GWAS-based Marker Selection Tool for Genomic Prediction from Genomic Data (for continuous phenotype)
- GMStool is a tool of selecting an optimal marker-set for predicting a continuous phenotype.
- This tool is based on genome-wide association study, and heuristically searches optimal markers for the phenotype prediction through statistic and machine-learning methods (ridge regression best linear unbiased prediction (RRB) and bootstrap trees (BTS)). Then, it performs genomic predictions using several statistical and machine/deep learning models (RRB, random forest (RF), deep neural network (DNN), and convoultion neural network (CNN)) and finally presents the best prediction model with the optimal marker-set.
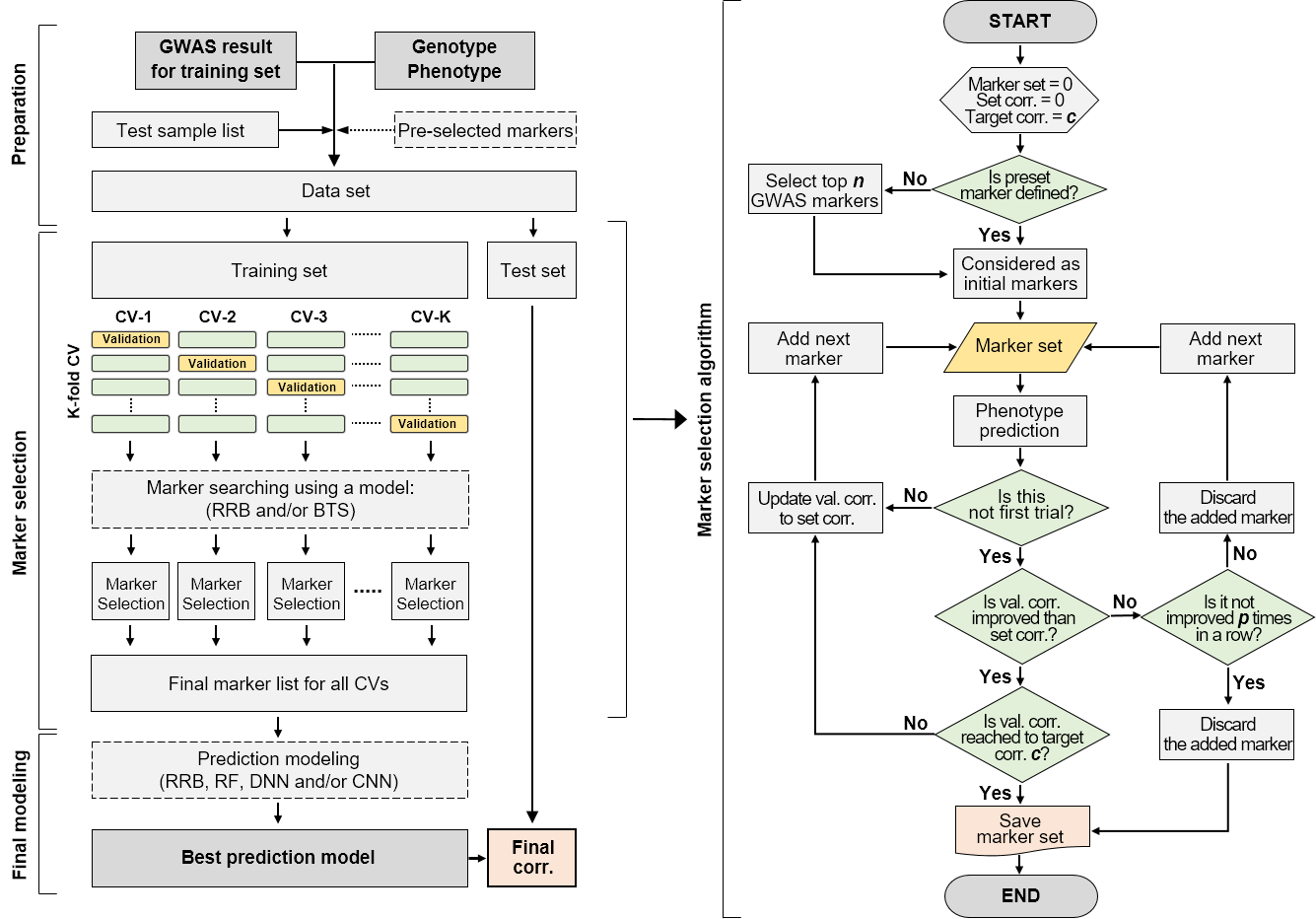
- GMStool consists of three phases, preparation, marker selection, and final modeling. Four input files, genotype, phenotype, GWAS result, and test list files, are prepared in the preparation phase, and optimal markers are then selected in the marker selectinon phase ("GMStools.MS.v1.R" or "GMStools.MS.MultiThreading.v1.R" scripts). Last, final prediction using the optimal marker-set is conducted in the final modeling phase ("GMStools.FM.v1.R" script).
