can use IBM Cloud CLI plugin
- Cloudant - You can use Cloudant on IBM Cloud. Create a database with the name
mqfunctions.
The manifest file is mqfunctions.yml. Sample script files have been provided that will deploy / undeploy the package using the manifest.
Deploy from the mq-package directory.
If deploying to IBM Cloud, use the command line to login to IBM Cloud. Edit the deploy.sh script to provide configuration details for your queue manager and cloudant database.
The actions uses MQ REST API. If you are using MQ in IBM Cloud the connection details will be of the form
export HOSTNAME="web-<something specific to your qm>.qm.<region>.mq.appdomain.cloud"
export QM_PORT=443
To deploy, run
./deploy.sh
### Undeploying the samples
From the mq-package directory run
./undeploy.sh
If you make any code changes, you may need undeploy before your updates deploy correctly.
Actions are the basic components of an OpenWhisk application. An action will take input as a json object, and will respond with output as a json object.
There are two actions defined in the manifest mqfunctions/mqpost and mqfunctions/mqdelete.
The environment variables are used to set defaults, but can these can be overriden when invoking actions with -p or -P (json file) parameters.
- mqfunctions/mqpost - Writes a message to a queue. If the input json contains
args.message, then that message is written. Else a default message containing a timestamp is posted. - mqfunctions/mqget - Reads a specific message from a queue. Input json must contain
args.messageId. It is this messageId that is used to fetch a message. Output json will contain the retrieved message, in the format:
{
'messageId' : ...,
'message' : ...
}The manifest maps src/utillib/*.js to ./lib/ for both actions. The actions
- Build REST call parameters
- Invoke a MQ function over the REST API
- Check the results
You can monitor the console output from the feed and actions by running.
ibmcloud fn activation poll
Once deployed you can invoke the mqpost action from the command line by running
ibmcloud fn action invoke mqfunctions/mqpost -p message "message posted from openwhisk action" --blocking
The logs should see something like
"stdout: Posting message to MQ Queue",
"stdout: Status code is 201",
"stdout: Message Id:",
"stdout: 414d5120514d3120202020202020202091fda061031f2740",
"stdout: Message successfully sent",
"stdout: msgid is 414d5120514d3120202020202020202091fda061031f2740"
To specify a queue manager name (eg. QM2) different from the manifest default run
ibmcloud fn action invoke mqfunctions/mqpost -p message "message posted from openwhisk action" -p qm_name "QM2" --blocking
Once deployed you can invoke the mqget action from the command line by running
ibmcloud fn action invoke mqfunctions/mqget -p messageId "414d5120514d3120202020202020202091fda061031f2740" --blocking
substituting in your messageId.
The logs should show something like
"stdout: Retrieving message from MQ Queue",
"stdout: Status code is 200",
"stdout: Message Id:",
"stdout: 414d5120514d3120202020202020202091fda061031f2740",
"stdout: Data found : message posted from openwhisk action",
"stdout: Message successfully retrieved",
"stdout: msg is {",
"stdout: messageId: '414d5120514d3120202020202020202091fda061031f2740',",
"stdout: message: 'message posted from openwhisk action'",
" stdout: }"
A sequence is a series of actions executed one after another. The output of one action becomes the input of the next action in the sequence.
A single sample sequence mq-default-sequence is provided, which in turn invokes the mqfunctions/mqget action followed by the mqfunctions/mqpost action. This sequence is designed to take a message off the queue and when successfull add another message. Thereby leaving a message on the queue for the next trigger round.
You can invoke the sequence from the command line by running
ibmcloud fn action invoke mqfunctions/mq-default-sequence -p messageId "<your message id>" --blocking
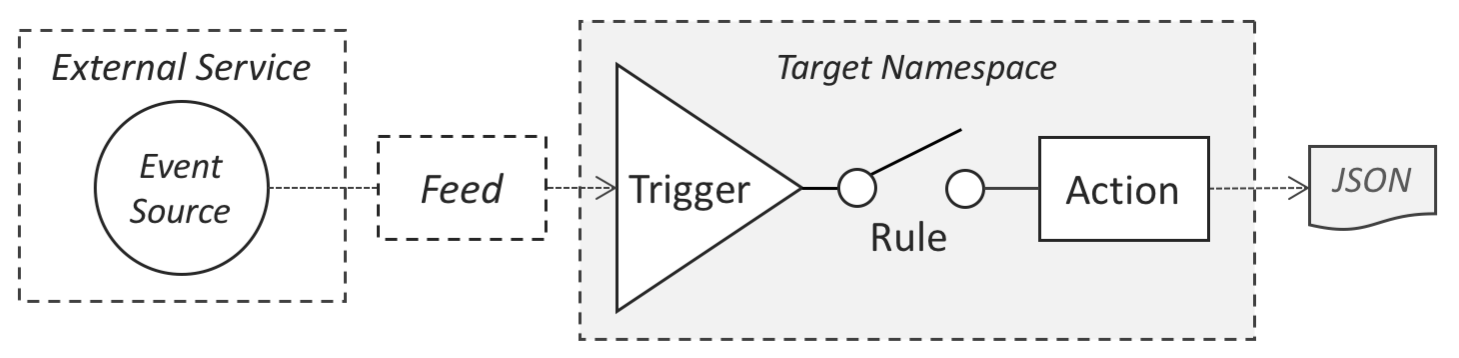
Triggers are used to invoke actions when an event occurs. By themselves triggers do nothing. They require rules to connect them to actions or sequences.