- GMStool supports both linux and windows platforms, and also supports multithreading and graphic processing unit (GPU) high-speed computation.
Executable and example files of GMStool can be downloaded as the following command in linux and window.
- git clone https://github.com/JaeYoonKim72/GMStool
R-package for using the various functions defined in GMStool can be downloaded as the following command in R (refer to https://github.com/lovemun/GMStool).
- devtools::install_github("lovemun/GMStool")
- Flow-chart of GMStool is as follows:
- GMStool essentially requires four input files, genotype, phenotype, GWAS result, and test list files. Preset file is optional.
- "Genotype file" consists of markers (rows) and samples (columns), and genotypes are coded as -1, 0, 1, and 2 along missing, homozygous reference, heterozygous, and homozygous alternative genotypes.
- "Phenotype file" consists of samples (rows) and phenotype values (a column). Only one phenotype column is acceptable to GMStool, and an output directory is created based on the phenotype column name (see https://github.com/JaeYoonKim72/GMStool/tree/master/Results).
- "GWAS result file" consists of SNPIDs (marker names), chromosome number, physical position, and p-value columns, in order. Additional columns may be present in the GWAS results file, but these four columns must be organized in order.
- "Test list file" consists of a single column with sample names of test set.
- "Preset file" means a list of markers that must be selected, and consists of a column with marker names (optional).
- Note that the GWAS result file must be a result file calculated using only the train set excluding the test set.
- Both genotype and phenotype files must contain samples of the test set. Test samples in these files are automatically recognized through the "test list file".
- Marker selection phase is executed by either "GMStools.MS.v1.R" or "GMStools.MS.MultiThreading.v1.R" scripts. The only difference between the two scripts is whether multithreading is performed. All options are the same each other.
- Selection models are provided by RRB or BTS. RRB is a linear model that estimates the effects of marker variables with the best linear unbiased predictor, and BTS is a nonlinear model that is similar to RF but applies only bootstrap to the train samples (0.632 bootstrap).
- If markers are not selected in a row by a number of x% of the total number of markers (=If the correlation rates of markers are not improved in a row by a number of x% of the total number of markers), the selection process is stopped and the selected markers up to that point are returned as a result.
- In the flowchart of the marker selection algorithm, the value of p represents a number equal to x% of the total number of markers.
Usage:
GMStools.MS.v1.R -m [METHOD] -g [GENO] -p [PHENO] -gw [GWAS] -i [INFO] -t [TEST]
-pre [PRESET] -cv [CV] -c [CORR] -d [INCREMENT] -x [STOPX]
-is [INTIAL SNPs] -ss [SNPS_SELECTED] -gpu [GPU_USAGE] -all [ALL_SNPs]
Description of arguments:
-m METHOD, Selection method (RRB, BTS, or RRB_BTS; Essential).
-g GENO, Genotype file (Essential).
-p PHENO, Phenotype file (Essential).
-gw GWAS, GWAS result file. If GWAS file is not provided, GMStool calculates marker effects internally (Essential or optional).
-i INFO, Marker information file. Required if GWAS file is not provided (Optional; Default NULL).
-t TEST, Test sample list file. This file contains the sample names of the test set (Essential).
-pre PRESET, Marker list to be selected in advance (Optional; Default NULL).
-cv CV, The number of cross validation (Default 3).
-c CORR, Target correlation rate for the validation set (Default 1.0).
-x STOPX, Stop condition: it uses a number corresponding to x% of the total number of input markers.
If the correlation rates of validation sets do not improve as many as this number in a row,
the marker selection for the corresponding CV is stopped and the results up to that point are returned (Default 20)
-d INCREMENT, Increament of correlation rate in marker selection (Default 0.00005).
-is INITIAL_SNPS, The number of initial markers to be selected (Default 1).
-ss SNPS_SELECTED, The number of markers to be selected at one time (Default 1).
-gpu GPU_USAGE, If TRUE, RRB is calculated using GPU (Only available in Linux) (Default FALSE).
-all ALL_SNPs, If TRUE, correlation rate of all markers for the validation set in each CV is calculated, but it takes a lot of time (Default FALSE).
- -m option specifies the selection method to be used, and "RRB" and "BTS" can be selected. If you want to use both RRB and BTS, put "_" between the two methods and specify the -m option to "RRB_BTS".
- -g and -p options are mandatory, and specify the genotype and phenotype files prepared in the previous phase.
- -gw option specifies the gwas result file obtained in the previous phase. If this option is not given by the user, GMStool internally estimates the effects of markers for conducting the marker selection. When RRB is selected as the selection method, marker effects are derived from the coefficients of genotype variables of the model. Also, when BTS is selected, variable importance values in the random forest model are estimated as marker effects. Although GMStool has the functions to estimate marker effects internally, it is recommended to use a separate GWAS result file with -gw option.
- -i option means the marker information file, and is only used when the -gw option is not given.
- -t option is mandatory, and specifies the sample names of test sets. the test samples are excluded in the marker selection phases and are used only in the evaluation of the final modeling phase.
- -pre option specifies markers that must be selected.
- -cv option means k value in k-fold cross validation, and indicates the number of cross validation.
- -c option specifies the target correlation rate for the validation set of the markers to be selected. The default value is 1.0, but 0.99 is recommended, in case of avoiding excessive calculation time.
- -x option is the stop condition. The x argument defines x at "x% percent of the total number of input markers". If the correlation rates of validation sets do not improve as many as the number corresponding to the x% in a row, the marker selection for the corresponding CV is stopped and the results up to that point are returned.
- -d option is an increment value of the correlation rate, and a marker to be selected must be higher than the correlation rate of the previous marker plus the increment value. This condition is applied to the validation set, and only a marker with higher values than the previous values are selected.
- -is option means the number of top markers to be selected initially from the priority of GWAS markers. If the preset option is defined (-pre), the -is option is ignored and the preset markers are considered initial markers.
- -ss option indicates the number of markers to be selected at one time in the marker selection algorithm. It is recommended to select one marker at one time.
- -gpu option determines whether to use the GPU when calculating the RRB method. This option supports only linux platform, and it may not be executed in some computational environments depending on the GPU and system settings.
- -all option determines whether to calculate the correlation rate of all markers for the validation set in each CV.
1) Example of marker selection not using multithreading
Rscript GMStools.MS.v1.R \
-m RRB_BTS \ # Chose the selection methods (RRB, BTS, or RRB_BTS)
-g ExampleData/Ex_genotype.txt \ # Genotype file
-p ExampleData/Ex_phenotype.txt \ # Phenotype file
-gw ExampleData/Ex_gwas.txt \ # GWAS result file
-t ExampleData/Ex_test_sample_list.txt \ # Sample name list file for the test set
-cv 3 \ # Cross validation value
-c 0.85 \ # Target correlation rate for the validation set
# In the case of this example, a low target correlation rate is set for quick results confirmation
-x 20 \ # Stop condition
-is 1 # The number of initial SNPs to be selected
2) Example of marker selection using multithreading:
Rscript GMStools.MS.MultiThreading.v1.R \
-m RRB_BTS \ # Chose the selection methods (RRB, BTS, or RRB_BTS)
-g ExampleData/Ex_genotype.txt \ # Genotype file
-p ExampleData/Ex_phenotype.txt \ # Phenotype file
-gw ExampleData/Ex_gwas.txt \ # GWAS result file
-t ExampleData/Ex_test_sample_list.txt \ # Sample name list file for the test set
-cv 3 \ # Cross validation value
-c 0.85 \ # Target correlation rate for the validation set
# In the case of this example, a low target correlation rate is set for quick results confirmation
-x 20 \ # Stop condition
-is 1 # The number of initial SNPs to be selected
- Final modeling phase is executed by "GMStools.FM.v1.R" script. For modeling, RRB, RF, DNN, and CNN models are provided, and after modeling, final predictions for the test set are automatically performed.
- The RRB model is the same as the model used for marker selection, and the RF model is a model in which bootstrap of variables is additionally considered in the BTS model of marker selection (sampling one-third of the input markers, with replacement).
- The models of DNN and CNN are constructed with architectures of 256-128-64-32-16-1 and 32-16-8-64-32-16-1, respectively, and their detailed structures are described in our paper (refer citation section in this web page). These DNN and CNN models support high-speed computation through GPU, in the modeling phase of the GMStool.
- CNN model automatically sorts the markers in ascending order according to the chromosome number and physical position, and uses them to modeling, in order to effectively consider the interaction between adjacent markers.
- The remaining models use markers sorted in the most selected order among all CVs (original sorting state of the marker selection phase).