The two triggers defined in the manfiest are:
- mq-feedtimer-trigger - Which uses the OpenWhisk system
/whisk.system/alarms/intervalto trigger every two minutes. - mq-feedtest-trigger - Which registers to the feed mqfunctions/mqfeed as a subscribed trigger.
The feed defined in the manifest is mqfunctions/mqfeed. Feeds are actions that conform to a feed pattern. They are the provider of events to which triggers can register.
A feed listens for OpenWhisk lifecyle events from triggers.
CREATEindicates a new trigger registration.DELETEindicates a trigger deregistration.TRIGGERevent is an application registered event. This ensures that when the feed is triggered for anything other than a OpenWhisk lifecyle event, that it is seen as a TRIGGER event.
When the feed is invoked, it checks for registered triggers. If there are registered triggers then the feed browses for the next message on the queue. If a message if found the feed fires registered triggers sending the messageId of the next message on the queue as a parameter.
The feed uses Cloudant actions to persist the details of registered triggers.
The supplied feed provides a simple Informs all subscribers when it detects a message. Different patterns can be integrated into the feed.
Alternative patterns (Note these are not included in this repository) that you may wish to consider for the feed are:
- detect all messages, fire single trigger with array of message Ids
- detect all messages, fire triggers in round robin with message Ids in groups
Rules connect triggers to actions. The two rules in the manifest are:
- rule-mq-fire-trigger - Which connects the trigger
mq-feedtimer-triggerto the feedmqfunctions/mqfeed. This invokes the feed every two minutes. Forcing the feed to check for registered triggers and firing them. This package registers themq-feedtest-trigger, so that trigger will be fired if there is a message available on the message queue. - rule-mq-default-sequence - Which connects the
mq-feedtest-triggerto the sequencemq-default-sequence. It will only be fired if a message is available on the queue, and the sequence will retrieve that message and post a fresh message on the queue.
The flow for this OpenWhisk application is
/whisk.system/alarms/intervalfires once every two minutes.- The trigger
mq-feedtimer-triggeris tripped - The rule
rule-mq-fire-triggeris invoked - The feed
mqfunctions/mqfeedis awakened. If a message is found then- The trigger
mq-feedtest-triggeris fired - The sequence
mq-default-sequenceis started, whereby- The action
mqfunctions/mqgetis invoked action followed by the - The action
mqfunctions/mqpost
- The action
- The trigger
Note: If you deploy with .deploy.sh then the rule-mq-fire-trigger rule is disabled. If you want to enable the rule and the flow then run
ibmcloud fn rule enable rule-mq-fire-trigger
To list the activations run:
ibmcloud fn activation list
To view the logs for each activation run
ibmcloud fn activation get <activation id>
To interact with the Queue, the feed and actions need the following MQ configuration details:
- QM_NAME - Queue manager name
- QUEUE - Queue name
- HOSTNAME - Host name or IP address of your queue manager
- PORT - HTTP Listener port for your queue manager
- MQ_USER - User name that application uses to connect to MQ
- MQ_PASSWORD - Password that the application uses to connect to MQ
To persist registered triggers the feed needs the following Cloudant configuration details:
- MQ_DB - The name of the database created in Cloudant for the feed to use
- MQ_DB_KEY - The key that the feed will use to persist registred triggers
- CLOUDANT_HOSTNAME - Cloudant instance hostname
- CLOUDANT_USERNAME - User name used to connect to Cloudant
- CLOUDANT_PASSWORD - Password used to connect to Cloudant
- CLOUDANT_KEY - IAM API Key for Cloudant