Usage:
GMStools.FM.v1.R -m [MODEL] -d [DIR] -gw [GWAS] -i [INFO] -pe [PERMUTATION] -gpu [GPU_USAGE] -t [TIME]
Description of arguments:
-m MODEL, Prediction model (RRB, RF, DNN, or CNN; Essential).
-d DIR, Result directory of marker selection (Essential).
-gw GWAS, GWAS result file. If GWAS file is not provided, marker information file should be provided (Essential or optional).
-i INFO, Marker information file. Required if GWAS file is not provided (Optional; Default NULL).
-pe PERMUTATION, The number of permutations per each modeling (Default 50).
-gpu GPU_USAGE, If TRUE, DNN and CNN are calculated using GPU (Default FALSE).
-t TIME, Runtime cut-off for permutatios of each modeling (Default 1 hour).
- -m option specifies the prediction model to be used. "RRB", "RF", "DNN", and "CNN" can be selected. If you want to use more than one model, put "_" between the methods and specify the -m option as like "RRB_DNN" or "RRB_RF_DNN_CNN".
- -d option specifies the path of the result directory derived from the marker selection phase. Final modeling script loads the result files in this path and saves all of modeling result to this path.
- -gw option specifies the identical gwas result file used in phases of preparation and marker selection. This option is used to generate a chromosomal distribution plot of the selected markers, and also used to sort the selected markers by chromosome and physical position when using the CNN model.
- -i option means the marker information file, and is used when the -gw option is not given. If the GWAS result file was not provided in the marker selection phase and marker effects were calculated internally in GMStool, this marker information file must be provided to generate a chromosomal distribution plot of selected markers.
- -pe option means the number of times to modeling per selected model. After modeling as much as the specified number, the model with the highest correlation rate for the validation set is presented as the final model for applying to the test set.
- -gpu option determines whether to use the GPU when modeling DNN and CNN. Depending on the GPU and system settings, it may not be possible in some computation environments.
- -t option means the maximum modeling time allowed per modeling of each model. The unit of time is hour(s).
1) Example of final modeling
Rscript GMStools.FM.v1.R \
-m RRB_RF_DNN_CNN \ # Chose the prediction models (RRB, RF, DNN, or CNN)
-d Results/Phenotype_RRblup_RF_PN_CV3_Ini5_Sel1_with_gwas/ \ # The path of result directory of marker selection
-gw ExampleData/Ex_gwas.txt \ # GWAS result file
-pe 5 \ # The number of permutations per modeling of each model
# In the case of this example, a low number is set for quick results confirmation
-gpu TRUE \ # Whether to use the GPU when modeling DNN or CNN
-t 1 # Runtime cut-off for permutatios of each modeling (hour)
- Examples of running screens for the marker selection and final modeling phases are shown in below.
- Due to the image size constraint, the screens below show only the beginning and end of the running screens.
- For a detailed description of all result files, see https://github.com/JaeYoonKim72/GMStool/tree/master/Results.
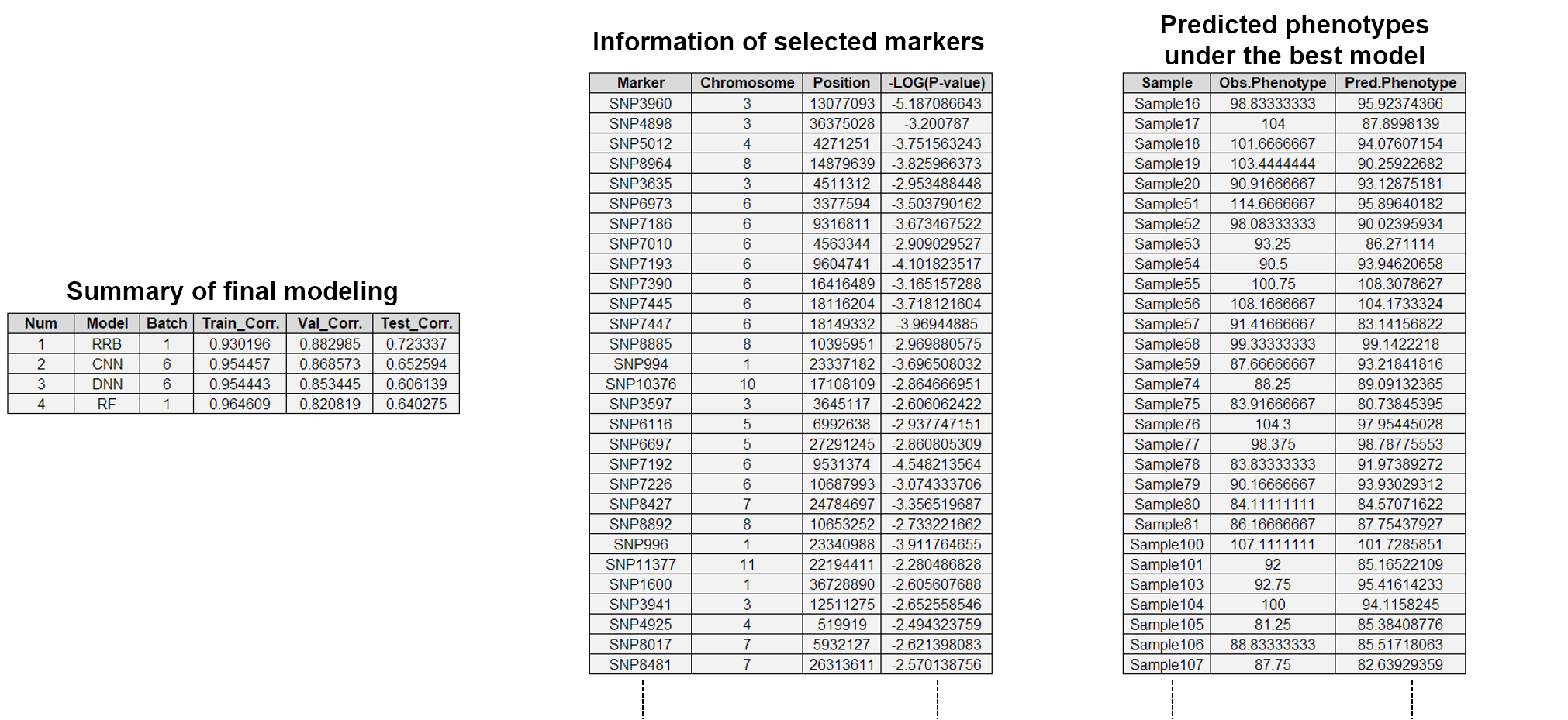
- Representative result files in the marker selection phase are a summary file of all CVs and a list file of selected markers.
- The summary file for all CVs records to the selection method used, the number of training and validation samples, the number of markers selected, the time spent, and so on.
- The list file of selected markers contains a list of all selected markers along with CV information. Markers are marked with "1" for the CV from which each marker was selected.
- The plots below are the summary file of all CVs and the list file of selected markers among the result files of the above examples ("CV_RRB_BTS_Selection_summary.txt" and "CV_RRB_BTS_Marker_scores.txt").
- Representative result files in the final modeling phase are a summary file of the final modeling, a information file of the selected markers, a phenotype file predicted from the final model, a chromosomal distribution plot of the selected markers, and a correlation plot between the predicted and observed phenotypes.
- The summary file of the final modeling shows the correlation rate of the final model on the test set.
- The information file of selected markers shows the information of the chromosome number, physical position, and GWAS p-value of all selected markers.
- The predicted phenotype file consists of the observed phenotype values and the phenotype values predicted from the final prediction model, for the test set.
- The chromosomal distribution plot shows the distribution of all selected markers according to chromosome numbers.
- The correlation plot shows the relationship between observed and predicted phenotype values, for the test set.
- The plots below are the representative result files derived from the above examples ("Final_modeling_results_for_all_models.txt", "Best_final_RRB_selected_markers_Info.txt", "Best_final_RRB_predPhenotype_list_76m_72c.txt", "Best_final_RRB_selected_markers_Chromosomal_distribution.png", and "Best_final_RRB_predPhenotype_plot.png").
Essential libraries for "GMStools.MS.v1.R" and "GMStools.FM.v1.R" scripts
- data.table (v1.12.8), tidyverse (v1.3.0), ggplot2 (v3.3.0), ggpmisc (v0.3.3), caret (v6.0-86), randomForest (v4.6-14), rrBLUP (v.4.6.1), tensorflow (v.2.2.0), keras (v2.3.0)
Essential libraries for "GMStools.MS.MultiThreading.v1.R" and "GMStools.FM.v1.R" scripts
- data.table (v1.12.8), tidyverse (v1.3.0), ggplot2 (v3.3.0), ggpmisc (v0.3.3), caret (v6.0-86), randomForest (v4.6-14), rrBLUP (v.4.6.1), tensorflow (v.2.2.0), keras (v2.3.0)
- doParallel (v1.0.15), foreach (v1.5.0), and iterators (v1.0.12)
Optional libraries for "GMStools.MS.v1.R" and "GMStools.MS.MultiThreading.v1.R" scripts to use GPU computation only on the Linux platform
- gpuR (v2.0.2)
- Paper is under review.